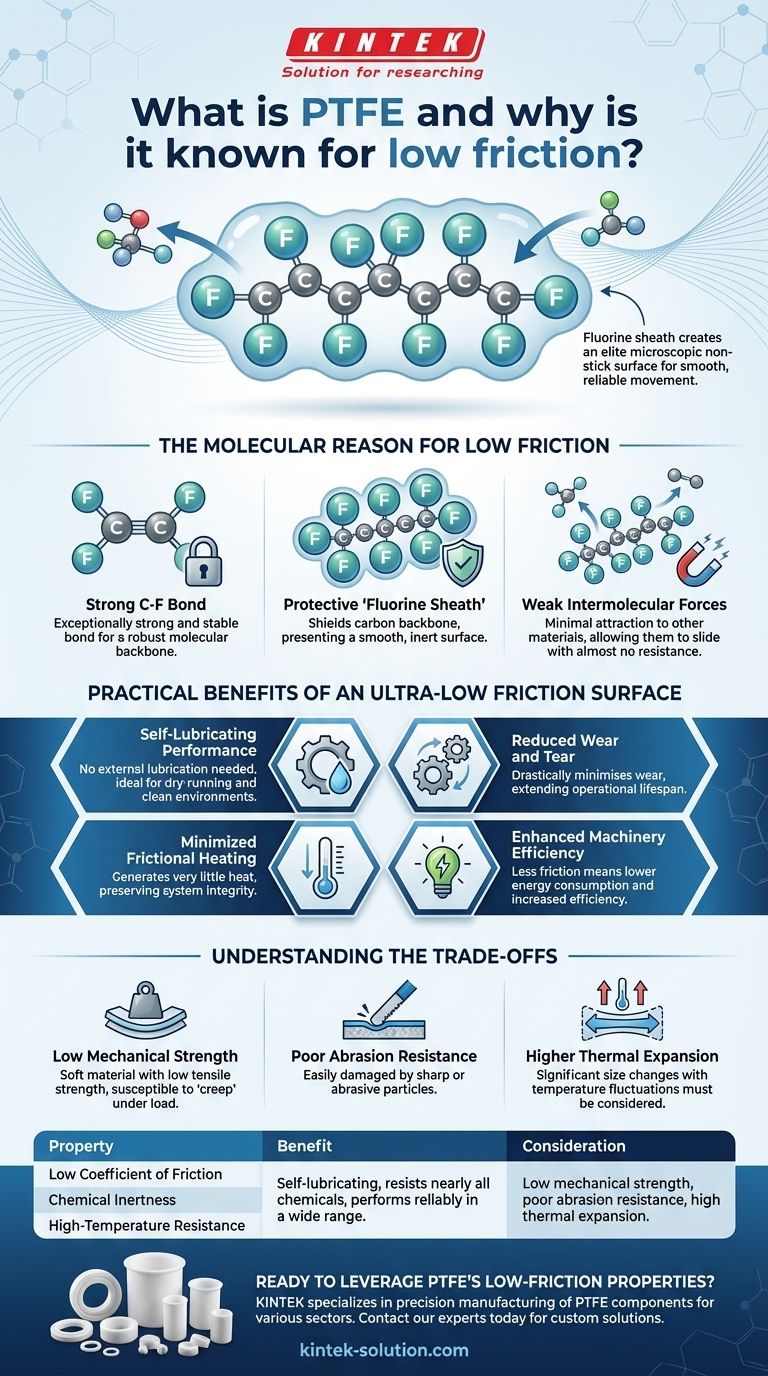
At its core, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a synthetic fluoropolymer whose exceptionally low friction is a direct result of its unique molecular structure. The fluorine atoms that encase its carbon backbone create a highly stable, non-reactive surface that resists bonding with other materials, allowing them to slide past with minimal resistance.
The defining characteristic of PTFE is not just its low friction, but why it exists: its molecules are wrapped in a "sheath" of fluorine atoms. This creates a microscopic non-stick surface, making it an elite material for applications where smooth, reliable movement is critical.

The Molecular Reason for Low Friction
To truly understand PTFE, we must look at its atomic composition. Its properties are not accidental; they are a direct consequence of its chemical makeup.
