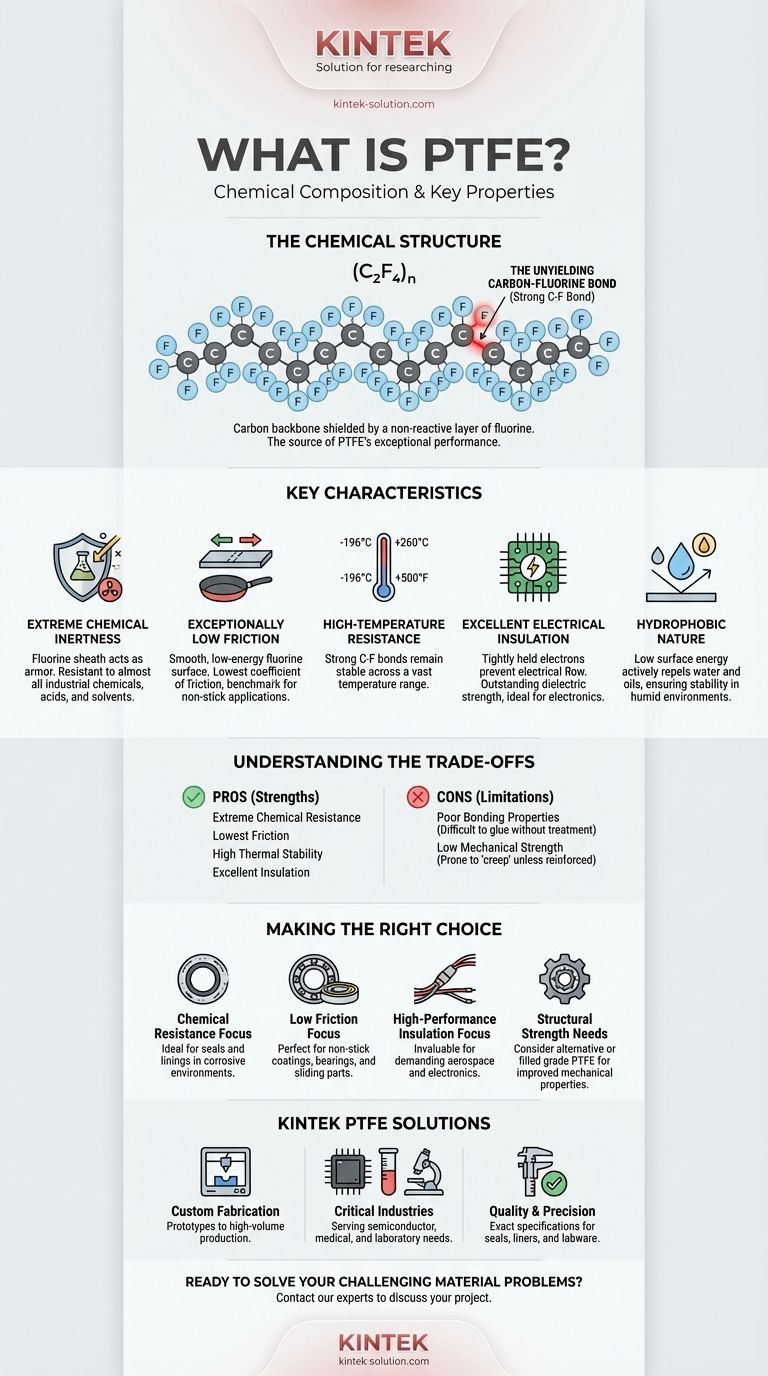
In short, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a high-performance synthetic polymer composed entirely of carbon and fluorine. Its chemical formula, (C₂F₄)n, describes a long chain of carbon atoms completely surrounded by a protective sheath of fluorine atoms. This unique and incredibly stable molecular structure is the direct source of its famous properties, such as its extreme slipperiness and chemical inertness, which are commercially recognized under brand names like Teflon.
The immense strength of the carbon-fluorine bond is the single most important concept to grasp. This bond is the origin of nearly all of PTFE's exceptional characteristics, making it one of the most chemically resistant, thermally stable, and lowest-friction materials known.

The Source of PTFE's Unique Properties
The remarkable capabilities of PTFE are not magic; they are a direct result of its simple but powerful chemical architecture. The entire structure is built around the bond between carbon and fluorine atoms.
The Unyielding Carbon-Fluorine Bond
Fluorine is the most electronegative element, meaning it forms an exceptionally strong and stable bond with carbon. This bond requires a tremendous amount of energy to break.
