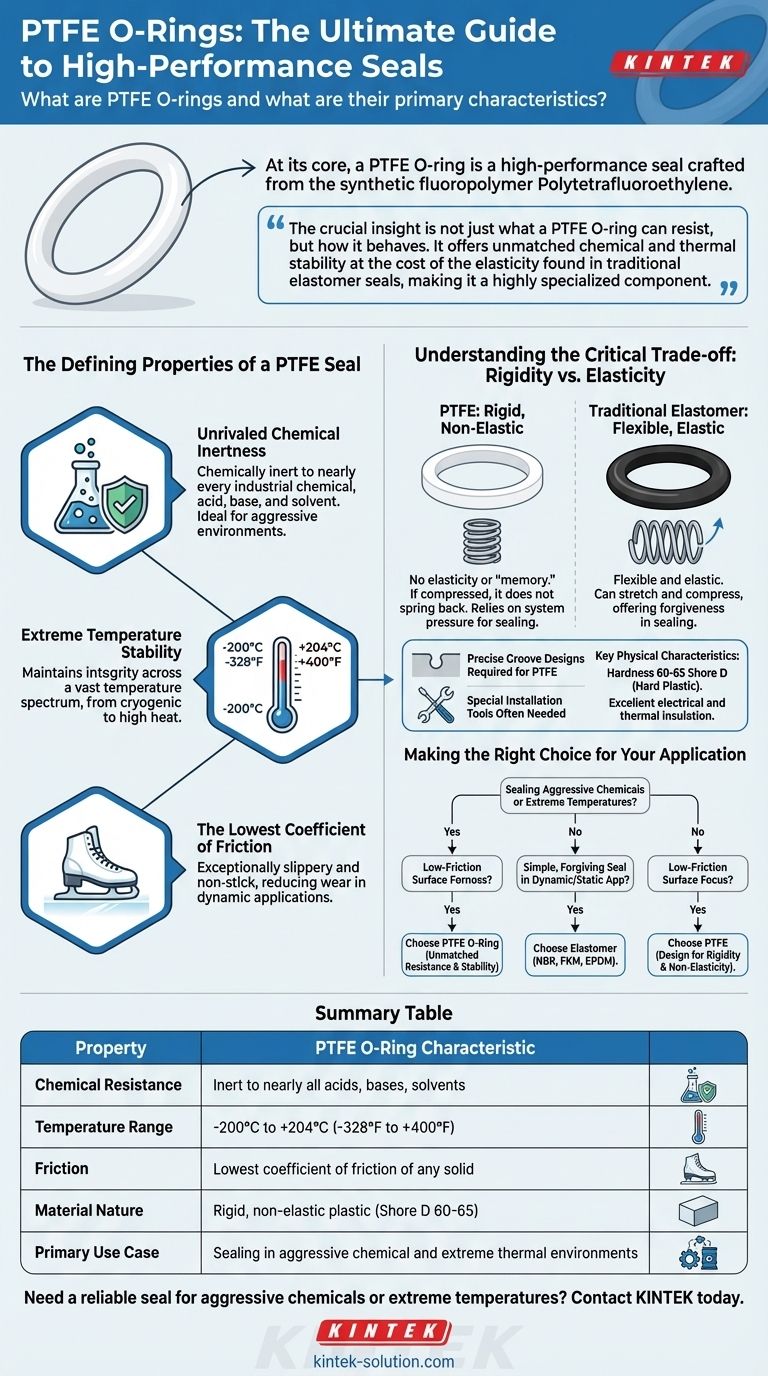
At its core, a PTFE O-ring is a high-performance seal crafted from the synthetic fluoropolymer Polytetrafluoroethylene. Its defining characteristics are near-universal chemical resistance, an extremely wide operating temperature range, and the lowest coefficient of friction of any solid material. Unlike common rubber O-rings, it is a rigid, non-elastic plastic.
The crucial insight is not just what a PTFE O-ring can resist, but how it behaves. It offers unmatched chemical and thermal stability at the cost of the elasticity found in traditional elastomer seals, making it a highly specialized component, not a general-purpose substitute for rubber.

