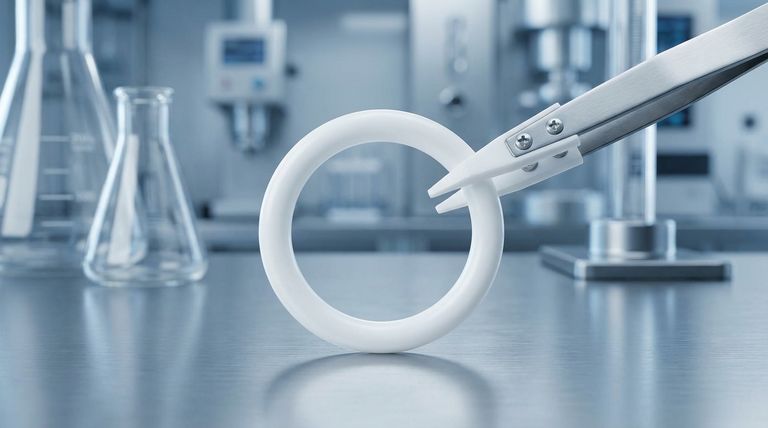
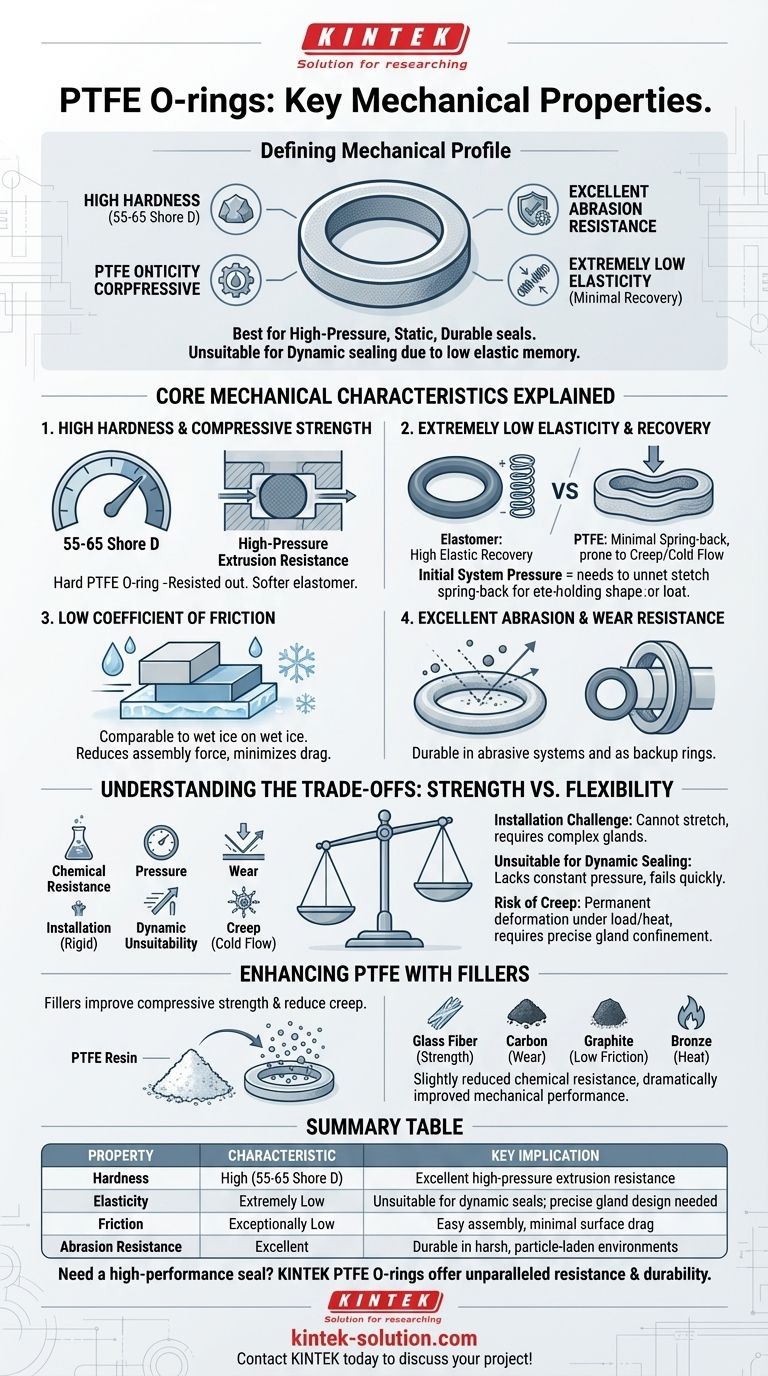
The defining mechanical properties of PTFE O-rings are a unique combination of high hardness, excellent abrasion resistance, and extremely low elasticity. This profile makes the material exceptionally durable in high-pressure, static applications but generally unsuitable for dynamic sealing where flexibility and elastic recovery are required.
