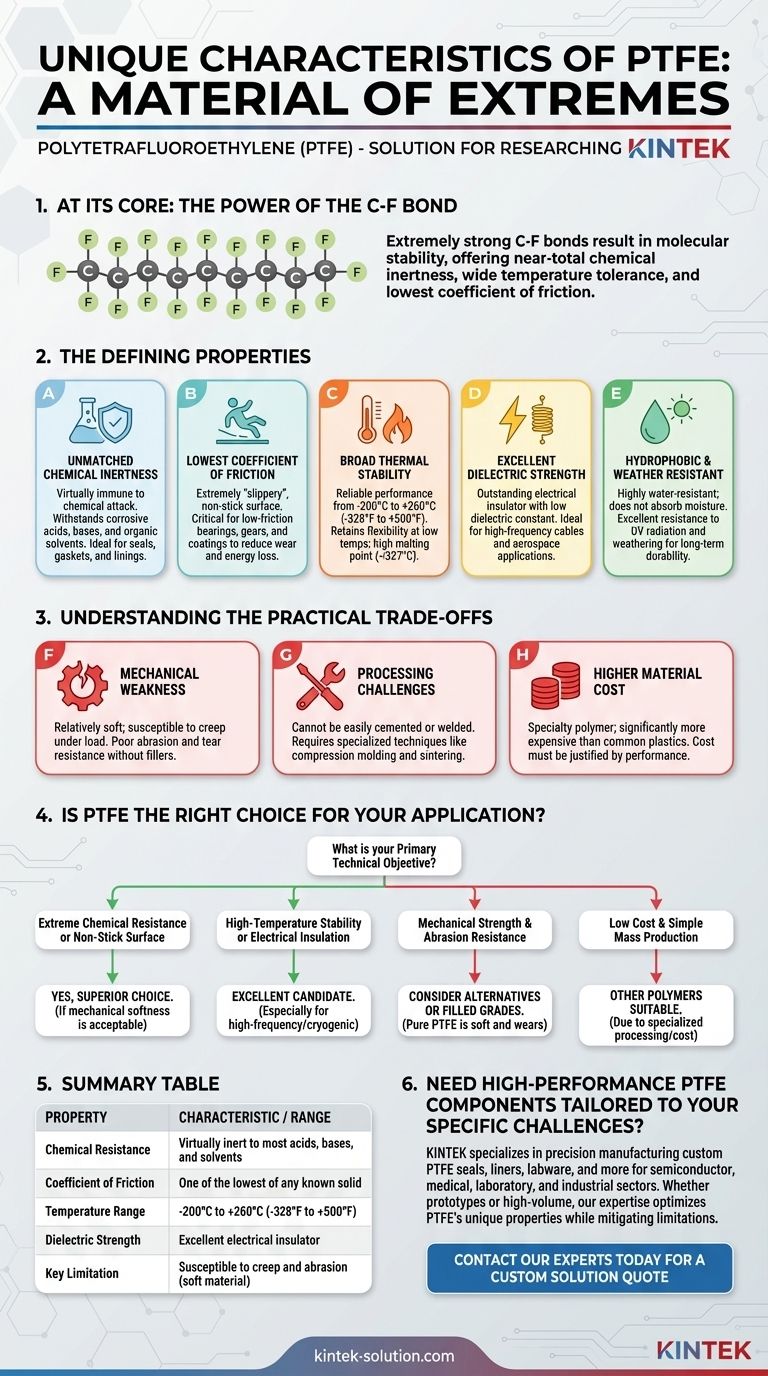
At its core, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a material of extremes. Best known by the brand name Teflon, its defining characteristics are a near-total chemical inertness, an exceptionally wide temperature tolerance, and one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any known solid. This unique combination makes it a powerful problem-solver in demanding chemical, electrical, and mechanical environments.
