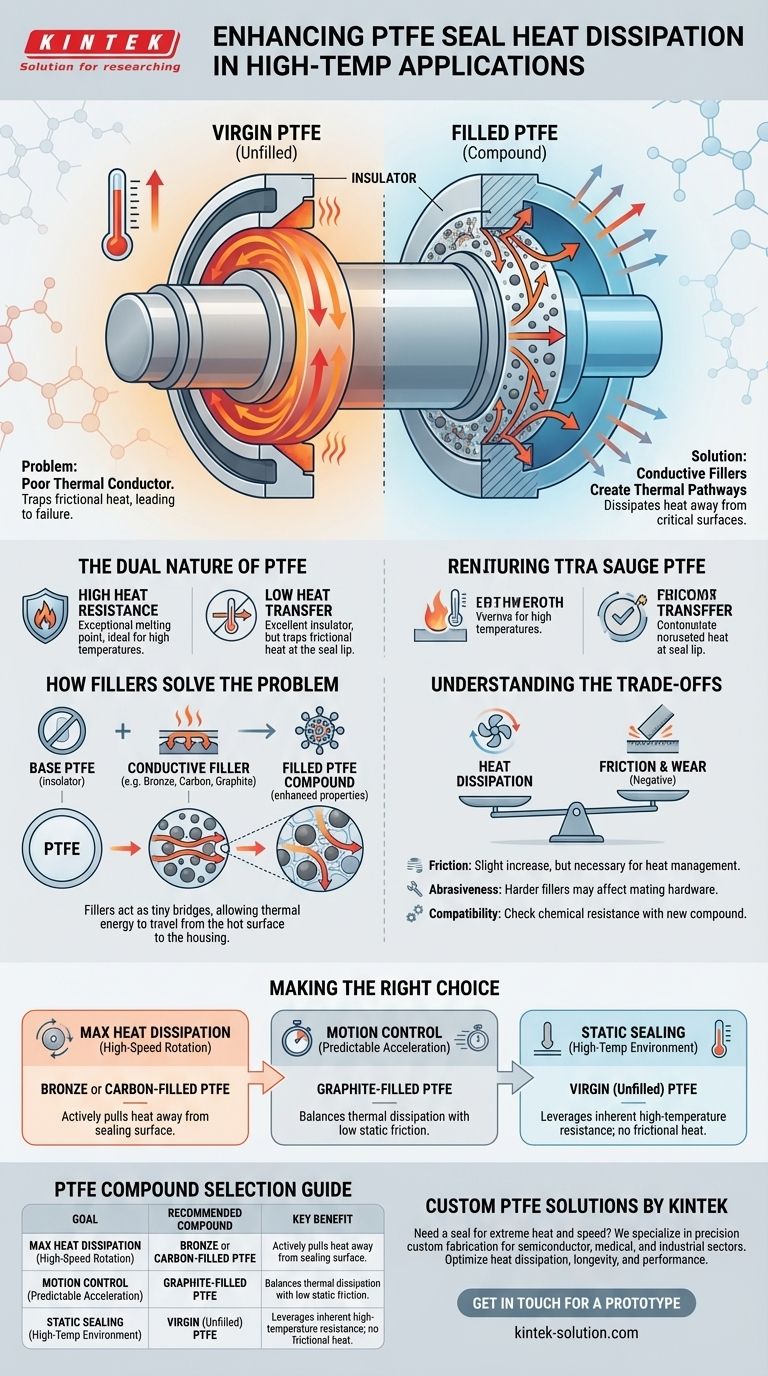
To improve heat dissipation in PTFE seals, you must incorporate a filler material into the base PTFE. While virgin PTFE is highly resistant to heat, it is also a poor thermal conductor. Adding a filler enhances the compound's ability to conduct heat away from the critical sealing surface, which is essential for reliability in high-temperature and high-velocity applications.
While pure PTFE excels in high-temperature environments due to its high melting point, its natural thermal insulating properties can be a liability. The strategic addition of specific fillers is the key to transforming PTFE into a material that not only withstands heat but actively dissipates it.

