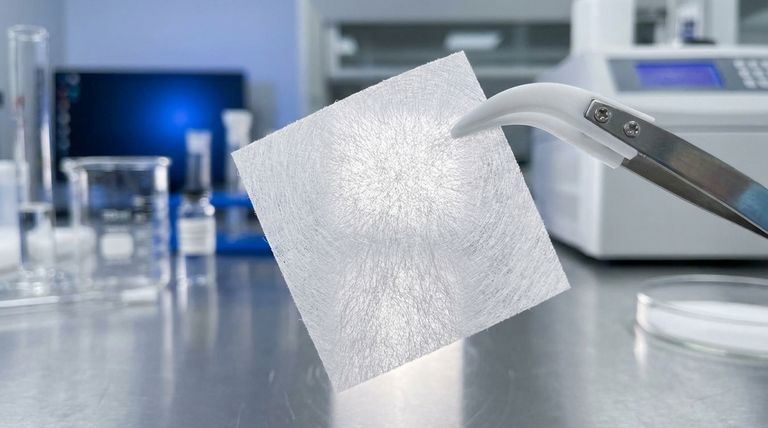
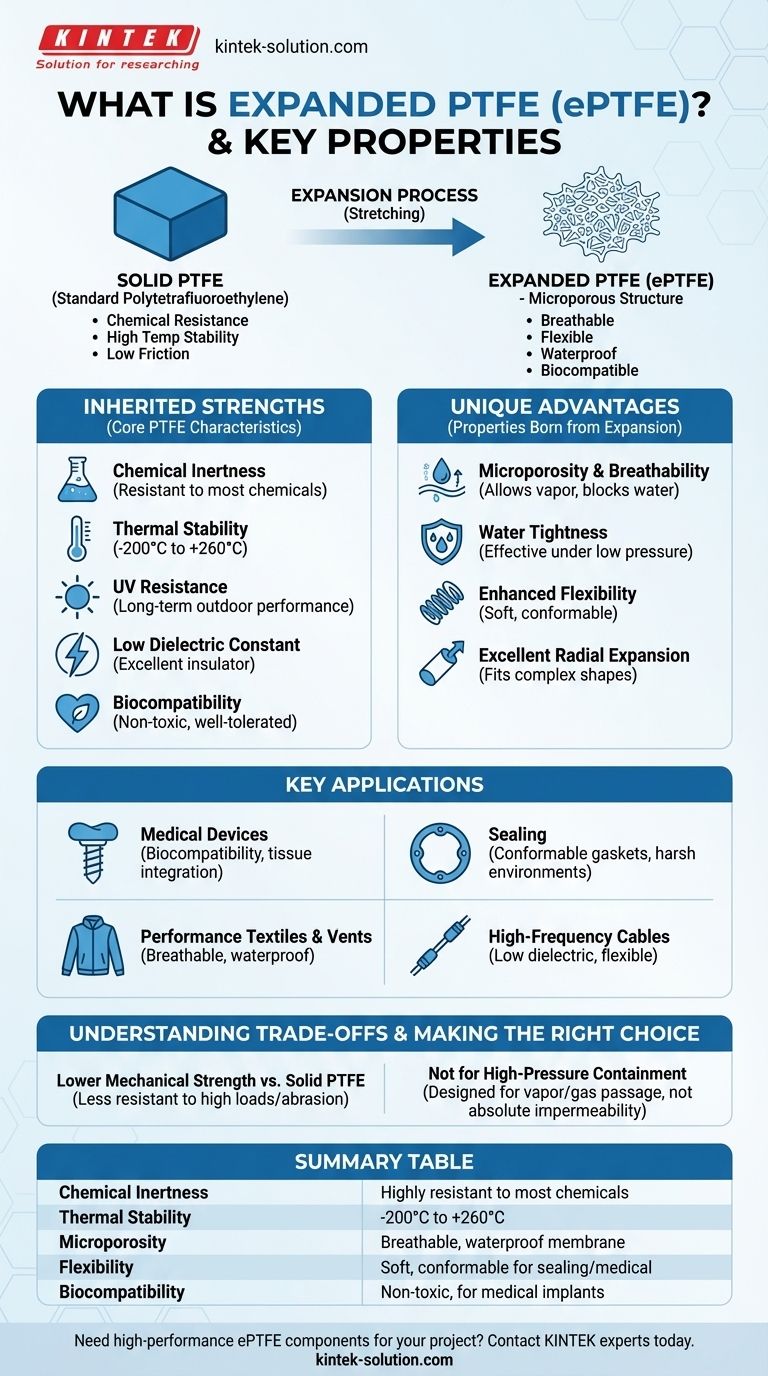
At its core, expanded Polytetrafluoroethylene (ePTFE) is a specialized form of PTFE that has been physically stretched to create a unique microporous structure. This process transforms the solid PTFE into a material that is not only strong and chemically inert but also remarkably flexible, soft, and breathable. Its structure consists of solid nodes of PTFE interconnected by a web of microscopic fibrils.
The critical insight is that ePTFE retains the exceptional chemical, thermal, and electrical resistance of standard PTFE while adding new mechanical properties like flexibility, porosity, and breathability, making it suitable for a completely different set of advanced applications.

Deconstructing ePTFE: From Standard Polymer to Advanced Material
To understand what makes ePTFE unique, we must first look at its parent material. This context reveals how a simple physical modification creates a material with entirely new capabilities.
The Foundation: Standard Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE)
PTFE is a high-performance synthetic fluoropolymer composed of carbon and fluorine atoms. It is renowned for its extreme resistance to chemical attack, high temperatures, and UV radiation.
