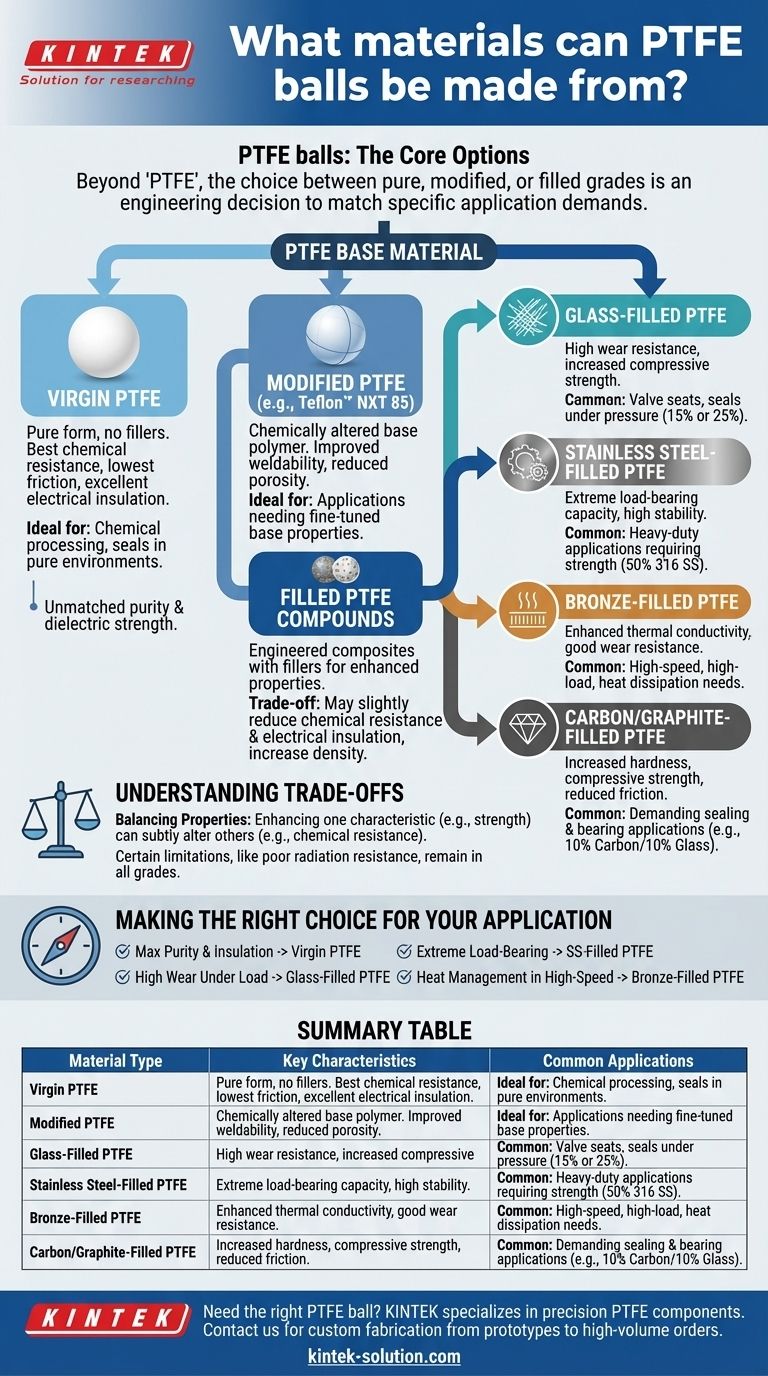
At its core, a PTFE ball can be made from pure (virgin) PTFE, modified PTFE, or a composite material where fillers are added to the PTFE base. These fillers, such as glass, carbon, bronze, or stainless steel, are not just additives; they are engineered to enhance specific properties like wear resistance, compressive strength, or thermal conductivity for demanding applications.
The fundamental choice is not just "PTFE," but which type of PTFE. While all options provide excellent chemical resistance and low friction, selecting a filled or modified grade is a deliberate engineering decision to overcome the mechanical limitations of pure PTFE in a specific environment.
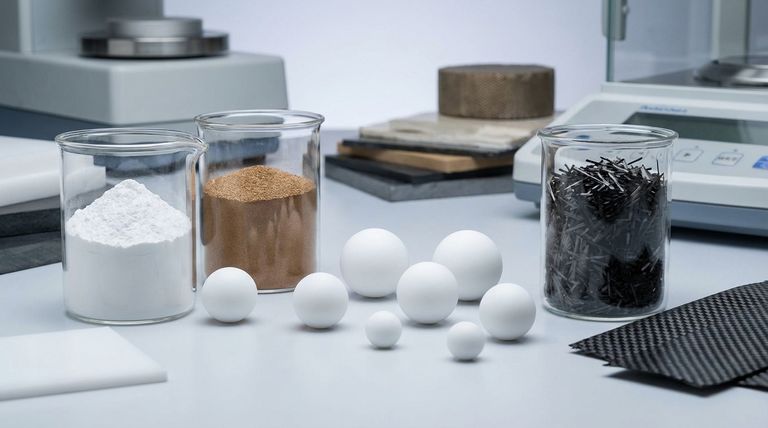

The Foundation: Virgin and Modified PTFE
Before exploring composites, it's essential to understand the baseline material. The properties of pure or modified PTFE are the foundation upon which all compounds are built.