This results in a polymer chain where the carbon "backbone" is completely shielded by a dense, non-reactive layer of fluorine atoms. This structure is the key to its performance.
Key Characteristics Explained
Each of PTFE's famous traits can be traced back to its fundamental chemical makeup. Understanding this connection is key to understanding the material itself.
Extreme Chemical Inertness
The fluorine sheath acts like armor, protecting the carbon backbone from attack. This makes PTFE virtually inert to almost all industrial chemicals, acids, and solvents, even at high temperatures.
Exceptionally Low Friction
The fluorine atoms create a very smooth, low-energy surface. Other molecules have little to nothing to "grab onto," causing them to slide right off. This gives PTFE the lowest coefficient of friction of any known solid, making it the benchmark for non-stick and low-friction applications.
High-Temperature Resistance
Because the carbon-fluorine bonds are so strong, they remain stable across an incredibly wide temperature range. PTFE can perform consistently from cryogenic temperatures (-196°C / -320°F) up to around +260°C (+500°F).
Excellent Electrical Insulation
The same forces that make the C-F bond strong also mean that electrons are held very tightly. This prevents the flow of electricity, making PTFE an outstanding electrical insulator with high dielectric strength, ideal for high-frequency electronics.
Hydrophobic Nature
PTFE's low surface energy actively repels water and oils. It does not absorb moisture, which ensures its properties remain stable even in humid environments.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No material is perfect, and PTFE's greatest strengths are also the source of its limitations. Being objective about these trade-offs is critical for successful application.
Poor Bonding Properties
The same non-stick quality that makes PTFE so valuable also makes it extremely difficult to glue or bond to other materials. Special surface treatments like chemical etching are often required to achieve any adhesion.
Low Mechanical Strength
Compared to engineering plastics or metals, PTFE is a relatively soft material. It can be prone to "creep" or deforming under a sustained load and has poor abrasion resistance unless it is reinforced with fillers like glass or carbon.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting PTFE is a decision that must be aligned with the primary demand of your application.
- If your primary focus is extreme chemical resistance: PTFE is a top-tier choice for seals, gaskets, and linings in corrosive chemical environments where other materials would quickly fail.
- If your primary focus is the lowest possible friction: PTFE is the ideal solution for non-stick coatings on cookware, low-friction bearings, and medical devices that require a slippery surface.
- If your primary focus is high-performance insulation: PTFE's stability at high temperatures and excellent dielectric properties make it invaluable for wiring and components in demanding aerospace and electronics applications.
- If your primary focus is structural strength or easy bonding: You should consider alternative materials or use a filled grade of PTFE specifically engineered to improve its mechanical properties.
Understanding PTFE's simple chemical foundation is the key to leveraging its extraordinary capabilities in the world's most demanding applications.
Summary Table:
| Key Property | Root Cause (Chemical Structure) | Common Application |
|---|---|---|
| Extreme Chemical Inertness | Protective sheath of fluorine atoms | Seals, Liners, Labware |
| Exceptionally Low Friction | Smooth, low-energy fluorine surface | Non-stick Coatings, Bearings |
| High-Temperature Resistance | Strong Carbon-Fluorine (C-F) bonds | High-Temp Seals, Insulation |
| Excellent Electrical Insulation | Tightly held electrons | High-Frequency Electronics |
Leverage PTFE's Superior Properties for Your Application
PTFE's unique combination of chemical resistance, thermal stability, and low friction makes it ideal for demanding applications in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
KINTEK specializes in the precision manufacturing of high-performance PTFE components. We offer:
- Custom Fabrication: From prototypes to high-volume production runs.
- Expertise in Critical Industries: Serving semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and specialized industrial needs.
- Quality & Precision: Ensuring every seal, liner, or piece of labware meets your exact specifications.
Ready to solve your most challenging material problems? Contact our experts today to discuss your project requirements and discover how our custom PTFE solutions can enhance your product's performance and reliability.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Volumetric Flasks for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Use
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- What are the material advantages of machining Teflon? Unlock Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- What are the key benefits of PTFE in custom fabrication? Unlock Performance in Extreme Conditions
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? Unlock Unmatched Performance in Demanding Applications
- What are the primary applications of PTFE fasteners and custom parts? Critical Solutions for Extreme Environments
- What are the base characteristics of PTFE? Unlocking Extreme Performance in Friction, Temperature, and Chemical Resistance



















