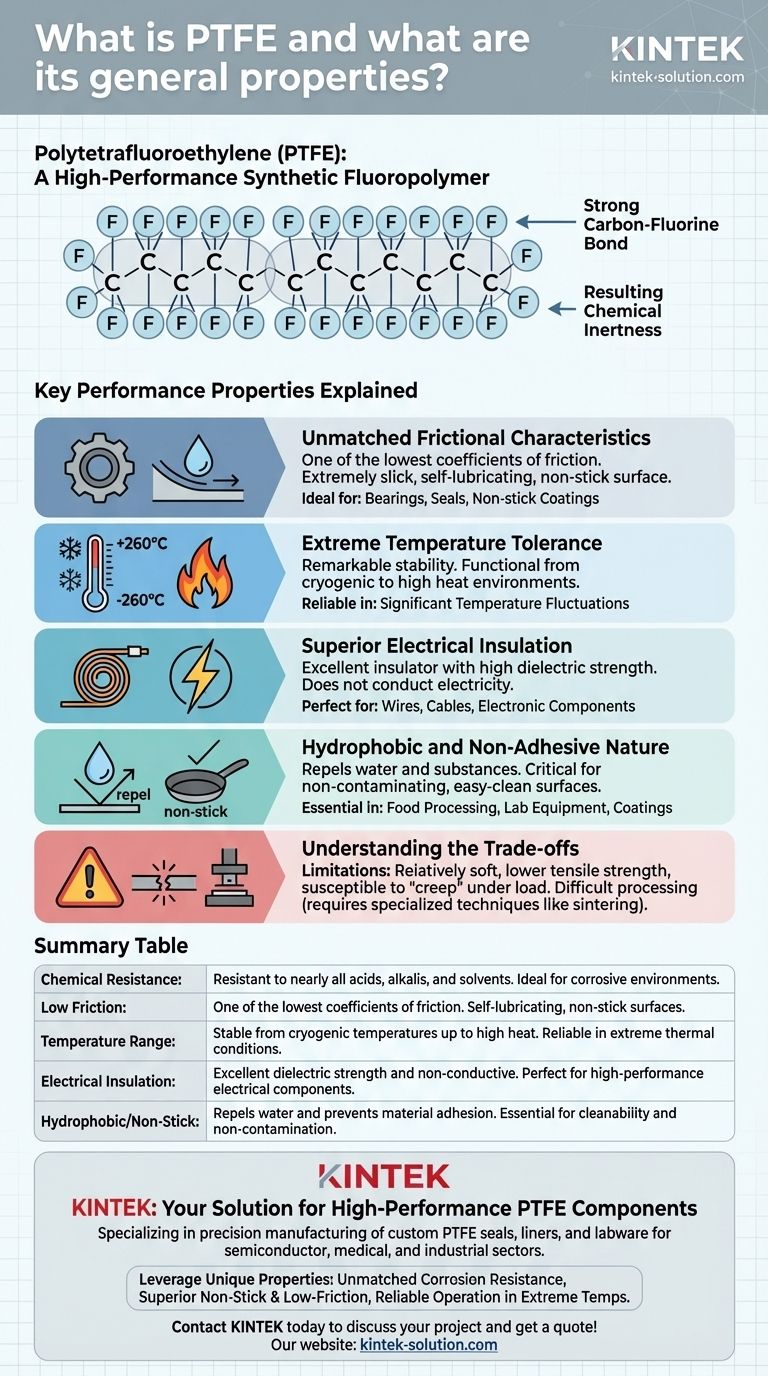
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a high-performance synthetic fluoropolymer, most commonly known by the brand name Teflon. It is a material defined by its exceptional resistance to chemicals, extreme temperatures, and friction. Its unique properties stem from its molecular structure, which consists of a carbon backbone completely shielded by fluorine atoms.
The true value of PTFE lies not in a single attribute, but in its rare combination of near-total chemical inertness, an extremely wide operating temperature range, and one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid material on Earth.

The Foundation: An Exceptionally Stable Structure
At its core, PTFE's remarkable characteristics are a direct result of its simple yet powerful molecular makeup. This structure is the key to understanding why it behaves the way it does.
The Carbon-Fluorine Bond
PTFE is a polymer built from repeating tetrafluoroethylene units. This creates a long chain of carbon atoms protected by a dense, helical sheath of fluorine atoms.