Virgin Grade PTFE
Virgin PTFE is polytetrafluoroethylene in its pure form, without any fillers or recycled material. It offers the best performance in terms of chemical resistance, electrical insulation, and having the lowest coefficient of friction. Its molecular structure, defined by strong carbon-fluorine bonds, gives it its signature non-stick and inert characteristics.
Modified PTFE
This category includes materials like Teflon™ NXT 85. Modified PTFE is a chemically altered version of the base polymer. These modifications are made to improve specific properties, such as reducing porosity or enhancing weldability, without introducing a separate filler material.
Enhancing Performance with PTFE Compounds (Fillers)
Fillers are added to virgin PTFE to create a composite material with superior mechanical or thermal properties. The choice of filler is directly related to the problem you need to solve.
Glass-Filled PTFE
Glass fibers, typically in concentrations of 15% or 25%, are added to significantly increase wear resistance and compressive strength. This makes it a common choice for valve seats and seals that experience consistent friction and pressure.
Stainless Steel-Filled PTFE
By compounding virgin PTFE with 50% 316 stainless steel powder, you create a material with exceptionally high strength and stability under heavy loads. This is ideal for applications requiring robust load-bearing capabilities combined with PTFE's inherent chemical resistance.
Bronze-Filled PTFE
Adding bronze powder to PTFE dramatically improves its thermal conductivity, allowing heat to dissipate more effectively. It also enhances compressive strength and wear resistance, making it suitable for high-load, high-speed applications where friction-generated heat is a concern.
Carbon and Carbon/Glass-Filled PTFE
Carbon is added to increase hardness, compressive strength, and wear resistance. A common blend combines 10% carbon and 10% glass, offering a balanced profile of improved mechanical properties suitable for demanding sealing and bearing applications.
Other Fillers
Other materials can be compounded with PTFE for specific needs. Graphite can be added to further reduce friction, while various colors can be used for part identification in complex assemblies.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a filled PTFE is an exercise in balancing properties. Enhancing one characteristic can subtly alter others.
The Cost of Enhancement
While fillers improve mechanical strength, they can slightly reduce the overall chemical resistance of the composite. The filler material itself may not be as inert as pure PTFE, which can be a factor in extremely aggressive chemical environments.
Impact on Core Properties
Adding fillers generally increases the material's density and can slightly increase the coefficient of friction compared to virgin PTFE. The exceptional electrical insulating properties of virgin PTFE are also often diminished by conductive fillers like carbon, bronze, or stainless steel.
Baseline Limitations
It is critical to remember that certain properties are inherent to PTFE itself and are not improved by fillers. All grades of PTFE, for example, have poor radiation resistance and can become brittle with exposure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final selection should be driven entirely by the primary demands of the operating environment.
- If your primary focus is maximum chemical purity and electrical insulation: Choose virgin grade PTFE for its unmatched inertness and dielectric strength.
- If your primary focus is high wear resistance under load: Select a glass-filled PTFE (15% or 25%) for its durability in sliding applications.
- If your primary focus is extreme load-bearing capacity: Use stainless steel-filled PTFE for its superior strength and deformation resistance.
- If your primary focus is managing heat in a high-speed system: Opt for bronze-filled PTFE to leverage its excellent thermal conductivity.
Ultimately, choosing the right PTFE material is about matching the specific enhancements of a compound to the challenges of your application.
Summary Table:
| Material Type | Key Characteristics | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Virgin PTFE | Best chemical resistance, lowest friction, excellent electrical insulation | Chemical processing, seals in pure environments |
| Modified PTFE | Reduced porosity, improved weldability | Applications requiring fine-tuned base polymer properties |
| Glass-Filled PTFE | High wear resistance, increased compressive strength | Valve seats, seals under friction and pressure |
| Stainless Steel-Filled PTFE | Extreme load-bearing capacity, high stability | Heavy-duty applications requiring strength and chemical resistance |
| Bronze-Filled PTFE | Enhanced thermal conductivity, good wear resistance | High-speed, high-load applications with heat dissipation needs |
| Carbon/Graphite-Filled PTFE | Increased hardness, compressive strength, reduced friction | Demanding sealing and bearing applications |
Need the right PTFE ball for your specific application? KINTEK specializes in manufacturing precision PTFE components—from seals and liners to custom labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether you require the pure chemical resistance of virgin PTFE or the enhanced mechanical properties of a filled compound, our custom fabrication services cover everything from prototypes to high-volume orders. Contact us today to discuss your project requirements and leverage our expertise in material selection and precision production.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of PTFE balls over metals or alloys? Superior Chemical & Friction Resistance
- How do the chemical properties of PTFE balls influence their performance? Unmatched Durability in Harsh Environments
- What temperature range can Teflon (PTFE) balls withstand? -200°C to +260°C Performance Guide
- What are the overall advantages of using PTFE balls in fluid management systems? Enhance Reliability & Efficiency
- How do PTFE balls contribute to reduced maintenance costs? Extend Component Life and Cut Downtime



















