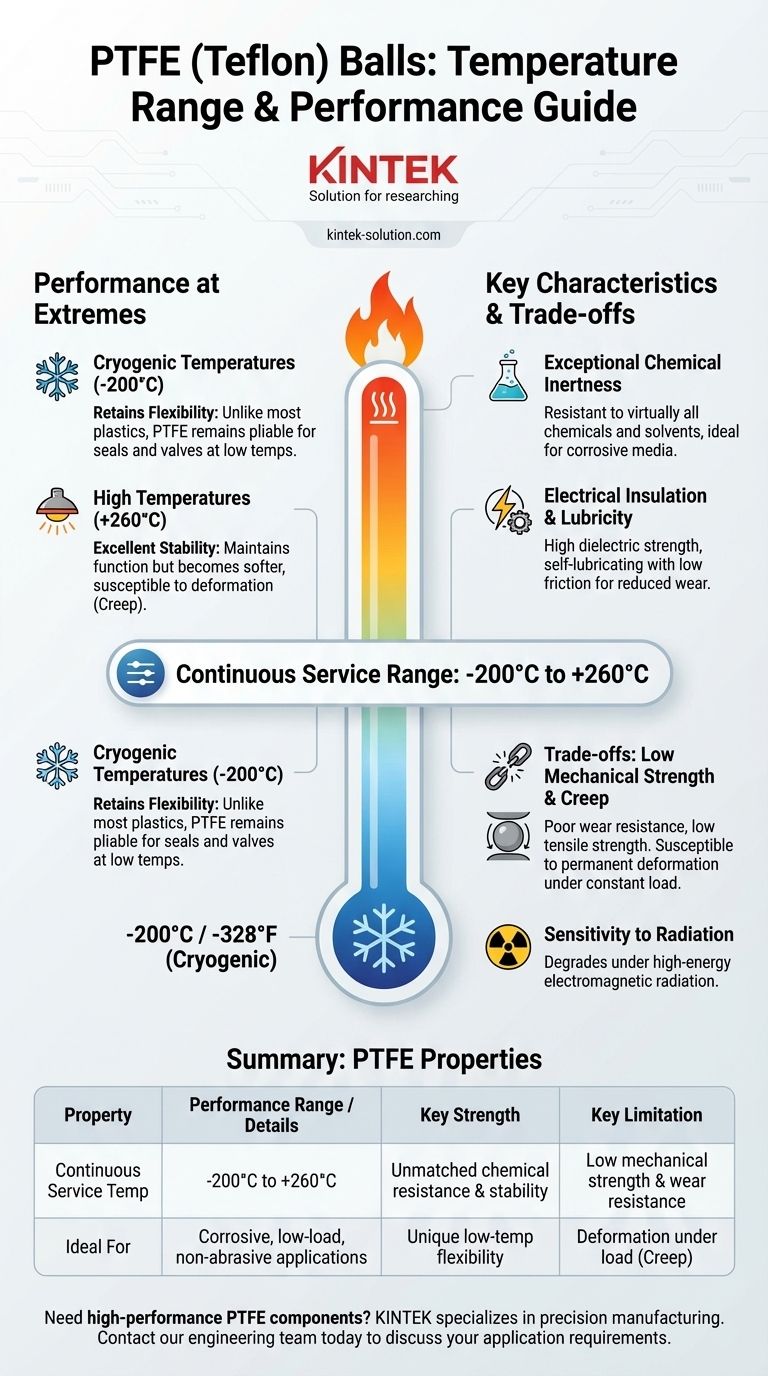
In short, Teflon (PTFE) balls can typically operate within a continuous service temperature range of -200°C to +260°C (-328°F to +500°F). While some sources may cite slightly narrower ranges, this represents the material's effective operational window where it maintains its most useful properties.
While PTFE offers an exceptionally wide temperature range and unmatched chemical resistance, this performance comes at the cost of significantly lower mechanical strength and wear resistance compared to other engineering plastics.

Understanding the Operating Range in Detail
To properly specify PTFE balls for an application, you must understand how the material behaves at the extremes of its temperature range. It is not just about survival; it is about performance.
Performance at High Temperatures
PTFE maintains excellent stability and most of its properties as it approaches its upper limit of +260°C (+500°F). Unlike many plastics that melt or degrade rapidly, PTFE remains highly functional.
However, it's crucial to remember that PTFE is an inherently soft material. At elevated temperatures, it becomes even softer and more susceptible to deformation, a phenomenon known as creep.
