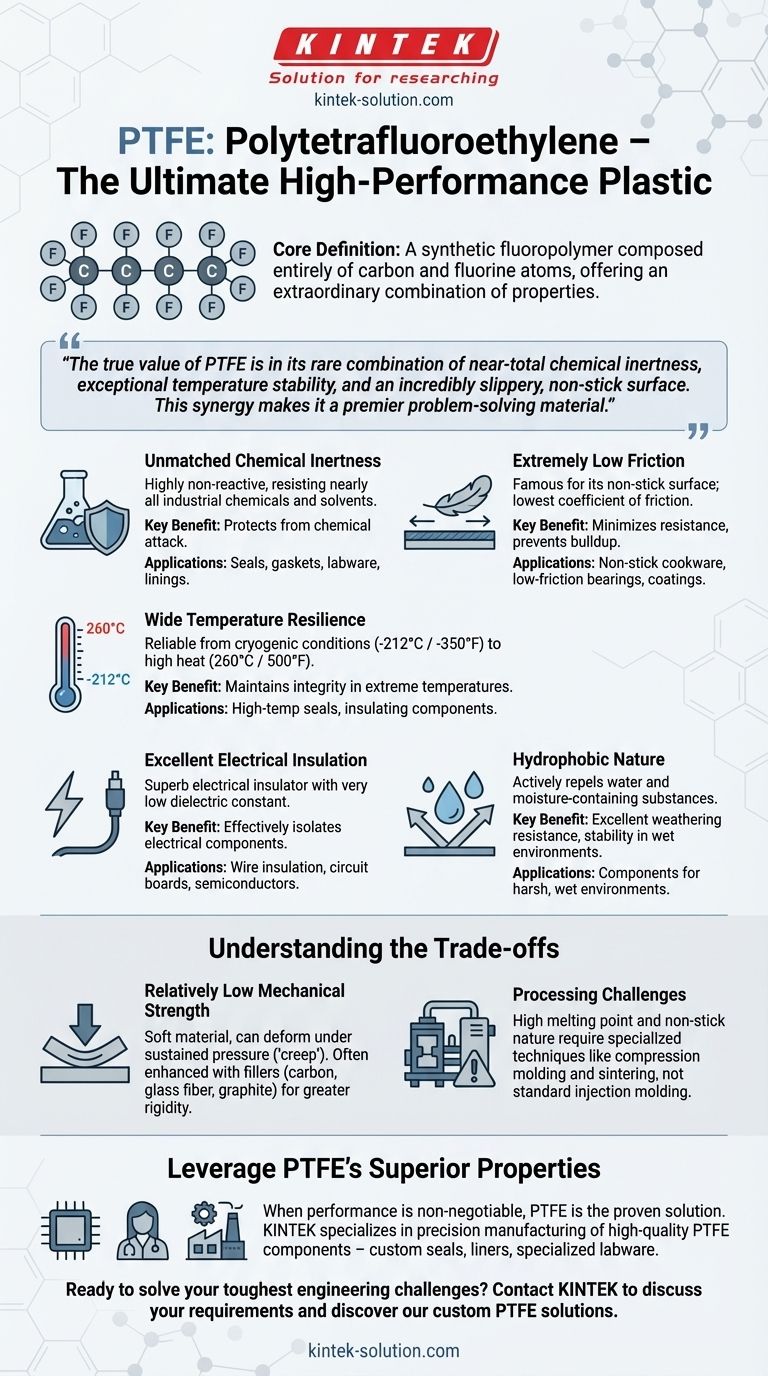
At its core, PTFE stands for Polytetrafluoroethylene. It is a synthetic fluoropolymer, a high-performance plastic composed entirely of carbon and fluorine atoms. This unique chemical structure gives it an extraordinary combination of properties, including extreme chemical resistance, a very wide operating temperature range, and one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any known solid material.
The true value of PTFE isn't found in a single characteristic, but in its rare combination of near-total chemical inertness, exceptional temperature stability, and an incredibly slippery, non-stick surface. This synergy makes it a premier problem-solving material for the most demanding engineering environments.

The Fundamental Properties of PTFE
To understand why PTFE is so widely used, we must examine the core characteristics that stem from its simple but powerful carbon-fluorine molecular structure.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
PTFE is highly non-reactive. It offers extreme resistance to nearly all industrial chemicals, solvents, and corrosive substances.
This stability comes from the very strong bonds between its carbon and fluorine atoms, which protect the molecule from chemical attack.
Extremely Low Friction
PTFE is famous for its non-stick surface. It has one of the lowest coefficients of friction known for any solid material, making it incredibly slippery.
This property is invaluable for applications like non-stick cookware, low-friction bearings, and coatings for pipes or medical devices.
