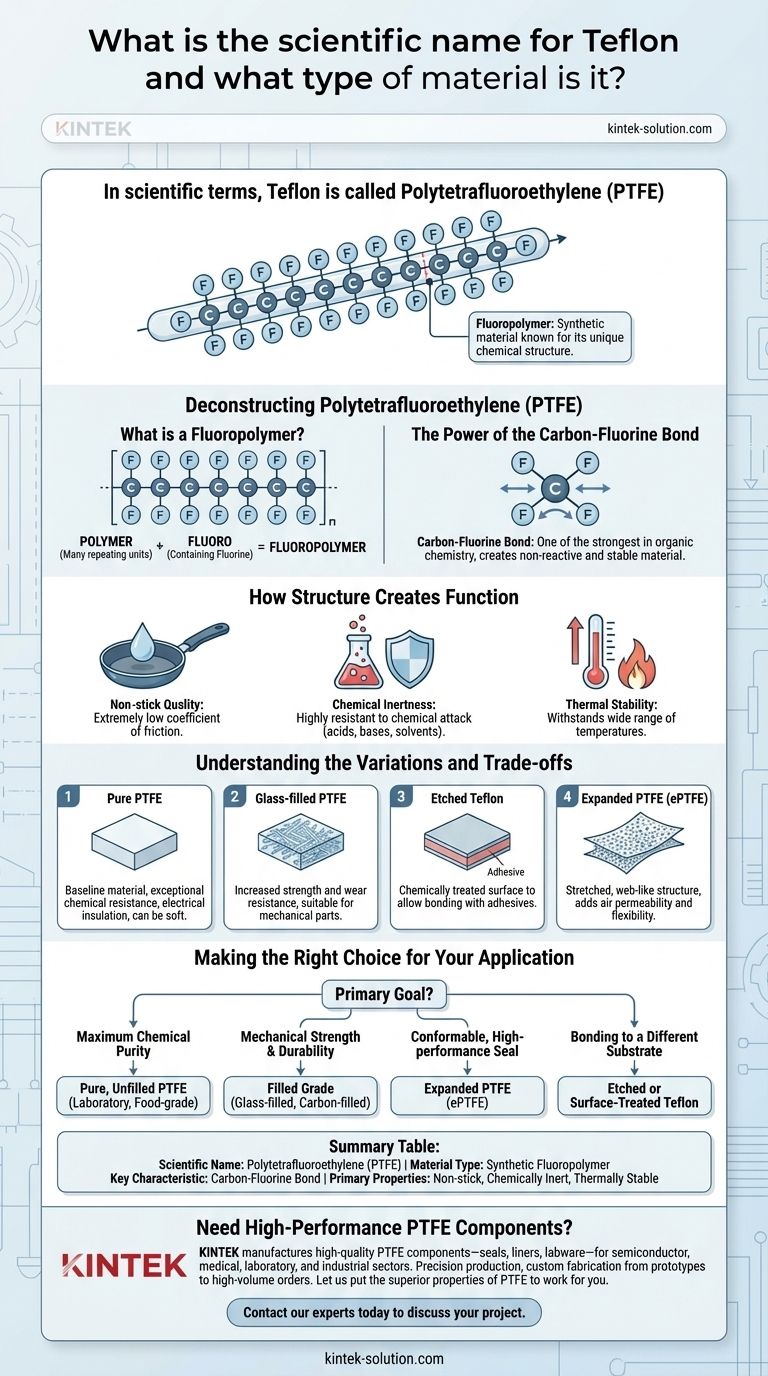
In scientific terms, Teflon is called Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE). It is a high-performance synthetic material known as a fluoropolymer, a classification that points directly to its unique chemical structure and the remarkable properties that result from it.
The core reason Teflon is so unique is its simple but powerful molecular structure: a long chain of carbon atoms completely shielded by a layer of fluorine atoms. This carbon-fluorine bond is one of the strongest in organic chemistry, making the material incredibly non-reactive and stable.

Deconstructing Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE)
To truly understand Teflon, we need to break down its name and structure. The name itself provides the blueprint for the material.