The Dual Nature of PTFE: High Heat Resistance, Low Heat Transfer
Exceptional Temperature Tolerance
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) has a significantly higher melting temperature than most conventional plastics. This inherent characteristic makes it a primary candidate for seals used in high-heat applications.
The Challenge of Thermal Insulation
The downside to PTFE's molecular structure is that it is an excellent thermal insulator. This means it traps heat rather than transferring it.
In a dynamic sealing application, heat generated from friction can become concentrated at the sealing lip. If this heat cannot escape, the localized temperature can rise dramatically, even if the surrounding environment is cooler.
Heat Generation in High-Speed Applications
PTFE seals are ideal for high-velocity equipment, capable of handling shaft surface speeds up to 35 m/s. Their extremely low coefficient of friction minimizes heat generation compared to other materials.
However, at very high speeds, even this low friction will generate a continuous amount of heat. Without a way to dissipate it, this thermal energy can build up and lead to premature seal failure.
How Fillers Solve the Heat Dissipation Problem
What is a Filler?
A filler is a material that is blended with a base polymer like PTFE to enhance specific properties. These additives can improve everything from wear resistance and compressive strength to thermal conductivity.
Enhancing Thermal Conductivity
The primary function of a thermally conductive filler is to create a pathway for heat to travel through the PTFE matrix.
These fillers have a much higher thermal conductivity than the PTFE itself. They act like tiny bridges, allowing thermal energy to move from the hot sealing lip, through the body of the seal, and into the metal housing, where it can be safely dissipated.
Balancing Properties
The selection of a filler is a critical design choice. Materials like carbon, graphite, or bronze are often used to improve thermal conductivity, but they also alter other characteristics of the seal, such as its friction, wear rate, and chemical compatibility.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Impact on Friction and Wear
While PTFE is known for its low friction, adding certain fillers can slightly increase the friction coefficient. However, this is often a necessary trade-off to gain the crucial benefit of heat dissipation, which ultimately extends the seal's life.
Abrasiveness and Hardware
Some fillers, particularly harder materials like glass fiber, can be more abrasive than pure PTFE. This must be considered in relation to the hardness and finish of the mating hardware (the shaft or bore) to prevent premature wear of the system components.
Chemical Compatibility
Introducing a new material into the PTFE compound changes its chemical resistance profile. The chosen filler must be compatible with any system media to prevent degradation of the seal.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct PTFE compound requires balancing the need for heat dissipation with other operational demands.
- If your primary focus is maximum heat dissipation in high-speed rotation: Choose a PTFE compound with a highly conductive filler like bronze or carbon to actively pull heat away from the dynamic sealing surface.
- If your primary focus is motion control with predictable acceleration: A graphite-filled PTFE can offer a good balance of improved thermal dissipation while maintaining the very low static friction needed for precise movement.
- If your primary focus is static sealing in a high-temperature environment: Virgin (unfilled) PTFE is often sufficient, as its inherent temperature resistance is the key requirement and there is no frictional heat being generated.
By selecting a filled PTFE compound, you are engineering a component that is not just resistant to heat, but is optimized to manage it effectively.
Summary Table:
| Goal | Recommended PTFE Compound | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Maximum Heat Dissipation in High-Speed Rotation | Bronze or Carbon-Filled PTFE | Actively pulls heat away from the sealing surface |
| Motion Control with Predictable Acceleration | Graphite-Filled PTFE | Balances thermal dissipation with low static friction |
| Static Sealing in High-Temp Environment | Virgin (Unfilled) PTFE | Leverages inherent high-temperature resistance |
Need a PTFE seal that can handle extreme heat and speed? At KINTEK, we specialize in custom PTFE component fabrication for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our expertise in precision production and material science allows us to engineer the perfect filled PTFE compound for your specific application—ensuring optimal heat dissipation, longevity, and performance. Contact us today to discuss your high-temperature sealing challenge and request a prototype: Get in Touch
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability



















