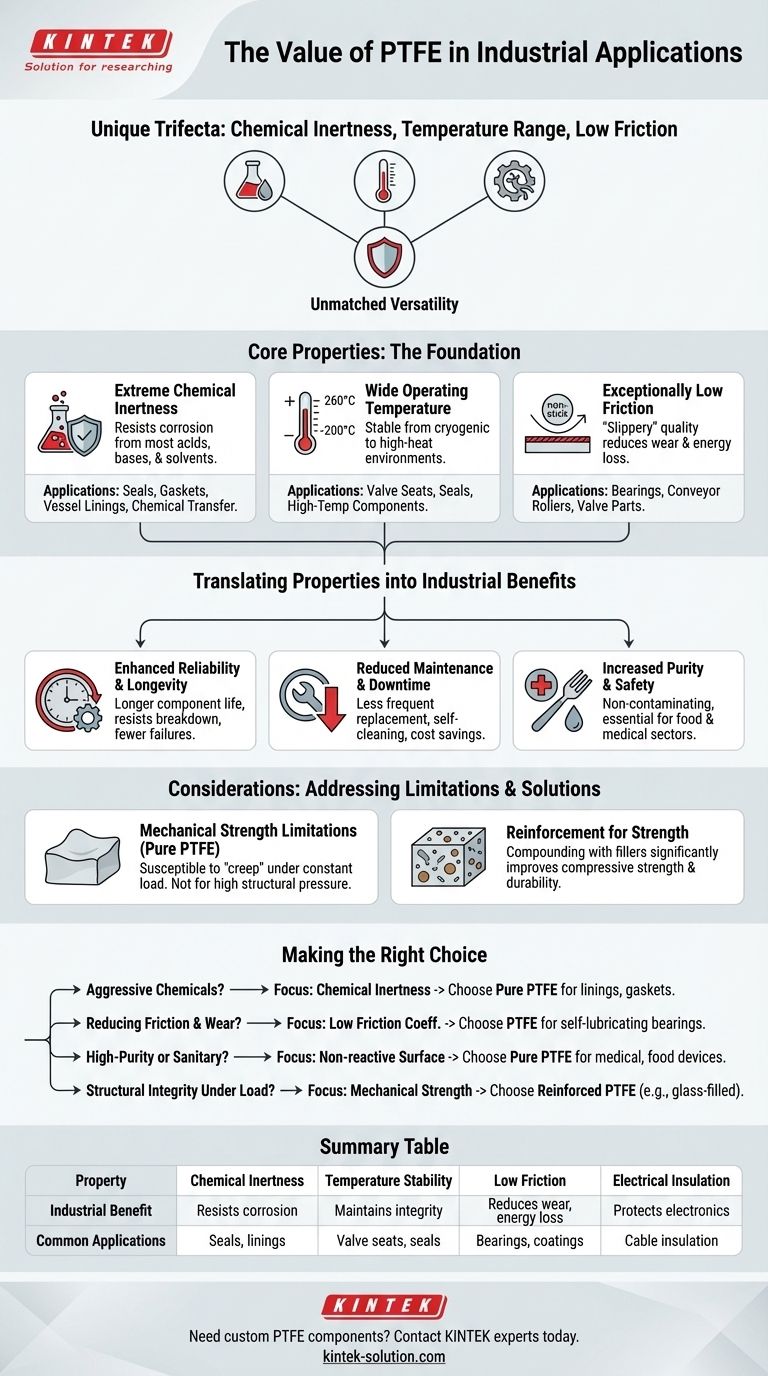
In the world of high-performance materials, few polymers are as uniquely versatile as Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE). Its value in demanding industrial applications stems from a powerful combination of three core properties: extreme chemical inertness, a very wide operating temperature range, and an exceptionally low coefficient of friction. This unique trifecta makes it the go-to material for components that must survive and perform where others would quickly fail.
PTFE's true value isn't just one single attribute, but its rare ability to solve three critical industrial challenges—corrosion, temperature, and friction—simultaneously. This makes it an indispensable problem-solver for enhancing reliability and longevity in the most demanding environments.

The Fundamental Properties of PTFE
To understand PTFE's role, we must first examine the core characteristics that set it apart. These properties are not just theoretical; they directly translate into tangible performance benefits in real-world machinery and processes.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
PTFE is one of the most non-reactive substances known. It resists corrosion and degradation from the vast majority of industrial chemicals, acids, and bases.
This makes it an ideal material for seals, gaskets, and linings in chemical processing, pharmaceutical production, and oil and gas industries where contact with aggressive media is constant.
