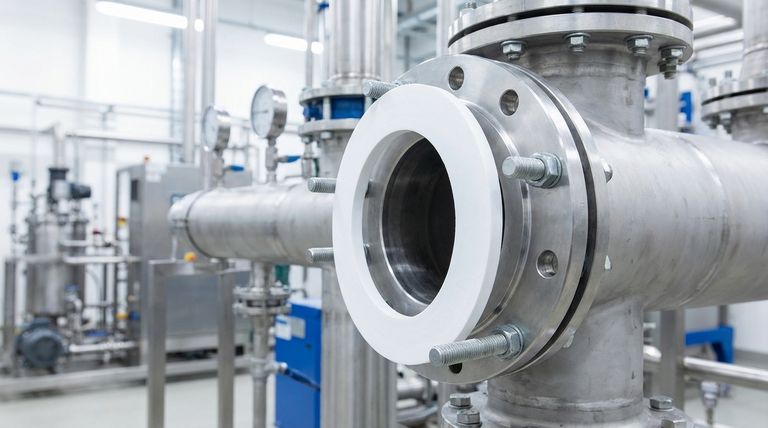
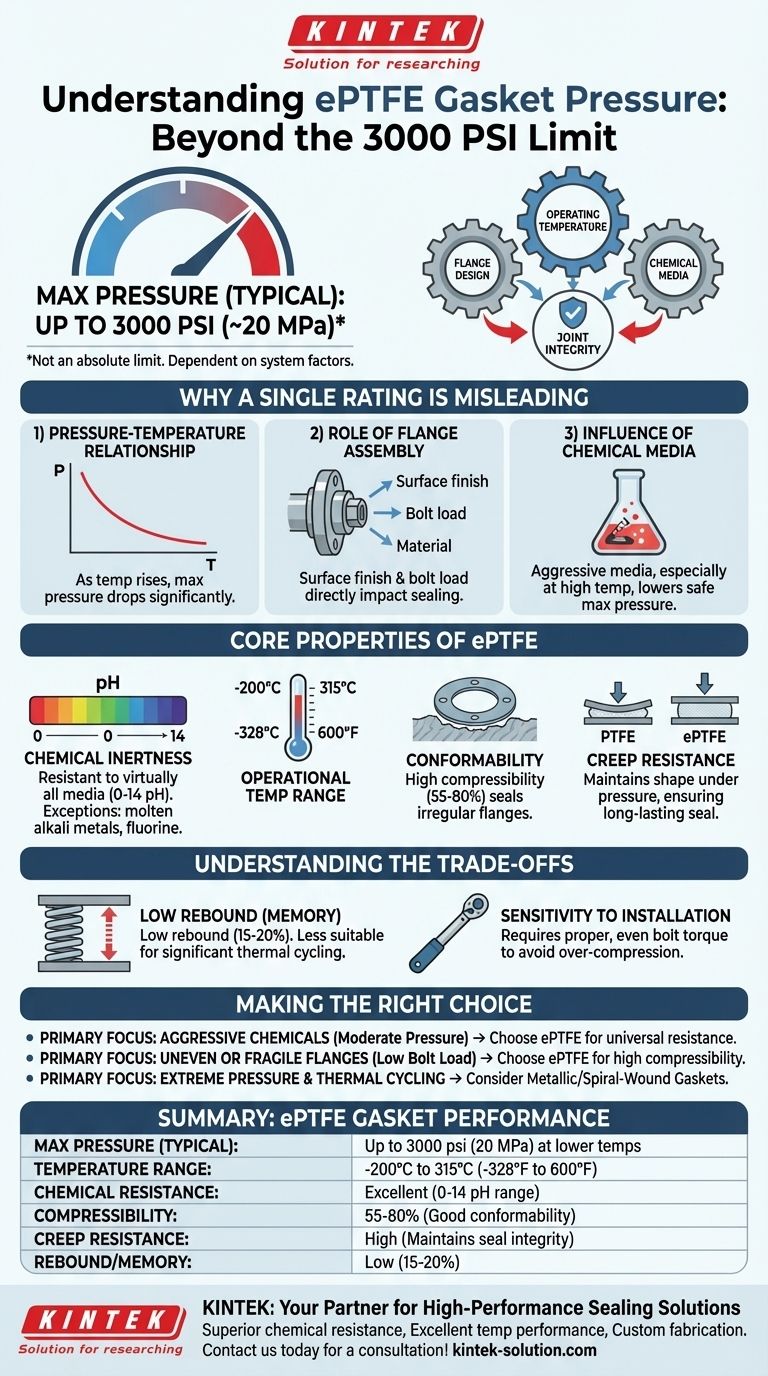
In short, ePTFE gaskets can typically withstand pressures up to 3000 psi (approximately 20 MPa). However, this number is not an absolute limit. The actual pressure a gasket can handle is critically dependent on the flange design, operating temperature, and the specific chemical media it is sealing.
The true performance of an ePTFE gasket is not defined by a single pressure rating. Instead, it is a function of the entire sealing system—where pressure, temperature, and chemical compatibility interact to determine the joint's integrity.

Why a Single Pressure Rating Is Misleading
Relying on a single pressure value can lead to seal failure. A gasket's ability to hold pressure is part of a dynamic system. To select the right gasket, you must consider the interplay between several key factors.
