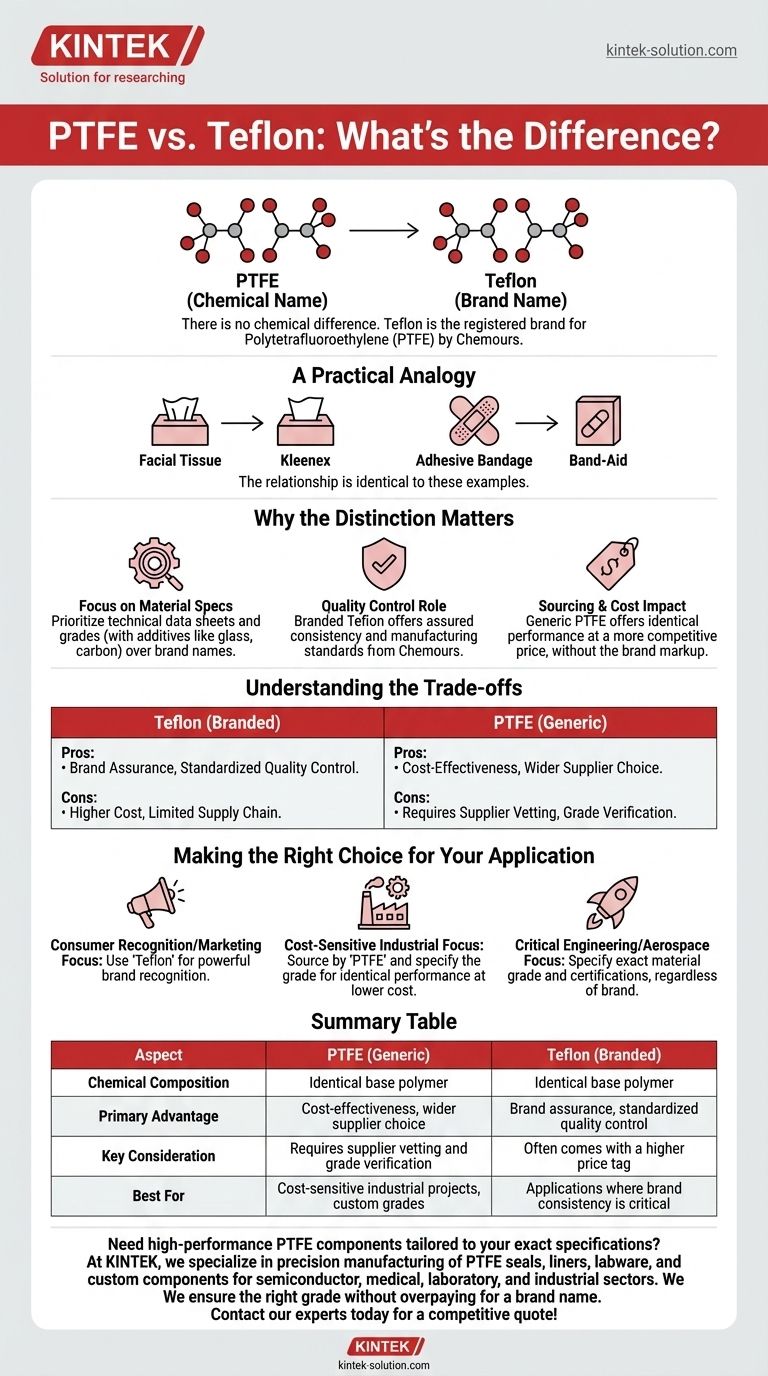
There is no chemical difference between PTFE and Teflon. They are two names for the exact same material. Teflon is simply the registered brand name for the polymer Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), commercialized by the company Chemours.
The distinction between PTFE and Teflon is not one of substance but of branding. Understanding this allows you to focus on the material's actual properties and grade rather than its name, ensuring you select the right material for your application without overpaying for a label.

The Fundamental Relationship: Chemical vs. Brand
To make informed decisions when sourcing materials or specifying components, it's crucial to understand the relationship between a chemical compound and its commercial brand name.
What is PTFE?
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is the chemical name for a specific synthetic fluoropolymer. It is a highly versatile material known for its exceptional properties.
