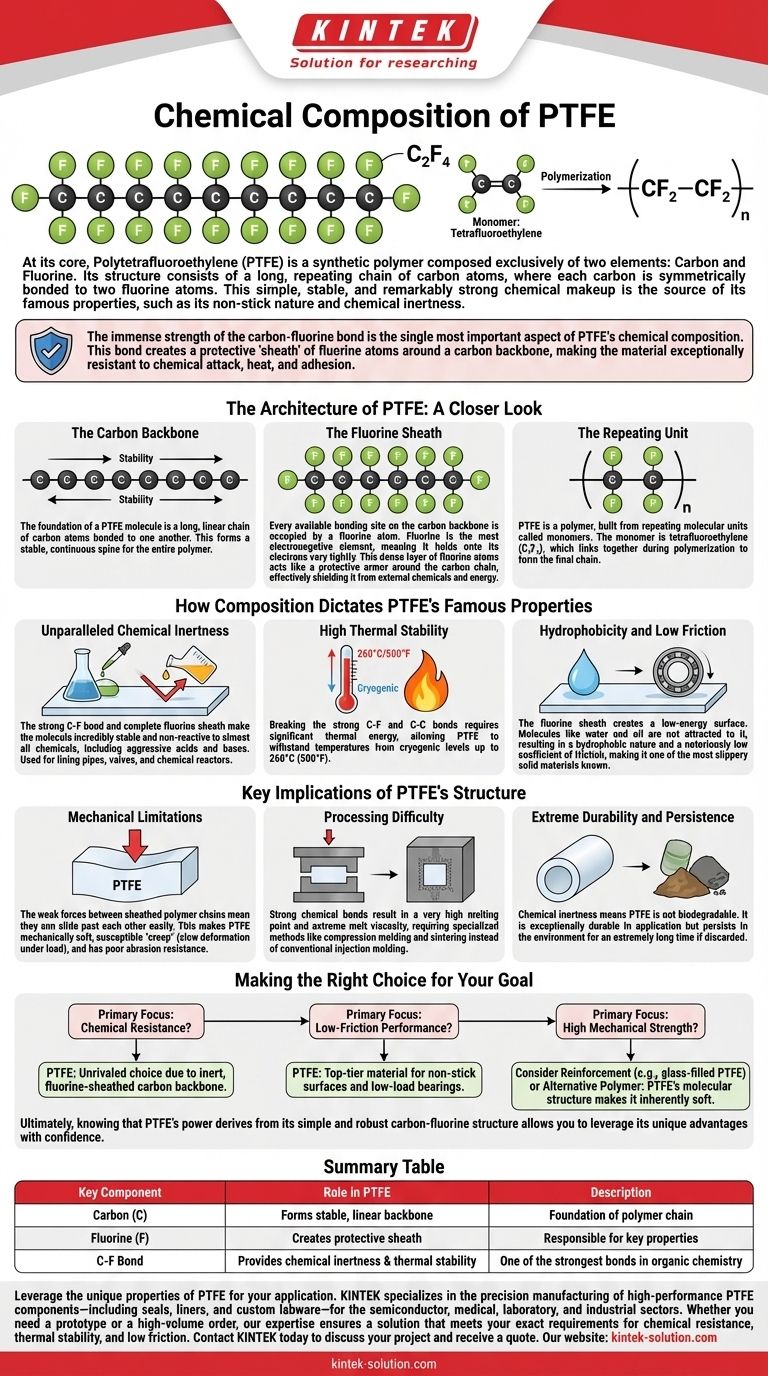
At its core, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a synthetic polymer composed exclusively of two elements: carbon and fluorine. Its structure consists of a long, repeating chain of carbon atoms, where each carbon is symmetrically bonded to two fluorine atoms. This simple, stable, and remarkably strong chemical makeup is the source of its famous properties, such as its non-stick nature and chemical inertness.
The immense strength of the carbon-fluorine bond is the single most important aspect of PTFE's chemical composition. This bond creates a protective "sheath" of fluorine atoms around a carbon backbone, making the material exceptionally resistant to chemical attack, heat, and adhesion.

The Architecture of PTFE: A Closer Look
To understand why PTFE behaves the way it does, we must examine its molecular structure. It's an elegant design where simplicity leads to extraordinary performance.
The Carbon Backbone
The foundation of a PTFE molecule is a long, linear chain of carbon atoms bonded to one another. This forms a stable, continuous spine for the entire polymer.