Performance at Cryogenic Temperatures
At the low end of its range, down to -200°C (-328°F), PTFE exhibits a remarkable and valuable property: it retains its flexibility.
Most materials, especially plastics, become extremely brittle and prone to fracture at cryogenic temperatures. PTFE's ability to remain pliable makes it a unique solution for low-temperature seals, valves, and components.
Key Characteristics Beyond Temperature
Temperature resistance is PTFE's most famous attribute, but its utility comes from a combination of unique properties.
Exceptional Chemical Inertness
PTFE is resistant to virtually all industrial chemicals, acids, and solvents. There is no known solvent that can dissolve it at room temperature.
This makes PTFE balls an ideal choice for applications involving aggressive or corrosive media, such as in chemical processing pumps, valves, and mixers where other materials would quickly fail.
Electrical Insulation and Lubricity
PTFE is an excellent electrical insulator with high dielectric strength. This property is stable across a wide range of temperatures and frequencies.
Furthermore, PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid material, making it self-lubricating. This reduces wear and energy consumption in moving parts, such as in bearings or non-lubricated valves.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No material is perfect. The decision to use PTFE must be balanced against its significant limitations, primarily its poor mechanical performance.
Low Mechanical and Wear Resistance
Compared to other engineering plastics like PEEK or even Nylon, PTFE is a very soft material with low tensile strength (around 3900 psi) and poor wear resistance.
This makes it unsuitable for applications involving high loads, sharp edges, or abrasive conditions. In a high-pressure or high-wear scenario, a PTFE ball will deform or wear away quickly.
Deformation Under Load (Creep)
PTFE is highly susceptible to "creep," which is the tendency of a solid material to move slowly or deform permanently under the influence of persistent mechanical stress.
If a PTFE ball is used in an application where it is under a constant load (like a loaded bearing or a valve seat under high pressure), it will gradually change shape over time, potentially leading to leaks or mechanical failure.
Sensitivity to Radiation
It is important to note that exposure to high-energy electromagnetic radiation (like gamma rays or electron beams) can degrade the molecular structure of PTFE, causing it to lose its beneficial properties and become brittle.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct material requires looking beyond a single specification and considering the entire operational environment.
- If your primary focus is extreme temperature range and chemical resistance: PTFE is an excellent choice, especially for low-load applications like check valves, floats, or bearings in corrosive environments.
- If your primary focus is high mechanical strength or wear resistance: You should immediately consider alternative materials like PEEK, Torlon, or even stainless steel, as PTFE will almost certainly fail under high mechanical stress.
Ultimately, choosing PTFE is a strategic decision that leverages its incredible thermal and chemical stability while respecting its inherent mechanical weaknesses.
Summary Table:
| Property | Performance Range / Details |
|---|---|
| Continuous Service Temperature | -200°C to +260°C (-328°F to +500°F) |
| Key Strength | Unmatched chemical resistance & stability |
| Key Limitation | Low mechanical strength & wear resistance |
| Ideal For | Corrosive, low-load, non-abrasive applications |
Need high-performance PTFE components for demanding environments?
KINTEK specializes in the precision manufacturing of PTFE seals, balls, liners, and custom labware. We understand the critical balance between thermal stability, chemical resistance, and mechanical requirements for industries like semiconductor, medical, and laboratory processing.
Whether you need a custom prototype or a high-volume order, our expertise ensures your components perform reliably from cryogenic temperatures up to +260°C.
Contact our engineering team today to discuss your specific application requirements.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What types of fasteners and custom parts can be made from Teflon (PTFE)? Explore Its Unique Advantages
- How do PEEK and POM compare in terms of pressure resistance? A Guide for High-Performance Applications
- Why should negative pressure be avoided in PTFE lined butterfly valves? Prevent Catastrophic Liner Collapse
- How can PTFE lined butterfly valves be customized for different applications? Tailor Valves for Your Specific Needs
- Why are PTFE slide bearings advantageous for highway bridges? Key Benefits for Durable, Low-Maintenance Structures
- What are the common applications of expanded PTFE? Unlock High-Performance Sealing, Filtration & Medical Solutions
- What are the different types of PTFE lined valves and their key features? Choose the Right Valve for Your Corrosive Process
- What are the key differences between PTFE and EPDM valve seats? Choose the Right Material for Your Application



















