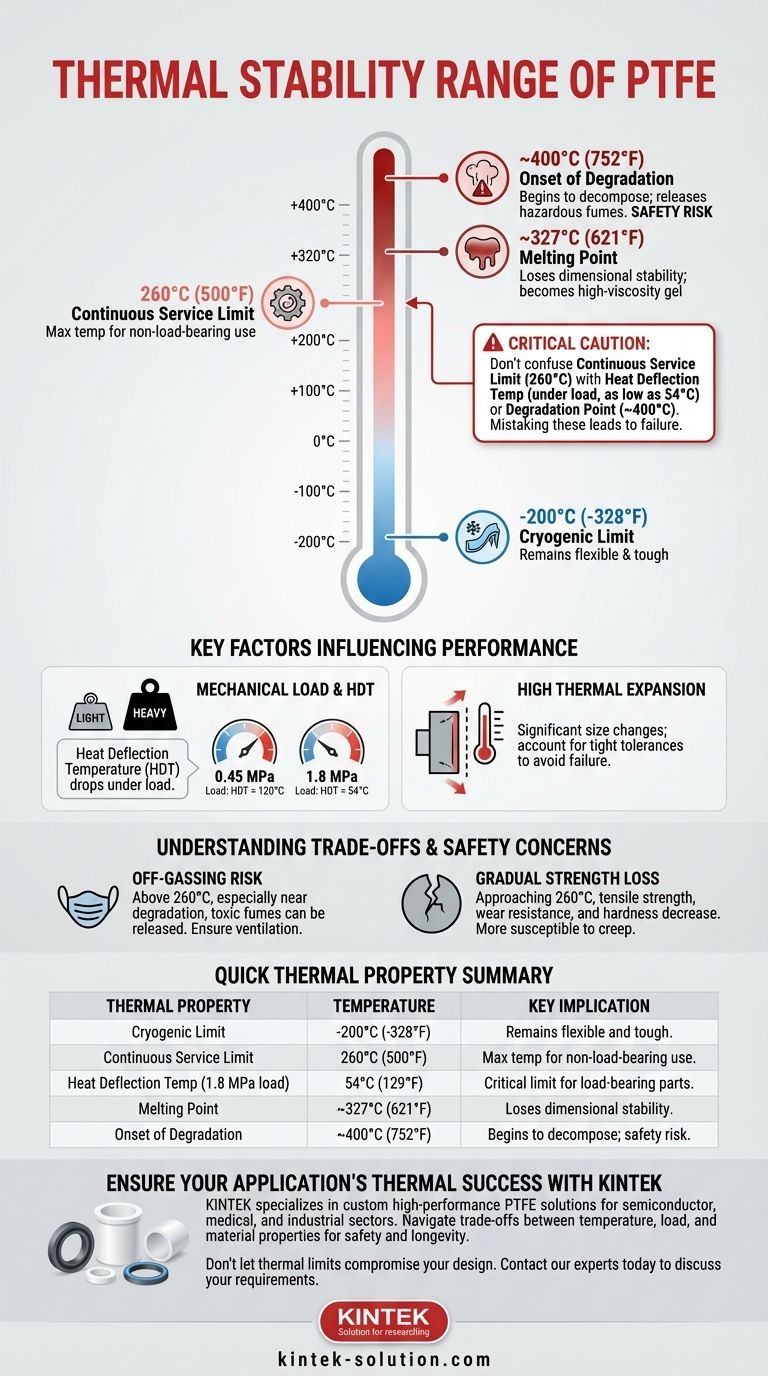
The accepted continuous service temperature range for PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) is from -200°C to 260°C (-328°F to 500°F). Within this extensive range, PTFE maintains its exceptional chemical resistance and mechanical integrity. However, this service limit is distinct from its melting point and the temperature at which it begins to chemically degrade, which occur at significantly higher temperatures.
The core challenge is not just knowing PTFE's service temperature range, but understanding the critical difference between its continuous service limit (260°C), its heat deflection temperature under load (as low as 54°C), and its degradation point (~400°C). Mistaking one for the other can lead to application failure.

Deconstructing PTFE's Thermal Behavior
To use PTFE effectively, it's essential to understand its behavior at several key thermal thresholds. Each point represents a different physical or chemical change in the material.
The Cryogenic Limit: -200°C (-328°F)
Even at extremely low temperatures, PTFE retains a high degree of its toughness and flexibility. This makes it a premier choice for cryogenic applications where other materials would become brittle and fail.