Extreme Temperature Stability
The material maintains its integrity across an incredibly broad temperature spectrum. It can be used in applications ranging from cryogenic (-200°C) to high-heat environments (up to 260°C).
This thermal resilience ensures that components like valve seats and seals remain stable and functional without becoming brittle or degrading, a critical factor for both safety and reliability.
An Exceptionally Low Coefficient of Friction
PTFE has one of the lowest friction coefficients of any solid material, giving it a characteristic "slippery" or non-stick quality.
This property is invaluable for moving parts like valve components, bearings, and conveyor rollers, as it reduces wear, minimizes energy loss, and prevents material buildup. Its non-wetting nature also promotes a self-cleaning effect in certain applications.
Superior Electrical Insulation
Beyond its mechanical traits, PTFE is an excellent electrical insulator with high dielectric strength. This makes it essential for insulating high-voltage cables and protecting sensitive electronic components.
Translating Properties into Industrial Benefits
These fundamental properties are not isolated advantages. They combine to produce significant operational and financial benefits that drive PTFE's adoption across industries.
Enhanced Reliability and Longevity
Components made from PTFE simply last longer, especially in harsh conditions. Valves, gaskets, and seals resist chemical attack and thermal breakdown, leading to a longer operational lifespan.
Reduced Maintenance and Downtime
The durability and non-stick nature of PTFE mean less frequent replacement and cleaning. This directly reduces maintenance costs, minimizes waste, and, most importantly, decreases costly industrial downtime.
Increased Purity and Safety
In industries like food processing, medicine, and laboratory science, PTFE's non-reactive nature is critical. It does not contaminate the media it contacts, ensuring product purity in applications from medical catheters to food production equipment.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While PTFE is a remarkable material, it is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Mechanical Strength Limitations
In its pure, or "virgin," state, PTFE is a relatively soft material. It can be susceptible to "creep" or deformation when placed under a constant, heavy load.
For high-pressure or structural applications, pure PTFE may not provide the necessary rigidity or wear resistance.
The Role of Reinforcement
To overcome its mechanical limitations, PTFE is often compounded with reinforcing agents. Materials like glass fiber, carbon, graphite, or bronze are added to the polymer.
These reinforced grades offer significantly improved compressive strength, stiffness, and durability, making them suitable for more demanding mechanical roles, such as high-performance valve seats and bearings.
Proper Selection and Installation
The ultimate success of a PTFE component depends on choosing the correct grade for the application and ensuring proper installation. An unreinforced PTFE part used in a high-pressure system will fail, just as a poorly installed valve will compromise system efficiency and safety.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right material requires aligning its properties with your primary operational goal.
- If your primary focus is handling aggressive chemicals: Choose PTFE for its unmatched inertness in components like gaskets, vessel linings, and chemical transfer systems.
- If your primary focus is reducing friction and wear: Leverage PTFE's low friction coefficient for self-lubricating bearings, non-stick coatings, and dynamic seals.
- If your primary focus is high-purity or sanitary processes: Rely on its non-reactive and non-stick surface for medical devices, food processing equipment, and laboratory instruments.
- If your primary focus is structural integrity under load: You must specify a reinforced grade, such as glass- or carbon-filled PTFE, to prevent mechanical failure.
By understanding these distinct characteristics, engineers can leverage PTFE to solve some of the most persistent challenges in modern industry.
Summary Table:
| Key Property | Industrial Benefit | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Inertness | Resists corrosion from acids, bases, and solvents | Seals, gaskets, linings in chemical processing |
| Temperature Stability (-200°C to 260°C) | Maintains integrity in cryogenic to high-heat environments | Valve seats, high-temperature seals |
| Low Coefficient of Friction | Reduces wear, prevents material buildup, lowers energy loss | Bearings, conveyor rollers, non-stick coatings |
| Electrical Insulation | Protects sensitive components with high dielectric strength | High-voltage cable insulation, electronic parts |
Need high-performance PTFE components tailored to your specific industrial challenges?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing precision PTFE components—including custom seals, liners, and labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether you require prototypes or high-volume orders, our expertise in custom fabrication ensures you get components that deliver enhanced reliability, reduced maintenance, and increased safety in even the most demanding environments.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our PTFE solutions can solve your unique application needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- Why is PTFE suitable for cryogenic or high-temperature applications? Unmatched Thermal Stability from -450°F to 500°F
- What are some common applications of machined PTFE? Leverage its Unique Properties for Demanding Applications
- What are the key benefits of PTFE in custom fabrication? Unlock Performance in Extreme Conditions
- What are the material advantages of machining Teflon? Unlock Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- What is PTFE commonly known as and what are its unique properties? Unlock Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance



















