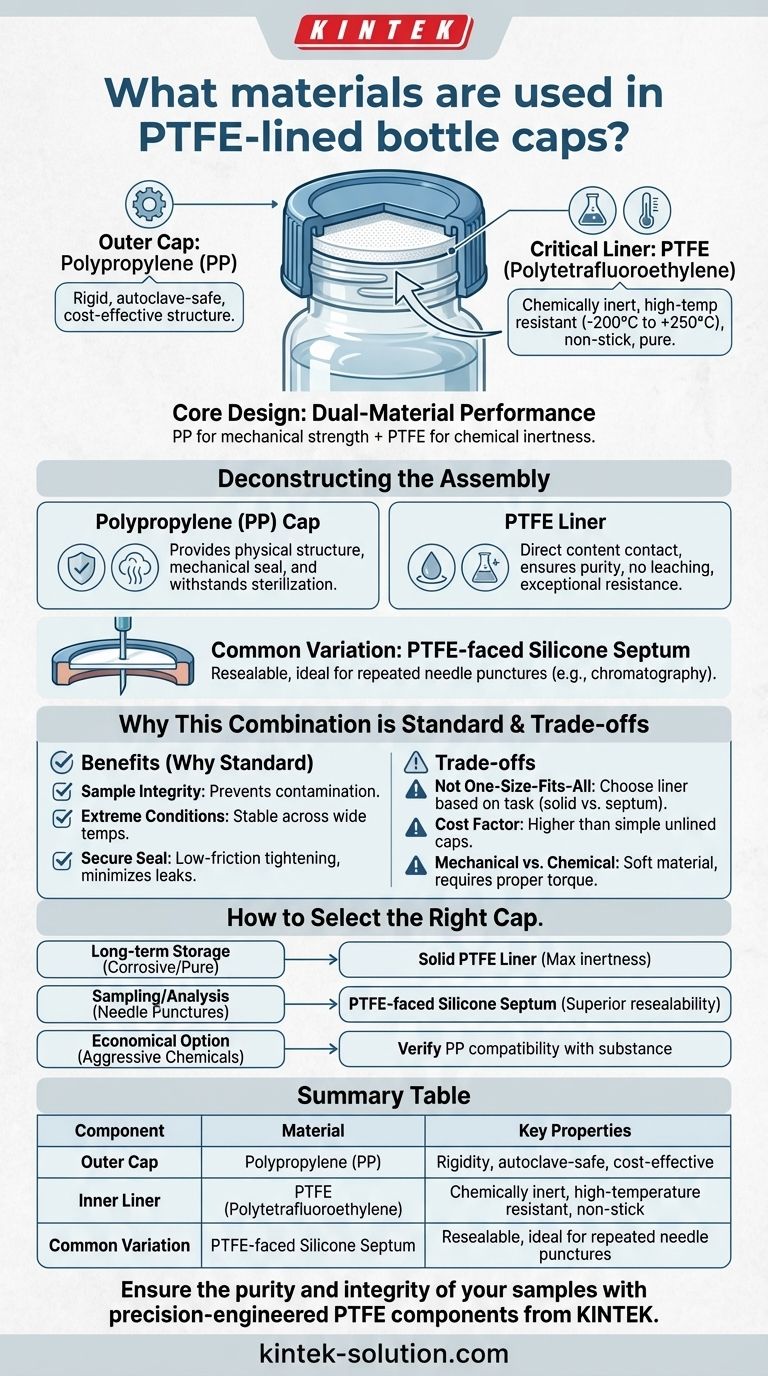
At their core, PTFE-lined bottle caps are a composite of two primary materials: the cap itself, which is most commonly made of polypropylene (PP), and the critical inner lining, which is made of PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene). This design combines the structural integrity and cost-effectiveness of polypropylene with the superior chemical inertness and temperature resistance of the PTFE liner that contacts the contents.
The fundamental purpose of this dual-material design is to create a closure that is both mechanically robust and chemically non-reactive. This ensures the absolute purity of the container's contents, which is critical in laboratory, pharmaceutical, and industrial settings.

Deconstructing the Cap: Material Roles and Properties
To understand why this combination is so effective, we must look at the specific role each material plays in the assembly.
The Outer Cap: Polypropylene (PP)
The outer screw cap provides the physical structure and the mechanical seal. Polypropylene is the standard choice for this component due to its excellent balance of properties.
It offers good rigidity, chemical resistance to many common substances, and crucially, the ability to withstand the high temperatures of an autoclave (steam sterilization), making the caps reusable. In some cases, polyethylene (PE) is used as a lower-cost alternative for less demanding applications.