The Fluorine Sheath
The critical feature of PTFE is that every available bonding site on the carbon backbone is occupied by a fluorine atom. Fluorine is the most electronegative element, meaning it holds onto its electrons very tightly.
This dense layer of fluorine atoms acts like a protective armor around the carbon chain, effectively shielding it from external chemicals and energy.
The Repeating Unit
PTFE is a polymer, which means it's built from repeating molecular units called monomers. The monomer for PTFE is tetrafluoroethylene, which has the chemical formula C₂F₄.
During polymerization, these monomer units link together to form the long -(CF₂-CF₂)-n chain that constitutes the final material.
How Composition Dictates PTFE's Famous Properties
The specific arrangement of carbon and fluorine atoms directly translates into the material properties that make PTFE so valuable in industrial and consumer applications.
Unparalleled Chemical Inertness
The carbon-fluorine bond is one of the strongest single bonds in organic chemistry. This, combined with the complete fluorine sheath, makes the molecule incredibly stable and non-reactive.
PTFE is inert to almost all chemicals, including aggressive acids and bases, which is why it's used extensively for lining pipes, valves, and chemical reactors.
High Thermal Stability
Breaking the strong C-F and C-C bonds in the PTFE molecule requires a significant amount of thermal energy.
This is why PTFE can withstand a very wide range of temperatures, performing reliably from cryogenic levels up to approximately 260°C (500°F).
Hydrophobicity and Low Friction
The fluorine sheath creates a surface with extremely low energy. Molecules, including water and oil, are not attracted to it and cannot easily wet the surface.
This low surface energy is responsible for PTFE's hydrophobic (water-repelling) nature and its famously low coefficient of friction, making it one of the most slippery solid materials known.
Key Implications of PTFE's Structure
While its chemical composition provides incredible strengths, it also results in certain limitations that are important to understand when selecting materials.
Mechanical Limitations
The same weak forces between the sheathed polymer chains that prevent things from sticking also mean the chains can slide past each other relatively easily.
This makes PTFE a mechanically soft material. It is susceptible to "creep" (slow deformation under load) and has poor abrasion resistance compared to harder plastics.
Processing Difficulty
The strong chemical bonds give PTFE a very high melting point and an extremely high melt viscosity.
This combination makes it impossible to process using conventional techniques like injection molding. Instead, specialized methods like compression molding and sintering are required.
Extreme Durability and Persistence
The flip side of its chemical inertness is that PTFE is not biodegradable. The same strong bonds that resist industrial chemicals also resist natural degradation processes.
This means the material is exceptionally durable in its application but will persist in the environment for an extremely long time if discarded.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding PTFE's composition allows you to determine if it is the correct material for your specific application.
- If your primary focus is chemical resistance: PTFE is an almost unrivaled choice due to its inert, fluorine-sheathed carbon backbone.
- If your primary focus is low-friction performance: The low surface energy created by the fluorine atoms makes PTFE a top-tier material for non-stick surfaces and low-load bearings.
- If your primary focus is high mechanical strength: You should recognize that PTFE's molecular structure makes it inherently soft and may require reinforcement (e.g., glass-filled PTFE) or an alternative polymer.
Ultimately, knowing that PTFE's power derives from its simple and robust carbon-fluorine structure allows you to leverage its unique advantages with confidence.
Summary Table:
| Key Component | Role in PTFE |
|---|---|
| Carbon (C) | Forms the stable, linear backbone of the polymer chain. |
| Fluorine (F) | Creates a protective sheath around the carbon chain, responsible for PTFE's key properties. |
| C-F Bond | One of the strongest bonds in organic chemistry, providing chemical inertness and thermal stability. |
Leverage the unique properties of PTFE for your application. KINTEK specializes in the precision manufacturing of high-performance PTFE components—including seals, liners, and custom labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether you need a prototype or a high-volume order, our expertise ensures a solution that meets your exact requirements for chemical resistance, thermal stability, and low friction.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your project and receive a quote.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- How does PTFE react to common solvents? Discover Its Near-Total Chemical Immunity
- What are the additional properties of PTFE? Beyond Non-Stick: Extreme Chemical, Thermal & Electrical Performance
- What environmental resistances does PTFE offer? Unmatched Durability for Harsh Conditions
- When was PTFE discovered and developed? The Accidental Invention That Changed Industries
- What is PTFE and what class of plastics does it belong to? A Guide to High-Performance Fluoropolymers



