While PTFE O-rings offer world-class resistance to chemicals, pressure, and wear, their core mechanical limitation is a near-total lack of elastic "memory." This makes proper gland design and use in static applications absolutely critical for achieving a reliable seal.

Core Mechanical Characteristics Explained
To properly select a PTFE O-ring, you must understand how its distinct properties dictate its performance under operational stress. These characteristics are fundamentally different from traditional rubber (elastomeric) O-rings.
High Hardness and Compressive Strength
PTFE is a hard plastic, not a soft elastomer. Its hardness typically falls between 55 and 65 Shore D.
This high hardness directly translates to excellent resistance against high-pressure extrusion. The material physically resists being squeezed out of the sealing groove (gland), making it ideal for high-pressure static face seals.
Extremely Low Elasticity and Recovery
This is the most critical mechanical property to understand. Unlike rubber, PTFE has minimal "spring-back" or elastic recovery.
When a PTFE O-ring is compressed, it does not push back with the same force as an elastomer. It tends to deform and hold its new shape, a phenomenon known as creep or cold flow. This is why the initial system pressure is essential for energizing the seal.
Low Coefficient of Friction
PTFE is famous for its exceptionally low coefficient of friction, often compared to wet ice on wet ice. It has one of the most slippery surfaces of any solid material.
This property reduces the force required for assembly and minimizes surface drag in any application with intermittent movement, though it cannot compensate for the material's poor performance in true dynamic seals.
Excellent Abrasion and Wear Resistance
Connected to its hardness and low-friction nature, PTFE exhibits very strong resistance to abrasion and wear.
This makes it highly durable in systems where abrasive particles might be present or where it acts as a backup ring, protecting a softer, primary elastomeric seal from damage.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Strength vs. Flexibility
The mechanical strengths of PTFE come with significant trade-offs that are crucial for any designer or engineer to recognize. Misunderstanding these limitations is a common source of sealing failure.
The Challenge of Installation
Because PTFE O-rings do not stretch, they cannot be installed in the same way as elastomeric rings. They can be easily nicked, scratched, or permanently deformed if forced over sharp edges or into improperly designed grooves.
Groove designs must often be more complex, sometimes requiring two-part glands, to allow the rigid ring to be installed without damage.
Unsuitability for Dynamic Sealing
The lack of elastic recovery makes standard PTFE O-rings a poor choice for dynamic applications like rotating shafts or reciprocating pistons.
A dynamic seal requires constant pressure against the moving surface to prevent leakage. A PTFE ring will not maintain this force, quickly leading to seal failure. For these applications, specialized spring-energized PTFE seals are used instead.
The Risk of Creep (Cold Flow)
Under a constant compressive load, especially at elevated temperatures, PTFE will slowly and permanently deform over time.
This cold flow can reduce the sealing force to zero, creating a leak path. This must be accounted for in the design of the gland, which must provide precise physical confinement for the O-ring.
Enhancing PTFE with Fillers
To mitigate some of PTFE's mechanical weaknesses, various filler materials can be blended into the base resin before it is sintered.
Why Add Fillers?
Fillers are added to improve key mechanical properties that are critical for more demanding applications. The primary goal is to enhance strength and reduce the tendency to creep.
Common Filler Materials and Their Benefits
While adding fillers can slightly reduce PTFE's exceptional chemical resistance, they dramatically improve its mechanical performance.
Common fillers include glass fiber, carbon, graphite, or bronze. These agents significantly increase compressive strength, stability, and overall wear resistance, making the O-ring more robust.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct material requires matching these mechanical properties to your specific operational goal.
- If your primary focus is a high-pressure, static seal in a chemically aggressive environment: An unfilled PTFE O-ring is an excellent choice, provided the gland is correctly designed to accommodate a non-elastic material.
- If your primary focus is a dynamic seal (e.g., rotating shaft or piston): A standard PTFE O-ring is unsuitable; consider an elastomeric O-ring (like FKM) or a specialized spring-energized PTFE seal.
- If your primary focus is improving durability and reducing creep in a demanding static application: A filled-PTFE compound will offer significantly better mechanical strength and dimensional stability than an unfilled grade.
Ultimately, understanding PTFE's unique mechanical profile—strong, slick, and chemically inert, but rigid and inflexible—is the key to deploying it effectively.
Summary Table:
| Property | Characteristic | Key Implication |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness | High (55-65 Shore D) | Excellent resistance to high-pressure extrusion |
| Elasticity | Extremely Low | Unsuitable for dynamic seals; requires precise gland design |
| Friction | Exceptionally Low | Easy assembly, minimal surface drag |
| Abrasion Resistance | Excellent | Durable in harsh, particle-laden environments |
Need a high-performance seal for a demanding application?
PTFE O-rings from KINTEK offer unparalleled chemical resistance and durability for the semiconductor, medical, and industrial sectors. Our precision manufacturing and custom fabrication services ensure you get the exact PTFE component—from prototypes to high-volume orders—to solve your toughest sealing challenges.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your project and get a quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers



