The Continuous Service Limit: 260°C (500°F)
This is the most widely cited upper limit for PTFE. It represents the maximum temperature at which the material can operate continuously without a significant loss of its fundamental properties. This makes it ideal for high-temperature seals, gaskets, and linings in non-load-bearing scenarios.
The Melting Point: ~327°C (621°F)
Unlike many materials, PTFE does not transition to a true liquid state. At its crystalline melting point, it becomes a translucent, high-viscosity gel. It loses its solid shape and dimensional stability at this temperature, but it does not yet decompose.
The Onset of Degradation: ~400°C (752°F)
Thermal degradation, where the strong carbon-fluorine bonds begin to break, does not occur until approximately 400°C. Above this temperature, the material will decompose and release potentially hazardous fumes. This threshold is a critical safety boundary, not an operational limit.
Key Factors That Influence Performance
A material's datasheet temperature range is only part of the story. Real-world conditions, particularly mechanical stress, dramatically influence PTFE's effective thermal stability.
The Critical Role of Mechanical Load
PTFE's ability to resist deformation under load drops significantly as temperature increases. This is measured by the Heat Deflection Temperature (HDT).
Under a moderate load of 0.45 MPa, PTFE's HDT is only 120°C. Under a heavier load of 1.8 MPa, it drops to just 54°C. This means a PTFE component supporting a load will fail far below its 260°C service limit.
High Thermal Expansion
PTFE has a relatively high coefficient of thermal expansion. This means it will expand and contract significantly with temperature changes. This property must be accounted for in any design with tight tolerances to avoid part seizure or failure.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Safety Concerns
While PTFE is exceptionally stable, it's crucial to be aware of its limitations, especially at the upper end of its temperature range.
The Risk of Off-Gassing
When heated above its service limit of 260°C, and especially as it approaches its degradation temperature, PTFE can release microscopic particles and toxic fumes. In poorly ventilated areas, inhaling these fumes can cause a temporary flu-like illness known as polymer fume fever.
Gradual Loss of Mechanical Strength
As PTFE approaches its 260°C service limit, its tensile strength, wear resistance, and hardness decrease. The material becomes softer and more susceptible to creep and deformation, even under light loads.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Use these guidelines to determine if PTFE's thermal properties align with your project's demands.
- If your primary focus is cryogenic or low-temperature flexibility: PTFE is an excellent choice, remaining robust and functional down to -200°C.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature resistance in a no-load or low-load scenario: PTFE is reliable up to its 260°C continuous service limit for applications like seals, liners, or coatings.
- If your primary focus is a load-bearing component at elevated temperatures: You must design based on the Heat Deflection Temperature (as low as 54°C), not the service limit, and consider filled grades of PTFE or alternative materials.
By understanding the distinction between service temperature, load-dependent limits, and degradation, you can confidently specify PTFE for its intended thermal environment.
Summary Table:
| Thermal Property | Temperature | Key Implication |
|---|---|---|
| Cryogenic Limit | -200°C (-328°F) | Remains flexible and tough. |
| Continuous Service Limit | 260°C (500°F) | Max temp for non-load-bearing use. |
| Heat Deflection Temp (under 1.8 MPa load) | 54°C (129°F) | Critical limit for load-bearing parts. |
| Melting Point | ~327°C (621°F) | Loses dimensional stability. |
| Onset of Degradation | ~400°C (752°F) | Begins to decompose; safety risk. |
Ensure Your Application's Thermal Success with KINTEK
Understanding PTFE's complex thermal behavior is the first step. The next is sourcing precision-manufactured components that perform reliably within these limits. At KINTEK, we specialize in the custom fabrication of high-performance PTFE components—from seals and liners to complex labware—for the semiconductor, medical, and industrial sectors.
We help you navigate the trade-offs between temperature, load, and material properties to deliver a solution that ensures safety, longevity, and performance. Whether you need a prototype or a high-volume order, our commitment to precision production guarantees a perfect fit for your demanding environment.
Don't let thermal limits compromise your design. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific requirements and get a quote for your project.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Volumetric Flasks for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Use
People Also Ask
- What are the key benefits of PTFE in custom fabrication? Unlock Performance in Extreme Conditions
- What are the material advantages of machining Teflon? Unlock Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- What are the primary applications of PTFE fasteners and custom parts? Critical Solutions for Extreme Environments
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? Unlock Unmatched Performance in Demanding Applications



