These properties include an extremely low coefficient of friction (making it very slippery), high chemical resistance, and excellent performance at a wide range of temperatures.
Where "Teflon" Comes From
Teflon is the trademarked brand name that Chemours (formerly part of DuPont) uses to market its family of fluoropolymer products, the most famous of which is PTFE.
The brand became a household name primarily through its use as a non-stick coating on cookware, creating powerful public recognition.
A Practical Analogy
The relationship is identical to that between "facial tissue" and the brand Kleenex, or "adhesive bandage" and the brand Band-Aid.
While many people use the brand name to refer to the generic product, the underlying material or item is the same regardless of what it's called.
Why This Distinction Matters in Practice
While the base polymer is identical, the naming distinction can have practical implications for sourcing, cost, and quality assurance in professional environments.
Focus on Material Specifications
The term "PTFE" refers to the chemical itself. However, manufacturers produce many different grades and formulations of PTFE with varying additives (like glass, carbon, or bronze) to enhance specific properties like strength or conductivity.
Your primary focus should always be on the technical data sheet for the specific material grade, not just whether it is branded or unbranded.
The Role of Quality Control
Purchasing a product under the Teflon brand often provides an assurance of consistent quality control and manufacturing standards set by Chemours.
For critical applications, specifying a branded product can sometimes simplify the process of ensuring that the material meets a known performance benchmark.
Impact on Sourcing and Cost
Generally, a product marketed simply as "PTFE" from a reputable supplier can offer identical performance to a branded "Teflon" product at a more competitive price.
The cost difference is often attributed to branding and marketing rather than a difference in the quality of the base polymer itself.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing between a product labeled "Teflon" and one labeled "PTFE" involves weighing brand assurance against cost and supply chain flexibility.
The "Teflon" Guarantee
The primary benefit of specifying Teflon is the trust associated with a long-standing, globally recognized brand. You are buying a product with a known history and standardized quality.
The potential trade-off is a higher cost and a more limited supply chain, as it is tied to a single company and its licensed distributors.
The "Generic PTFE" Advantage
The key advantage of sourcing generic PTFE is cost-effectiveness and a much wider range of suppliers.
The trade-off is that the burden of vetting the supplier and verifying the quality and grade of the material falls more heavily on you. You must ensure the product's specifications precisely match your application's requirements.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision should be guided by the specific needs of your project, balancing performance requirements, budget, and risk tolerance.
- If your primary focus is consumer recognition or marketing: Using the term "Teflon" leverages its powerful brand recognition and perceived quality.
- If your primary focus is cost-sensitive industrial applications: Sourcing by the chemical name "PTFE" and specifying the required grade can provide identical performance at a lower cost.
- If your primary focus is a critical engineering or aerospace application: You must specify the exact material grade and certifications required, regardless of whether the product is branded Teflon or sourced as PTFE from another qualified manufacturer.
Ultimately, your focus should be on the material's technical specifications and grade, as these—not the name—will determine its performance in your application.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | PTFE (Generic) | Teflon (Branded) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Composition | Identical base polymer | Identical base polymer |
| Primary Advantage | Cost-effectiveness, wider supplier choice | Brand assurance, standardized quality control |
| Key Consideration | Requires supplier vetting and grade verification | Often comes with a higher price tag |
| Best For | Cost-sensitive industrial projects, custom grades | Applications where brand consistency is critical |
Need high-performance PTFE components tailored to your exact specifications?
At KINTEK, we specialize in the precision manufacturing of PTFE seals, liners, labware, and custom components for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether you require prototypes or high-volume orders, our expertise ensures you get the right material grade and performance without overpaying for a brand name.
Contact our experts today to discuss your project and receive a competitive quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- What are some common applications of machined PTFE? Leverage its Unique Properties for Demanding Applications
- Why is PTFE suitable for cryogenic or high-temperature applications? Unmatched Thermal Stability from -450°F to 500°F
- What are the base characteristics of PTFE? Unlocking Extreme Performance in Friction, Temperature, and Chemical Resistance
- What are the primary applications of PTFE fasteners and custom parts? Critical Solutions for Extreme Environments



















