In the construction industry, expanded Polytetrafluoroethylene (ePTFE) sheets and related PTFE materials are used as high-performance components where extreme durability is essential. Their primary applications include long-lasting roofing membranes, weatherproof seals for windows and doors, and low-friction bearing pads that accommodate structural movement in buildings and bridges.
The true value of ePTFE in construction is not just what it does, but why it is chosen. It is an engineering solution for points of failure, selected for its unique combination of chemical inertness, weather immunity, and low-friction properties that allow structures to endure and move as designed for decades.

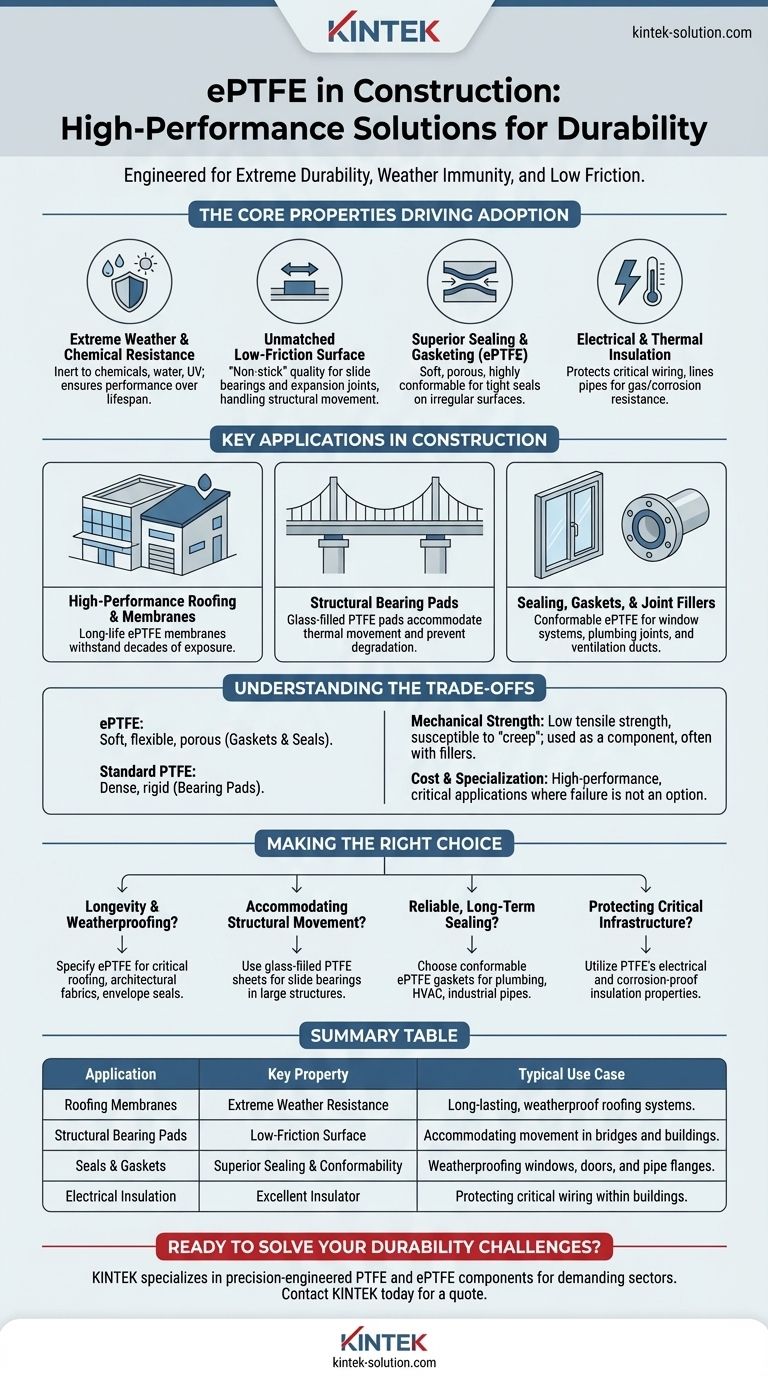
The Core Properties Driving Adoption
The use of ePTFE and its parent material, PTFE, in demanding construction environments is a direct result of its fundamental material characteristics. Understanding these properties explains its specific applications.
Extreme Weather and Chemical Resistance
PTFE is almost completely inert. It does not react with chemicals and is unaffected by water, UV radiation, or extreme temperatures.
This inherent stability makes it an ideal material for components exposed to the elements, guaranteeing performance over a project's entire lifespan without degradation.
Unmatched Low-Friction Surface
PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any known solid. This "non-stick" quality is its most famous attribute.
In construction, this allows for the creation of slide bearings and expansion joints. These components are critical for large structures like bridges and stadiums, allowing them to expand and contract with temperature changes without building up destructive stress.