The Pressure-Temperature Relationship
Pressure and temperature ratings are inversely related. A gasket can withstand its maximum rated pressure only at lower temperatures. As the operating temperature increases, the maximum allowable pressure decreases significantly.
Manufacturers provide P-T (Pressure-Temperature) diagrams for their specific products. Always consult these charts to ensure your application falls within the safe operating envelope.
The Role of the Flange Assembly
The gasket is only one component of the seal. The design and condition of the flange are equally important.
Factors like the flange material, surface finish, and the applied bolt load directly impact the gasket's ability to seal. A rough or damaged flange surface requires a more conformable gasket to create a tight seal.
The Influence of Chemical Media
While ePTFE is exceptionally resistant to most chemicals, aggressive media, especially at elevated temperatures, can impact the material's long-term stability and sealing performance. This interaction can effectively lower the maximum pressure the gasket can safely contain.
Core Properties of ePTFE
Expanded Polytetrafluoroethylene (ePTFE) is not the same as standard PTFE. The expansion process creates a unique microporous structure, giving it properties that are ideal for demanding sealing applications.
Exceptional Chemical Inertness
ePTFE gaskets are resistant to virtually all media across the entire 0-14 pH range. The only notable exceptions are molten alkali metals and elemental fluorine, making them suitable for the most corrosive services.
Wide Operational Temperature Range
The material maintains its properties across an extremely broad temperature spectrum, typically from -200°C to 315°C (-328°F to 600°F). This allows it to be used in everything from cryogenic processes to high-temperature chemical reactors.
Conformability and Creep Resistance
The key advantage of ePTFE is its combination of softness and strength. Its high compressibility (55-80%) allows it to conform easily to irregular or damaged flange surfaces, creating a reliable seal with low bolt load.
Crucially, it is highly resistant to creep (cold flow). Unlike standard PTFE, which can deform and extrude out of the flange over time, ePTFE maintains its shape under pressure, ensuring a long-lasting, reliable seal.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No material is perfect for every situation. Understanding the limitations of ePTFE is critical for its successful application.
Low Rebound or "Memory"
ePTFE has a relatively low rebound rate (15-20%). Once compressed, it does not spring back to its original shape effectively. This makes it less suitable for applications with significant thermal cycling or vibration, where the joint may expand and contract.
Sensitivity to Installation
Proper installation is paramount. The soft, conformable nature of ePTFE means it can be easily damaged by over-compression. Applying the correct bolt torque evenly across the flange is essential to create an effective seal without crushing the gasket material.
Not Ideal for All High-Pressure Systems
While it has a respectable pressure rating, ePTFE is not always the best choice for extremely high-pressure, high-temperature applications. In these cases, a metallic or semi-metallic gasket, such as a spiral-wound gasket, may provide a more robust and reliable seal.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Use your primary goal to guide your decision-making process.
- If your primary focus is sealing aggressive chemicals at moderate pressures: ePTFE is an excellent choice due to its near-universal chemical resistance.
- If your primary focus is sealing uneven or fragile flanges (e.g., glass-lined steel): The high compressibility of ePTFE makes it ideal for creating a tight seal with low bolt load.
- If your primary focus is extremely high pressure combined with significant thermal cycling: You must carefully consult the manufacturer's P-T diagrams and consider alternative gasket types like spiral-wound.
Ultimately, treating the gasket as part of an engineered system—not just an isolated component—is the key to a reliable, long-lasting seal.
Summary Table:
| Key Factor | Impact on ePTFE Gasket Performance |
|---|---|
| Max Pressure (Typical) | Up to 3000 psi (20 MPa) at lower temperatures |
| Temperature Range | -200°C to 315°C (-328°F to 600°F) |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent across 0-14 pH range (exceptions: molten alkali metals, fluorine) |
| Compressibility | 55-80% - conforms well to irregular surfaces |
| Creep Resistance | High - maintains seal integrity under pressure |
| Rebound/Memory | Low (15-20%) - less suitable for thermal cycling |
Need a reliable sealing solution for your demanding application?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-performance PTFE and ePTFE components for semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial applications. Our precision-engineered gaskets deliver:
• Superior chemical resistance for aggressive media • Excellent temperature performance from cryogenic to high-heat processes • Custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders
Let our experts help you select or custom-design the perfect sealing solution for your specific pressure, temperature, and chemical requirements. Contact us today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the main types of PTFE lined valves? Find the Right Valve for Your Corrosive Application
- What types of movements can PTFE slide bearings accommodate? Handling Thermal, Seismic, and Structural Shifts
- What are the primary uses of Expanded PTFE? Unlock Its Unique Properties for Your Application
- Why should traditional lubricants not be used with PTFE-lined bearings? Avoid Premature Failure and High Friction
- How is a PTFE lip seal constructed? A Deep Dive into High-Performance Sealing Design
- What other fields can PTFE gaskets be used in? Beyond Chemical Plants to Electronics & Pharma
- What types of applications are PTFE / FEP / PFA lined pipes suitable for? Handle Extreme Corrosive Fluids Safely
- How are PTFE O-ring seals used in the automotive industry? Critical Sealing Solutions for High-Performance Vehicles



