The Strong Carbon-Fluorine Bond
PTFE is built on a long chain of carbon atoms, much like other polymers. However, each carbon atom is bonded to two fluorine atoms.
The bond between carbon and fluorine is exceptionally strong and stable. This creates a very robust and inert molecular backbone.
The Protective "Fluorine Sheath"
The fluorine atoms are larger than the carbon atoms they are attached to. They effectively wrap around the carbon chain, creating a tight, uniform, and protective "sheath."
This sheath shields the carbon backbone from interacting with other substances. It presents a smooth, electrically neutral surface at the molecular level.
Weak Intermolecular Forces
Because of this fluorine sheath, the forces of attraction between a PTFE molecule and other molecules are extremely weak. This is the fundamental reason for its non-stick and low-friction properties.
Other materials simply don't have anything to "grab onto." They slide off the surface with almost no resistance, which is what we observe as a very low coefficient of friction.
Practical Benefits of an Ultra-Low Friction Surface
This unique molecular property translates directly into significant real-world advantages, particularly in dynamic or moving systems.
Self-Lubricating Performance
PTFE's inherent slipperiness means it requires no external lubrication. It performs exceptionally well in dry-running conditions where oils or greases cannot be used.
This makes it ideal for components like seals and bearings in clean environments or food-grade applications.
Reduced Wear and Tear
By minimizing resistance during movement, PTFE drastically reduces wear on both itself and the surfaces it contacts.
This quality is crucial for components like bearings, bushings, and gears, as it extends their operational lifespan and reduces maintenance frequency and costs.
Minimized Frictional Heating
In high-speed or high-load applications, friction generates heat, which can lead to material degradation and system failure.
PTFE's extremely low friction generates very little heat, preserving the integrity of the system and ensuring consistent performance.
Enhanced Machinery Efficiency
Less friction means less energy is wasted overcoming resistance. Using PTFE components in machinery can lead to lower energy consumption.
This is particularly valuable in automotive and manufacturing industries where efficiency is a primary design goal.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No material is perfect. While PTFE's low friction is a tremendous asset, its other properties present limitations that must be considered.
Low Mechanical Strength
PTFE is a relatively soft material. It has low tensile strength and is susceptible to "creep," which is slow deformation under a persistent load.
It is not suitable for high-load structural applications without reinforcement, often in the form of glass or carbon fillers.
Poor Abrasion Resistance
While PTFE excels at smooth sliding, it is easily damaged by sharp or abrasive particles. Contaminants in a system can quickly score or wear away a PTFE surface, compromising its performance.
Higher Thermal Expansion
PTFE expands and contracts with temperature changes more significantly than many other materials. This must be accounted for in designs requiring tight tolerances across a wide temperature range.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting PTFE should be a deliberate decision based on its unique strengths, not a default choice.
- If your primary focus is smooth, unlubricated sliding: PTFE is an elite choice for bearings, seals, and slide plates where reducing stick-slip motion is paramount.
- If your primary focus is chemical inertness: The same molecular structure that creates low friction also makes PTFE highly resistant to nearly all chemicals.
- If your primary focus is high mechanical load or abrasion resistance: A filled grade of PTFE or an entirely different material like PEEK or nylon may be a more durable solution.
Ultimately, harnessing the power of PTFE means leveraging its unparalleled low-friction surface while respecting its mechanical limitations.
Summary Table:
| Property | Benefit | Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Low Coefficient of Friction | Self-lubricating, reduces energy consumption | Soft material with low mechanical strength |
| Chemical Inertness | Resists nearly all chemicals, ideal for harsh environments | Poor abrasion resistance against sharp particles |
| High-Temperature Resistance | Performs reliably in a wide temperature range | High thermal expansion requires design consideration |
Ready to leverage PTFE's low-friction properties in your application?
KINTEK specializes in the precision manufacturing of PTFE components—including seals, liners, and custom labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether you need prototypes or high-volume orders, we deliver solutions that minimize friction, reduce wear, and enhance efficiency.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific requirements and get a custom solution quote.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments
- Why is CNC machining preferred for Teflon parts over other methods? Unlock Precision & Complex Designs
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials



















