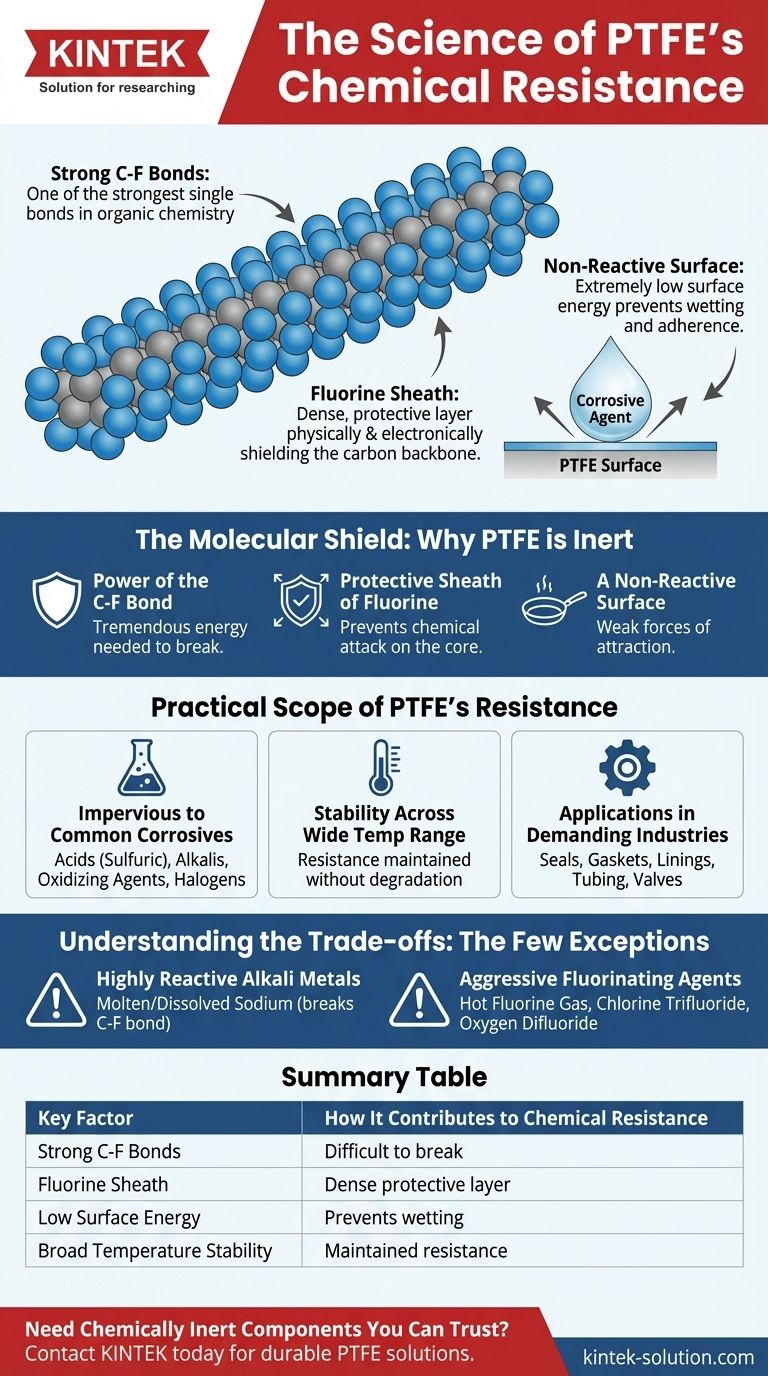
At its core, the exceptional chemical resistance of Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is due to the incredibly strong and stable bonds between its carbon and fluorine atoms. This molecular structure creates a non-reactive polymer that is virtually immune to attack from the vast majority of chemicals, including aggressive acids, bases, and solvents.
PTFE's chemical inertness is not a surface-level property; it is a fundamental consequence of its molecular architecture. Fluorine atoms form a tight, protective sheath around the carbon backbone, physically and electronically shielding it from chemical interaction.

The Molecular Shield: Understanding PTFE's Inertness
To understand why PTFE is so unreactive, we must look at its atomic structure. The properties that make it so robust are not accidental; they are a direct result of fundamental chemistry.
The Power of the Carbon-Fluorine Bond
The bond between a carbon atom and a fluorine atom is one of the strongest single bonds known in organic chemistry. Fluorine is the most electronegative element, meaning it holds onto its electrons very tightly. This creates an extremely stable, low-energy bond that requires a tremendous amount of energy to break.