Its molecular structure gives it a very low coefficient of friction, making it one of the most non-stick, or "lubricious," substances known. These core properties make it a staple material for seals, bearings, and non-stick coatings.
The Transformation: The Expansion Process
Expanded PTFE is created by taking standard PTFE and subjecting it to a precise stretching or "expansion" process under specific conditions. This action pulls the material's molecular structure apart in a controlled way.
Instead of breaking, the PTFE forms a web-like structure. This physical change is what fundamentally differentiates ePTFE from its solid counterpart.
The Result: A Microporous Membrane
The expansion process creates a material filled with billions of microscopic pores per square inch. The final product is a membrane that is both waterproof and breathable.
The size of these pores can be carefully controlled during manufacturing to tailor the material for specific performance requirements, such as airflow rate or resistance to water penetration.
The Key Properties of Expanded PTFE
ePTFE inherits the best qualities of standard PTFE while gaining new advantages from its microporous structure. These properties can be divided into two categories.
Inherited Strengths: Core PTFE Characteristics
These are the foundational properties that ePTFE shares with solid PTFE.
- Chemical Inertness: It is highly resistant to nearly all industrial chemicals, acids, and solvents, making it ideal for harsh environments.
- High Thermal Stability: ePTFE performs reliably across an exceptionally wide temperature range, from -200°C (-328°F) to +260°C (500°F).
- UV Resistance: The material does not degrade or become brittle when exposed to sunlight, ensuring long-term outdoor performance.
- Low Dielectric Constant: It is an excellent electrical insulator, making it invaluable for high-frequency cables and electronics.
- Biocompatibility: ePTFE is non-toxic, non-allergenic, and well-tolerated by the human body, leading to its widespread use in medical implants.
Unique Advantages: Properties Born from Expansion
These are the characteristics that arise directly from the microporous structure.
- Microporosity and Breathability: The interconnected pores allow water vapor and gases to pass through easily while being small enough to block liquid water penetration.
- Water Tightness: While breathable, the material is waterproof under low pressure, a key feature in performance textiles and venting applications.
- Enhanced Flexibility: ePTFE is exceptionally soft, flexible, and conformable, allowing it to seal irregular surfaces or be used in applications requiring repeated bending.
- Excellent Radial Expansion: This property makes it particularly useful for liners and tubing that need to fit snugly over complex shapes.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No material is perfect for every situation. Acknowledging the limitations of ePTFE is crucial for proper material selection.
Mechanical Strength vs. Flexibility
The process that makes ePTFE flexible also makes it less resistant to high compressive loads and abrasive wear compared to solid PTFE. Its porous nature means it has lower density and tensile strength.
Permeability and Pressure
While ePTFE is water-tight at low pressure, it is not designed for high-pressure containment of liquids or gases. Its fundamental purpose is to allow vapor or gas to pass through, making it unsuitable for applications requiring absolute impermeability.
Cost and Complexity
The expansion process is an additional manufacturing step that adds complexity and cost. Consequently, ePTFE is typically more expensive than standard, unprocessed PTFE materials.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting ePTFE is about targeting a problem where its unique combination of properties provides a clear advantage.
- If your primary focus is medical devices or implants: ePTFE is a superior choice due to its proven biocompatibility and porous structure that can encourage tissue integration.
- If your primary focus is sealing in harsh chemical environments: ePTFE gaskets are ideal for their ability to conform to irregular flange surfaces while resisting aggressive chemicals.
- If your primary focus is breathable, waterproof textiles or vents: The microporous membrane is the defining technology, allowing you to manage moisture and pressure differentials.
- If your primary focus is high-frequency cable insulation: The combination of an extremely low dielectric constant and enhanced flexibility makes ePTFE a premier material.
Ultimately, choosing ePTFE means leveraging its unique microporous structure to add flexibility and breathability to the already formidable resistance of standard PTFE.
Summary Table:
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Chemical Inertness | Highly resistant to nearly all industrial chemicals, acids, and solvents. |
| Thermal Stability | Performs from -200°C to +260°C (-328°F to 500°F). |
| Microporosity | Breathable, waterproof membrane created by a web of microscopic fibrils. |
| Flexibility | Exceptionally soft and conformable, ideal for sealing and medical devices. |
| Biocompatibility | Non-toxic and well-tolerated by the human body, suitable for medical implants. |
Need high-performance ePTFE components for your project?
At KINTEK, we specialize in the precision manufacturing of PTFE and expanded PTFE components—including custom seals, liners, and labware. Whether you're in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, or industrial sector, our expertise in custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders ensures you get a solution that leverages ePTFE's unique properties for superior performance.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific requirements and discover how our ePTFE solutions can benefit your application.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
People Also Ask
- What is the scientific name for Teflon and what type of material is it? A Guide to PTFE
- What are the dielectric properties of PTFE? The Ultimate Insulator for Demanding Applications
- How is PTFE used in food processing applications? Ensuring Hygiene, Efficiency, and Product Integrity
- What contributes to PTFE's high heat stability? Unlocking Its Molecular Secrets for Superior Performance
- When did Teflon become a registered trademark, and what was an early use of the material? Discover Its Industrial Origins
- What are some alternatives to Teflon/PTFE? Explore High-Performance Polymers for Your Application
- How is PTFE fine powder resin produced? The Key Role of Dispersion Polymerization
- What are the common filler materials used in RPTFE and their purposes? Enhance PTFE Performance for Demanding Applications



