The Critical Liner: Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE)
The liner is the most important part of the assembly, as it is the only material that comes into direct contact with the stored substance. PTFE is a high-performance fluoropolymer renowned for its extreme inertness.
Its key properties include:
- Exceptional Chemical Resistance: It is virtually unaffected by strong acids, bases, solvents, and other corrosive chemicals.
- Wide Temperature Tolerance: It remains stable and functional across an extreme temperature range, typically from -200°C to +250°C.
- Non-Stick Surface: Its low-friction, non-stick nature ensures that every bit of a sample can be retrieved and prevents material from adhering to the liner.
- Purity: As an inert material, it does not leach contaminants into the stored substance, which is vital for high-purity chemicals and analytical samples.
Common Variations: Septa and Alternative Liners
While solid PTFE is common for storage, other liner configurations exist for specific tasks, often referred to as septa.
A PTFE-faced silicone septum is a popular choice. This design features a thin layer of PTFE facing the contents, backed by a thicker layer of silicone. This combines the chemical resistance of PTFE with the elasticity and resealability of silicone, making it ideal for applications involving repeated needle punctures, such as in chromatography vials.
Why This Combination is the Standard for Demanding Applications
The PP and PTFE combination isn't just a random choice; it's an engineered solution to common challenges in scientific and industrial work.
Ensuring Sample Integrity
The primary goal is to prevent any interaction between the container and its contents. The inert PTFE liner acts as a perfect barrier, ensuring that diagnostic reagents, environmental samples, and high-purity chemicals remain uncontaminated.
Performance Under Extreme Conditions
The ability to withstand a vast temperature range and repeated autoclaving cycles makes these caps highly durable and versatile for various laboratory processes, from cryogenic storage to high-temperature reactions.
Creating a Secure and Reliable Seal
The low-friction surface of PTFE allows the cap to be tightened securely without binding or galling, creating a tight seal that prevents leaks and minimizes moisture transmission, protecting sensitive materials from the outside environment.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, it's important to recognize that PTFE-lined caps have specific characteristics that make them suitable for certain tasks over others.
Not a One-Size-Fits-All Solution
The choice between a solid PTFE liner and a PTFE-faced silicone septum is critical. A solid liner provides the absolute best chemical barrier for long-term storage. However, its rigidity makes it unsuitable for applications requiring repeated punctures, where a silicone-backed septum is necessary to ensure a reliable reseal.
The Cost Factor
PTFE is a premium, high-performance material. Consequently, these caps are more expensive than simpler, unlined polypropylene caps or those with less robust liners like LDPE. The higher cost is a direct trade-off for superior performance and purity.
Mechanical Properties vs. Chemical Resistance
While PTFE's chemical resistance is nearly universal, its mechanical properties can be a limitation. It is a relatively soft material, and the seal relies on proper torque. Over-tightening can deform the liner, while under-tightening can lead to leaks.
How to Select the Right Cap for Your Application
Choosing the correct cap assembly is a critical step in guaranteeing the integrity of your work.
- If your primary focus is long-term storage of highly corrosive or pure chemicals: A solid PTFE liner offers the maximum chemical inertness and the tightest seal for protecting contents.
- If you are performing sampling or analysis requiring needle punctures (e.g., chromatography): A PTFE-faced silicone septum is essential for its superior resealability and chemical resistance.
- If your application involves aggressive chemicals but requires a more economical option: Verify that the substance is compatible with the polypropylene cap material itself, as it may be exposed at the threads.
Ultimately, matching the material properties of the cap and liner to the specific demands of your application is fundamental to achieving reliable and accurate results.
Summary Table:
| Component | Material | Key Properties |
|---|---|---|
| Outer Cap | Polypropylene (PP) | Rigidity, autoclave-safe, cost-effective |
| Inner Liner | PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) | Chemically inert, high-temperature resistant, non-stick |
| Common Variation | PTFE-faced Silicone Septum | Resealable, ideal for repeated needle punctures |
Ensure the purity and integrity of your samples with precision-engineered PTFE components from KINTEK.
Whether you need reliable PTFE-lined caps for long-term chemical storage or custom-fabricated seals, liners, and labware, our expertise in PTFE manufacturing delivers the chemical resistance and precision your application demands. We serve the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors with custom solutions from prototypes to high-volume orders.
Contact us today to discuss your specific requirements and discover how KINTEK can support your critical processes.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are some common applications of machined PTFE? Leverage its Unique Properties for Demanding Applications
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- What are the key benefits of PTFE in custom fabrication? Unlock Performance in Extreme Conditions
- What are the primary applications of PTFE fasteners and custom parts? Critical Solutions for Extreme Environments
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? Unlock Unmatched Performance in Demanding Applications



















