In short, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is exceptionally durable because it is highly resistant to a wide range of environmental factors. Its inert chemical structure allows it to withstand degradation from UV radiation, moisture, weathering, and a vast spectrum of chemicals, including most acids and alkalis. This stability extends across extreme temperature ranges, making it a reliable material for harsh indoor and outdoor applications.
PTFE's remarkable durability is not due to immense physical strength, but rather its profound chemical stability. This inherent inertness makes it nearly immune to the environmental factors that degrade most other materials, though it has distinct limits regarding physical abrasion and high temperatures.

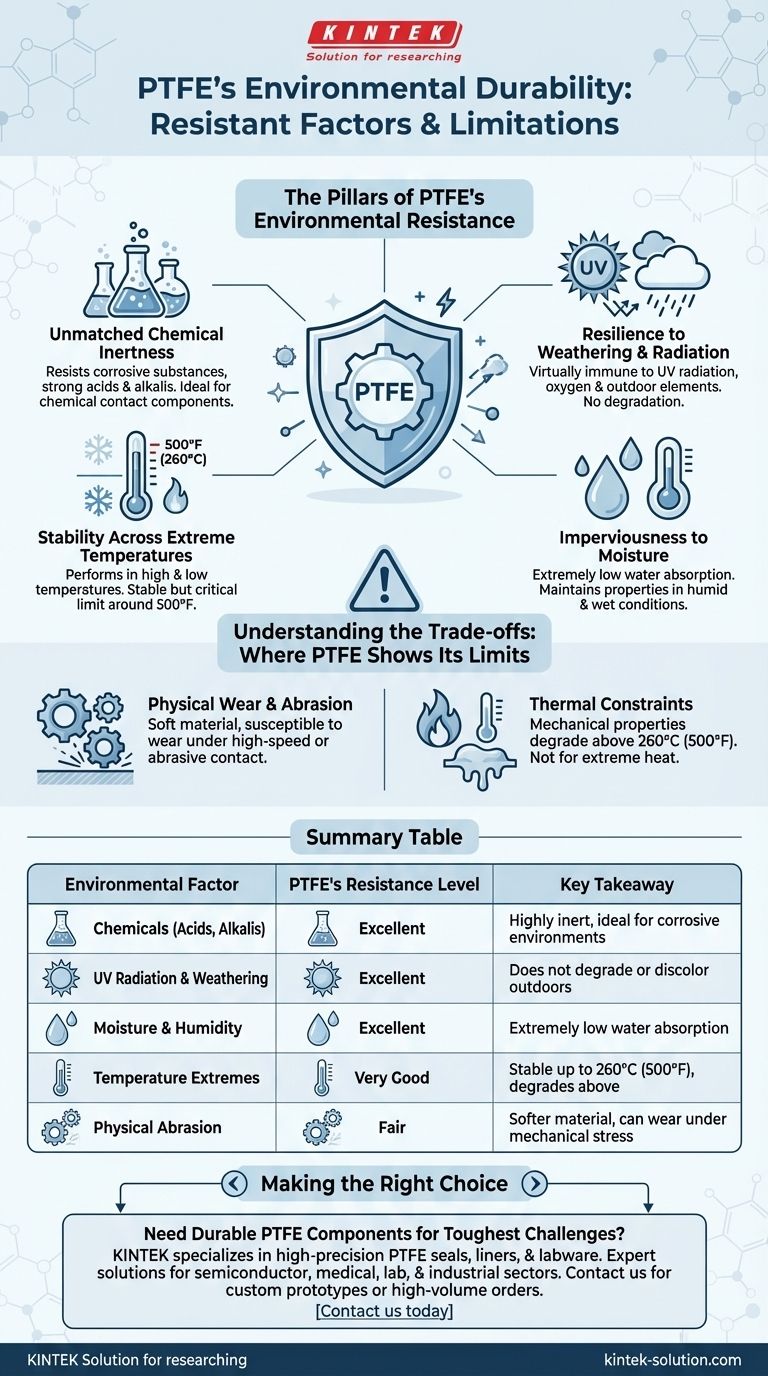
The Pillars of PTFE's Environmental Resistance
PTFE’s durability is a direct result of its unique molecular structure. The strong carbon-fluorine bonds are exceptionally stable, providing a formidable defense against common sources of material degradation.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
PTFE is one of the most chemically inert polymers known. It resists a wide variety of corrosive substances, including strong acids and alkalis.