What is a Fluoropolymer?
A polymer is simply a large molecule made of many smaller, repeating units. The "poly" in the name means "many."
The "fluoro" prefix indicates that these repeating units contain fluorine. Therefore, a fluoropolymer is a polymer built with fluorine atoms, which are key to its performance.
The Power of the Carbon-Fluorine Bond
Teflon's backbone is a long chain of carbon atoms. In PTFE, each carbon atom is bonded to two fluorine atoms.
These fluorine atoms effectively create a protective sheath around the carbon chain. This carbon-fluorine bond is exceptionally strong and stable.
How Structure Creates Function
This robust chemical structure directly leads to Teflon's most famous properties.
The fluorine sheath prevents almost anything from sticking to it, creating an extremely low coefficient of friction—its signature non-stick quality.
It also makes the material highly resistant to chemical attack, meaning it won't react with most acids, bases, or solvents. This is known as chemical inertness.
Finally, the strong bonds allow PTFE to withstand a wide range of temperatures without degrading, giving it excellent thermal stability.
Understanding the Variations and Trade-offs
While "Teflon" is often used as a blanket term, several forms of PTFE exist, each engineered to enhance certain properties or overcome limitations.
Pure vs. Modified PTFE
Pure PTFE is the baseline material, prized for its exceptional chemical resistance and electrical insulation. However, it can be relatively soft and prone to deforming under load.
To counteract this, fillers are often added. Glass-filled PTFE, for example, has significantly increased strength and wear resistance, making it suitable for mechanical parts.
The Challenge of Adhesion
The very non-stick nature of PTFE presents a significant challenge: it's extremely difficult to bond to other materials.
To solve this, a process called etching is used. Etched Teflon has one side chemically treated to allow adhesives to form a strong bond, combining its performance with the structural integrity of another material.
Structural Modifications
The physical structure of PTFE can also be altered. Expanded PTFE (ePTFE) is created by stretching the material, which introduces a porous, web-like structure.
This form maintains the chemical resistance of PTFE but adds new properties like air permeability and flexibility, making it ideal for high-performance seals, gaskets, and even medical implants.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct type of Polytetrafluoroethylene is critical for engineering success. Your primary goal will determine the best variant.
- If your primary focus is maximum chemical purity and inertness: Pure, unfilled PTFE is the definitive choice, especially in laboratory or food-grade applications.
- If your primary focus is mechanical strength and durability: A filled grade, such as glass-filled or carbon-filled PTFE, will provide the necessary resistance to wear and deformation.
- If your primary focus is creating a conformable, high-performance seal: Expanded PTFE (ePTFE) offers the required flexibility and chemical resistance for demanding sealing applications.
- If your primary focus is bonding the material to a different substrate: You must use an etched or otherwise surface-treated version of Teflon to ensure proper adhesion.
Ultimately, understanding that Teflon is Polytetrafluoroethylene empowers you to look beyond the brand name and select the material based on its fundamental chemistry.
Summary Table:
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Scientific Name | Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) |
| Material Type | Synthetic Fluoropolymer |
| Key Characteristic | Carbon-Fluorine Bond |
| Primary Properties | Non-stick, Chemically Inert, Thermally Stable |
Need High-Performance PTFE Components?
Understanding the science behind PTFE is the first step. The next is sourcing precision-manufactured components that meet your exact specifications.
KINTEK manufactures high-quality PTFE components—including seals, liners, and labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We prioritize precision production and offer custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders.
Let us put the superior properties of PTFE to work for you.
Contact our experts today to discuss your project
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What environmental resistances does PTFE offer? Unmatched Durability for Harsh Conditions
- What is Teflon and what is its chemical name? Unpacking the Science of PTFE
- What is PTFE and what class of plastics does it belong to? A Guide to High-Performance Fluoropolymers
- How was PTFE discovered and developed? From Lab Accident to Essential High-Performance Polymer
- What is PTFE commonly known as and what type of material is it? A Guide to High-Performance PTFE Properties



