The bond between carbon and fluorine is exceptionally strong and stable, making the entire molecule highly unreactive.
Resulting Chemical Inertness
This molecular shield gives PTFE its legendary chemical resistance. It is virtually immune to acids, alkalis, and nearly all organic solvents.
Only a few highly reactive substances, like molten alkali metals or hot fluorine gas, can attack it. This makes it one of the most corrosion-resistant materials available today.
Key Performance Properties Explained
The stable structure gives rise to a set of highly desirable physical properties that make PTFE invaluable across numerous industries, from aerospace to medicine.
Unmatched Frictional Characteristics
PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any known solid. This gives it an extremely slick, self-lubricating surface.
This property is the reason it is used for non-stick coatings on cookware and for high-performance bearings, gaskets, and seals that require minimal resistance.
Extreme Temperature Tolerance
The material demonstrates remarkable thermal stability. It can service applications at very high temperatures and remains functional and flexible at cryogenic (very low) temperatures.
This wide operating window makes it a reliable choice for components used in environments with significant temperature fluctuations.
Superior Electrical Insulation
PTFE is an excellent electrical insulator with high dielectric strength. It does not conduct electricity, making it ideal for insulating wires, cables, and other electronic components.
Its resistance to heat and weather also contributes to its durability in demanding electrical applications.
Hydrophobic and Non-Adhesive Nature
The material is hydrophobic, meaning it repels water and water-containing substances. This, combined with its low friction, creates a non-adhesive or "non-stick" surface.
Materials have a very difficult time sticking to PTFE, which is critical for applications in food processing, laboratory equipment, and coatings for machine parts.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While its properties are exceptional, PTFE is not the ideal solution for every problem. Objectivity requires acknowledging its limitations.
Mechanical Limitations
Compared to other engineering plastics, PTFE is relatively soft and has lower tensile strength and wear resistance.
Under a sustained load, it can be susceptible to "creep" or deformation over time. This is why it is often reinforced with other materials like glass or carbon for structural applications.
Processing Challenges
PTFE's very high melting point and melt viscosity make it more difficult to process than common thermoplastics. It cannot be easily injection molded or extruded using conventional methods.
Specialized techniques like sintering and compression molding are required, which can increase manufacturing complexity and cost.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting PTFE should be a deliberate decision based on its unique strengths.
- If your primary focus is extreme chemical resistance: PTFE is a world-class choice for seals, linings, valves, and lab equipment that handle highly corrosive substances.
- If your primary focus is low friction and non-stick surfaces: Its self-lubricating nature is ideal for high-performance bearings, bushings, and specialized coatings.
- If your primary focus is thermal and electrical stability: It is a go-to material for high-temperature electrical insulators and components used in harsh thermal environments.
Ultimately, PTFE should be considered when your application demands a level of performance that more common materials simply cannot provide.
Summary Table:
| Property | Description | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Resistant to nearly all acids, alkalis, and solvents. | Ideal for corrosive environments. |
| Low Friction | One of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid. | Self-lubricating, non-stick surfaces. |
| Temperature Range | Stable from cryogenic temperatures up to high heat. | Reliable in extreme thermal conditions. |
| Electrical Insulation | Excellent dielectric strength and non-conductive. | Perfect for high-performance electrical components. |
| Hydrophobic/Non-Stick | Repels water and prevents material adhesion. | Essential for cleanability and non-contamination. |
Need High-Performance PTFE Components?
Leverage the unique properties of PTFE for your most demanding applications. KINTEK specializes in the precision manufacturing of custom PTFE components—including seals, liners, and labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
We deliver solutions that prioritize:
- Unmatched Corrosion Resistance for handling aggressive chemicals.
- Superior Non-Stick & Low-Friction performance for moving parts and easy-clean surfaces.
- Reliable Operation across extreme temperature ranges.
From prototypes to high-volume production, we provide the material expertise and custom fabrication to meet your exact specifications.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your project and get a quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Volumetric Flasks for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Use
People Also Ask
- What are some common applications of machined PTFE? Leverage its Unique Properties for Demanding Applications
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? Unlock Unmatched Performance in Demanding Applications
- What are the key benefits of PTFE in custom fabrication? Unlock Performance in Extreme Conditions
- What are the material advantages of machining Teflon? Unlock Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications



