This property makes it indispensable for components like gaskets, seals, and liners that are in constant contact with aggressive chemicals in industrial and laboratory settings.
Resilience to Weathering and Radiation
PTFE demonstrates exceptional resistance to atmospheric aging. It is virtually immune to the damaging effects of UV radiation and oxygen.
Unlike many other plastics, PTFE does not discolor, degrade, or become brittle even after prolonged exposure to direct sunlight and the elements, ensuring long-term performance in outdoor applications.
Stability Across Extreme Temperatures
The material maintains its properties across a wide functional temperature range. It remains stable and performs reliably in both high and low-temperature environments.
While it has a high melting point, its performance can become compromised around 500°F (260°C), a critical factor for high-heat applications.
Imperviousness to Moisture
PTFE exhibits extremely low water absorption and permeability. It simply does not absorb moisture from the air or when submerged.
This ensures that its physical and electrical insulating properties remain consistent, even in humid or wet conditions, which is crucial for electrical components and medical devices.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Where PTFE Shows Its Limits
No material is perfect for every scenario. Understanding PTFE's limitations is just as important as knowing its strengths to ensure proper application.
Physical Wear and Abrasion
While chemically durable, PTFE is a relatively soft material. It is not as mechanically robust as metals like stainless steel.
In applications involving high-speed movement or contact with abrasive materials, such as certain industrial impellers, PTFE can be susceptible to wear and tear over time.
Thermal Constraints
The primary operational limit for PTFE is its temperature ceiling. As it approaches 260°C (500°F), its mechanical properties begin to degrade significantly.
For any application that will exceed this temperature, even for short periods, alternative materials must be considered to avoid component failure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To leverage PTFE's durability effectively, you must align its specific strengths and weaknesses with the demands of your project.
- If your primary focus is chemical exposure or outdoor weathering: PTFE is an exceptional choice due to its profound chemical inertness and UV stability.
- If your primary focus is high-speed mechanical stress or abrasion: You must carefully evaluate potential wear rates, as a harder material might offer a longer service life.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature performance: PTFE is reliable up to approximately 260°C (500°F), but you must select an alternative for applications that operate beyond this threshold.
Ultimately, understanding both PTFE's powerful resistances and its distinct physical limitations is the key to deploying it successfully.
Summary Table:
| Environmental Factor | PTFE's Resistance Level | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|---|
| Chemicals (Acids, Alkalis) | Excellent | Highly inert, ideal for corrosive environments |
| UV Radiation & Weathering | Excellent | Does not degrade or discolor outdoors |
| Moisture & Humidity | Excellent | Extremely low water absorption |
| Temperature Extremes | Very Good (up to 260°C/500°F) | Stable across a wide range, but degrades above limit |
| Physical Abrasion | Fair | Softer material; can wear under mechanical stress |
Need durable PTFE components that withstand your toughest environmental challenges? KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-precision PTFE seals, liners, and labware for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether you need custom prototypes or high-volume orders, our expertise ensures your components deliver long-lasting performance in harsh conditions. Contact us today to discuss your specific requirements and get a quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- What are the common characteristics of Teflon? Unlocking Extreme Chemical and Thermal Resistance
- What material is the PTFE bottle made from? Discover the Benefits of 100% Virgin PTFE
- What makes the PTFE bottle durable? Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Stability for Demanding Applications
- What are some exceptional properties of PTFE? Unlock Unmatched Performance in Extreme Environments
- Why are PTFE vials considered environmentally friendly? Reduce Lab Waste with Durable Reusables



