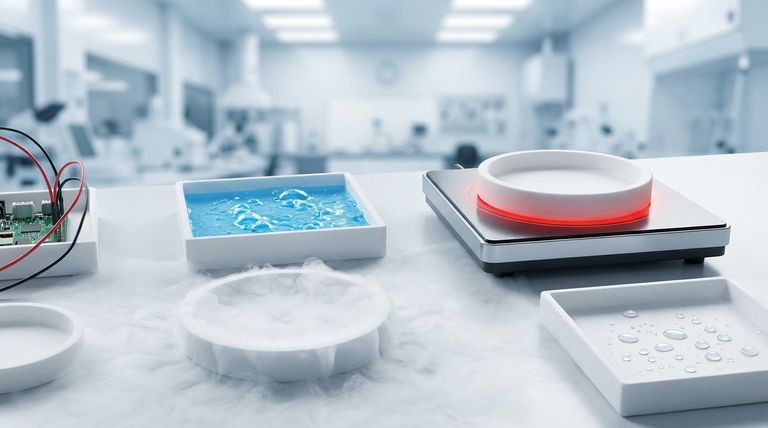
Wide Temperature Resilience
This material performs reliably across an exceptionally broad temperature range.
It maintains its integrity and properties from cryogenic conditions around -212°C (-350°F) up to continuous service at 260°C (500°F).
Excellent Electrical Insulation
PTFE is a superb electrical insulator. It has a very low dielectric constant, meaning it does not conduct electricity and can effectively isolate electrical components.
This makes it a critical material for high-frequency applications in electronics and for wire and cable insulation.
Hydrophobic Nature
PTFE is hydrophobic, meaning it actively repels water and substances that contain water.
This resistance to moisture contributes to its durability, excellent weathering resistance, and stability in diverse environments.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While its properties are exceptional, PTFE is not the ideal solution for every problem. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Relatively Low Mechanical Strength
PTFE is a relatively soft material. While it has good flexural strength, allowing it to bend without breaking, it can deform under sustained pressure, a phenomenon known as "creep."
For applications requiring greater rigidity and creep resistance, PTFE is often enhanced with fillers like carbon, glass fiber, or graphite.
Processing Challenges
The same properties that make PTFE so useful also make it difficult to process.
Its high melting point and non-stick nature prevent it from being processed using common methods like injection molding. Instead, it requires specialized techniques like compression molding and sintering.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right material depends entirely on the primary challenge you need to solve.
- If your primary focus is survival in extreme environments: PTFE's unmatched chemical resistance and broad temperature range make it the default choice for seals, gaskets, and linings exposed to corrosive chemicals or extreme heat.
- If your primary focus is a low-friction or non-stick surface: PTFE is the industry standard for creating surfaces that minimize resistance, prevent material buildup, or enable smooth movement in bearings and coatings.
- If your primary focus is high-performance electrical insulation: PTFE's low dielectric constant and high resistivity are essential for critical components in electronics, especially in high-frequency or high-temperature applications.
Ultimately, PTFE is the material of choice when performance under demanding conditions is non-negotiable.
Summary Table:
| Primary Characteristic | Key Benefit | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Inertness | Resists nearly all industrial chemicals and solvents. | Seals, gaskets, labware, linings. |
| Low Friction / Non-Stick | One of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid. | Bearings, coatings, non-stick surfaces. |
| Wide Temperature Range | Stable from -212°C to 260°C (-350°F to 500°F). | High-temperature seals, insulating components. |
| Excellent Electrical Insulation | Superior dielectric properties for high-frequency use. | Wire insulation, circuit boards, semiconductors. |
| Hydrophobic Nature | Repels water and resists weathering. | Components for harsh, wet environments. |
Leverage PTFE's Superior Properties for Your Critical Applications
When your project demands a material that can withstand extreme chemicals, high temperatures, or requires a reliable non-stick surface, PTFE is the proven solution. At KINTEK, we specialize in the precision manufacturing of high-quality PTFE components—from custom seals and liners to specialized labware.
We serve the most demanding industries, including semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial manufacturing, providing everything from custom prototypes to high-volume production runs.
Ready to solve your toughest engineering challenges? Contact our experts today to discuss your specific requirements and discover how our PTFE solutions can enhance your product's performance and reliability.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
People Also Ask
- Why is PTFE suitable for cryogenic or high-temperature applications? Unmatched Thermal Stability from -450°F to 500°F
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- What is the working temperature range of PTFE? Master Extreme Heat and Cryogenic Applications
- What are the base characteristics of PTFE? Unlocking Extreme Performance in Friction, Temperature, and Chemical Resistance
- What are some common applications of machined PTFE? Leverage its Unique Properties for Demanding Applications



