The Defining Properties of a PTFE Seal
PTFE (often known by the brand name Teflon®) is a material of extremes. Its properties make it an exceptional choice for environments where other sealing materials would quickly fail.
Unrivaled Chemical Inertness
A PTFE O-ring is chemically inert to nearly every industrial chemical, acid, base, and solvent. This makes it the default choice for sealing applications in aggressive chemical processing, pharmaceuticals, and manufacturing.
Only a few niche substances, like molten alkali metals and certain fluorine compounds, can affect it.
Extreme Temperature Stability
PTFE maintains its integrity across a vast temperature spectrum, from cryogenic levels around -200°C (-328°F) up to 204°C (400°F). This allows it to function in applications involving extreme cold or high heat where elastomers would become brittle or degrade.
The Lowest Coefficient of Friction
With the lowest friction of any known solid material, PTFE surfaces are exceptionally slippery and non-stick. This property reduces wear and prevents galling in dynamic applications, though its use is limited by its rigidity.
Key Physical Characteristics
PTFE O-rings are typically white and possess a hardness of 60-65 Shore D. This places them firmly in the category of hard plastics, starkly contrasting with the softness of rubber seals measured on the Shore A scale. They also provide excellent electrical and thermal insulation.
Understanding the Critical Trade-off: Rigidity vs. Elasticity
The most significant factor to understand when considering PTFE is its mechanical nature. It is a non-elastomeric material, and this fundamentally changes how it functions as a seal.
The Lack of "Memory"
Unlike a rubber O-ring, a PTFE O-ring has no elasticity or "memory." If compressed, it will not spring back to its original shape. This property, known as a low compression set, means it relies on system pressure to maintain a seal.
Implications for Sealing Design
Because it cannot stretch or compress easily, a PTFE O-ring requires highly precise groove designs and excellent surface finishes to be effective. It is far less forgiving of imperfections or variations than a flexible elastomer seal.
The seal is often energized by system pressure, which forces the ring to conform to the gland. This is a different sealing mechanism than the "squeeze" of a traditional O-ring.
Installation Challenges
The material's rigidity makes installation more difficult. PTFE rings cannot be stretched over components like rubber rings can be. This often necessitates special installation tools or gland designs (like two-part assemblies) to prevent the ring from being scratched or permanently deformed.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting a PTFE O-ring requires a clear understanding of its unique strengths and limitations. It is a problem-solver for specific, challenging conditions.
- If your primary focus is sealing aggressive chemicals or extreme temperatures: PTFE is almost certainly the correct choice, as few other materials can survive these conditions.
- If your primary focus is a simple, forgiving seal in a dynamic or static application: A standard elastomer like NBR, FKM (Viton®), or EPDM is likely a more reliable and cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is creating a low-friction surface: PTFE excels, but you must design the application around its rigidity and non-elastic nature.
Choosing the right seal is about matching the material's inherent properties to the specific demands of the environment.
Summary Table:
| Property | PTFE O-Ring Characteristic |
|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Inert to nearly all acids, bases, and solvents |
| Temperature Range | -200°C to +204°C (-328°F to +400°F) |
| Friction | Lowest coefficient of friction of any solid |
| Material Nature | Rigid, non-elastic plastic (Shore D 60-65) |
| Primary Use Case | Sealing in aggressive chemical and extreme thermal environments |
Need a reliable seal for aggressive chemicals or extreme temperatures?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-precision PTFE components, including O-rings, seals, and custom labware. Our expertise ensures your critical applications in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors are protected with seals that offer unmatched chemical resistance and thermal stability.
We provide custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders, guaranteeing a perfect fit and superior performance for your specific needs.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your sealing challenges and get a quote for your project.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What design considerations are important for custom PTFE parts? Design for Performance & Reliability
- What chemical processing applications involve PTFE-machined parts? Essential Components for Corrosive & High-Purity Systems
- What industrial benefits do PTFE-machined parts offer? Achieve Peak Performance in Demanding Applications
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? Unlock Unmatched Performance in Demanding Applications
- What factors should be considered when choosing between Nylon and PTFE? Select the Right Material for Your Application



