A Protective Sheath of Fluorine
The PTFE molecule consists of a long chain of carbon atoms. Each carbon atom is bonded to two fluorine atoms. Because fluorine atoms are larger than carbon atoms, they effectively wrap around the carbon backbone, creating a dense, helical sheath of fluorine.
This physical shield prevents other chemicals from getting close enough to attack the vulnerable carbon chain at the core of the molecule.
A Non-Reactive Surface
The fluorine-rich exterior gives PTFE an extremely low surface energy. This means there are very weak forces of attraction between PTFE and other substances, making it difficult for corrosive agents to "wet" or even physically adhere to the surface to initiate a reaction.
The Practical Scope of PTFE's Resistance
This molecular stability translates into reliable performance in the most demanding chemical environments. It is not just resistant to one or two types of chemicals; its inertness is broad and comprehensive.
Impervious to Common Corrosives
PTFE remains completely stable when exposed to nearly all industrial chemicals and solvents. This includes highly corrosive acids (like concentrated sulfuric acid), alkalis, strong oxidizing agents, and halogens (like chlorine gas).
Stability Across a Wide Temperature Range
This chemical resistance is maintained over PTFE's entire usable temperature range. It does not become more susceptible to chemical attack at elevated temperatures, which is a common failure point for lesser polymers.
Applications in Demanding Industries
Because of this durability, PTFE is the material of choice for components in chemical processing plants, laboratories, and manufacturing facilities. It is used for seals, gaskets, linings, tubing, and valves where material degradation is not an option.
Understanding the Trade-offs: The Few Exceptions
While its resistance is nearly total, PTFE is not invincible. Understanding its specific limitations is critical for safe and effective material selection in extreme applications.
Not a Universal Solution
It is a common misconception that PTFE is completely immune to everything. A very small and specific list of substances can, under certain conditions, attack the polymer.
Highly Reactive Alkali Metals
The most cited exceptions are molten or dissolved alkali metals, such as sodium. These are powerful reducing agents that are reactive enough to break the carbon-fluorine bond.
Aggressive Fluorinating Agents
A few exotic chemicals, often referred to as "super-halogens," can also degrade PTFE. These include hot fluorine gas, chlorine trifluoride, and oxygen difluoride, which are among the most aggressive fluorinating agents known.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a material requires understanding both its strengths and its boundaries. PTFE's profile makes the decision straightforward for most chemical applications.
- If your primary focus is handling aggressive acids, bases, or organic solvents: PTFE is one of the safest and most reliable choices for any component that will come into direct contact with the fluid.
- If your application involves the most extreme reactive chemicals: You must verify that your media does not include molten alkali metals or high-temperature fluorinating agents.
- If you need a versatile material for general chemical processing or laboratory use: PTFE's broad-spectrum inertness makes it an excellent default choice, minimizing the risk of unexpected material failure.
Ultimately, choosing PTFE is a decision based on its predictable and near-total chemical stability.
Summary Table:
| Key Factor | How It Contributes to Chemical Resistance |
|---|---|
| Strong C-F Bonds | One of the strongest bonds in organic chemistry, extremely difficult to break. |
| Fluorine Sheath | Fluorine atoms form a dense, protective layer around the carbon backbone. |
| Low Surface Energy | Prevents corrosive chemicals from wetting or adhering to the surface. |
| Broad Temperature Stability | Resistance is maintained across its entire usable temperature range. |
Need Chemically Inert Components You Can Trust?
PTFE's near-total chemical resistance makes it the ideal material for critical seals, liners, labware, and custom components in demanding environments. At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-precision PTFE products for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. From custom prototypes to high-volume production, our expertise ensures your components deliver unmatched reliability and performance.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific application and get a quote for durable, chemically inert PTFE solutions.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
People Also Ask
- What are the common characteristics of Teflon? Unlocking Extreme Chemical and Thermal Resistance
- In which industries is PTFE commonly used? Key Applications for Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- What industrial applications does PTFE have? Unlock Performance in Extreme Environments
- Why are PTFE vials considered environmentally friendly? Reduce Lab Waste with Durable Reusables
- What material is the PTFE bottle made from? Discover the Benefits of 100% Virgin PTFE



