Superior Sealing and Gasketing
The "expanded" form, ePTFE, is created with a microporous structure, making it soft and highly conformable.
When compressed, it forms an exceptionally tight seal against irregular surfaces. This makes it a premier material for high-reliability gaskets and sealants for window and door systems, pipe flanges, and ventilation ducts.
Electrical and Thermal Insulation
PTFE is an excellent electrical insulator and maintains its properties across a wide temperature range.
For this reason, it is used to sheathe and protect critical electrical wiring within buildings. It is also used to line pipes and hoses, particularly for gas, where its resistance to corrosion and abrasion is highly valued.
Key Applications in Construction
These fundamental properties translate directly into several high-value applications on a modern job site.
High-Performance Roofing and Membranes
Because of its weather immunity, ePTFE is used as a long-life roofing membrane. It can withstand decades of exposure to sun, rain, and pollutants without becoming brittle or failing, offering a significant advantage over traditional materials.
Structural Bearing Pads
Often filled with glass or other agents to increase compressive strength, PTFE sheets are cut into bearing pads.
These pads are placed between major structural elements, such as between a steel beam and a concrete pier. They provide a durable, weather-immune, and low-friction interface that allows for thermal movement and prevents material degradation.
Sealing, Gaskets, and Joint Fillers
The conformability of ePTFE makes it a superior choice for sealing building envelopes. It is used as a gasket material in high-performance window systems and as thread seal tape in plumbing to create durable, leak-proof joints.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, PTFE and ePTFE are specialized materials with specific limitations that every engineer and architect must consider.
ePTFE vs. Standard PTFE
It is critical to distinguish between the two. Standard PTFE is dense and rigid, making it suitable for solid, machined parts like bearing pads. ePTFE is soft, flexible, and porous, making it the ideal choice for gaskets and seals that need to conform to a surface.
Consideration of Mechanical Strength
By itself, PTFE is a relatively soft material with low tensile strength. It can be susceptible to "creep," or slow deformation under a constant load.
This is why it is almost always used as a component—a liner, a seal, or a sliding surface—rather than as a primary structural element. Fillers like glass or carbon are added to improve its strength for applications like bearing pads.
Cost and Specialization
These are high-performance polymers, and their cost reflects that. They are not general-purpose materials but are specified for critical applications where other materials would fail, and the cost of that failure would be immense.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When specifying materials, your decision should be driven by the primary engineering challenge you need to solve.
- If your primary focus is longevity and weatherproofing: Specify ePTFE for critical roofing membranes, architectural fabrics, and building envelope seals.
- If your primary focus is accommodating structural movement: Use glass-filled PTFE sheets for slide bearings and expansion joints in bridges and large-scale buildings.
- If your primary focus is reliable, long-term sealing: Choose conformable ePTFE gaskets and tapes for critical plumbing, HVAC, and industrial pipe connections.
- If your primary focus is protecting critical infrastructure: Utilize PTFE's properties for electrical wire insulation and for corrosion-proof linings in chemical or gas pipes.
Ultimately, PTFE and ePTFE are chosen not as a default, but as a precise engineering solution to construction's most demanding durability challenges.
Summary Table:
| Application | Key Property | Typical Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Roofing Membranes | Extreme Weather Resistance | Long-lasting, weatherproof roofing systems |
| Structural Bearing Pads | Low-Friction Surface | Accommodating movement in bridges and buildings |
| Seals & Gaskets | Superior Sealing & Conformability | Weatherproofing windows, doors, and pipe flanges |
| Electrical Insulation | Excellent Insulator | Protecting critical wiring within buildings |
Ready to solve your most demanding durability challenges with precision-engineered PTFE components? KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-performance PTFE and ePTFE components—including seals, liners, bearing pads, and custom labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We combine precision production with custom fabrication, from prototypes to high-volume orders, to deliver the reliability your projects require. Contact KINTEL today to discuss your specific application and get a quote.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- How do spiral and split PTFE backup rings compare in terms of sealing performance? High-Pressure vs. Easy Installation
- What are the primary properties of PTFE rod? Unlock Extreme Performance for Demanding Applications
- What are the drawbacks of using PTFE for sealing needs? The Critical Trade-offs in Chemical vs. Mechanical Performance
- How is rotation accommodated in PTFE sliding bearings? Solutions for Structural Movement
- How does PTFE's low friction performance benefit industrial applications? Enable Clean, Reliable Movement Without Lubricants
- What factors contribute to the durability of PTFE O-rings? Maximize Seal Life in Harsh Environments
- How do additives and fillers specialize PTFE-based PCB materials? Tailor High-Frequency Circuit Performance
- What are PTFE O-rings and what are their primary characteristics? High-Performance Seals for Extreme Conditions



