PTFE's remarkable properties stem from the incredibly strong bond between its carbon and fluorine atoms. This molecular stability makes it chemically non-reactive and thermally resilient, but it also results in a mechanically soft material with distinct processing challenges, creating a clear set of trade-offs for any application.

The Defining Properties of PTFE
To understand PTFE's utility, we must first examine the specific characteristics that set it apart from virtually all other polymers. These properties are not just incremental improvements; they represent a fundamental difference in performance.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
PTFE is virtually immune to chemical attack. It can withstand highly corrosive acids, bases, and organic solvents that would degrade most other materials.
This exceptional resistance makes it the default choice for seals, gaskets, and linings in chemical processing equipment and pipes handling aggressive substances.
The Lowest Coefficient of Friction
Often cited as having the lowest coefficient of friction of any solid, PTFE is extremely "slippery." This results in its signature non-stick, non-adhesive surface.
While famous for its use in cookware, this property is critical in industrial applications for low-friction bearings, gears, and surface coatings where reducing wear and energy loss is paramount.
Broad Thermal Stability
PTFE performs reliably across an exceptionally wide temperature range, typically cited as –200°C to +260°C (–328°F to +500°F).
Unlike many plastics that become brittle at low temperatures, PTFE retains its flexibility. It also has a high melting point of around 327°C (621°F), allowing it to function in high-heat environments.
Excellent Dielectric Strength
PTFE is an outstanding electrical insulator. It has a very low dielectric constant and high dielectric strength, meaning it resists the flow of electricity and can withstand a high voltage before breaking down.
These properties make it an ideal material for insulating high-frequency cables and wires, particularly in aerospace and computing applications.
Hydrophobic and Weather Resistant
The material is highly water-resistant (hydrophobic) and does not absorb moisture. It also exhibits excellent resistance to UV radiation and weathering.
This durability allows PTFE components to perform consistently over long periods, even with direct exposure to the elements.
Understanding the Practical Trade-offs
No material is perfect, and PTFE's unique strengths are balanced by significant limitations. Acknowledging these trade-offs is crucial for successful implementation.
Mechanical Weakness
PTFE is a relatively soft material. It is susceptible to creep, meaning it can slowly deform over time when under a constant load.
It also has poor abrasion and tear resistance compared to other engineering plastics. This makes it unsuitable for high-wear applications unless it is reinforced with fillers like glass fiber or carbon.
Processing and Fabrication Challenges
The same chemical inertness that makes PTFE so valuable also means it cannot be easily cemented or welded.
Furthermore, due to its high melting point and melt viscosity, it cannot be processed using conventional thermoplastic methods like injection molding. Instead, it requires specialized techniques like compression molding and sintering, which can increase production time and cost.
Higher Material Cost
PTFE is a specialty polymer and is significantly more expensive than common plastics like polyethylene or polypropylene. Its higher cost must be justified by the specific performance requirements of the application.
Is PTFE the Right Choice for Your Application?
The decision to use PTFE should be driven by a clear understanding of your primary technical objective.
- If your primary focus is extreme chemical resistance or a non-stick surface: PTFE is almost always the superior choice, provided its mechanical softness is acceptable for the design.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature stability or electrical insulation: PTFE is an excellent candidate, especially for high-frequency or cryogenic applications where other insulators fail.
- If your primary focus is mechanical strength and abrasion resistance: You should strongly consider alternative engineering plastics or filled grades of PTFE, as the pure material is inherently soft and prone to wear.
- If your primary focus is low cost and simple mass production: PTFE's specialized processing requirements and higher price point make other polymers more suitable.
By understanding both its unparalleled strengths and its inherent limitations, you can leverage PTFE to solve challenges that other materials simply cannot address.
Summary Table:
| Property | Characteristic / Range |
|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Virtually inert to most acids, bases, and solvents |
| Coefficient of Friction | One of the lowest of any known solid |
| Temperature Range | -200°C to +260°C (-328°F to +500°F) |
| Dielectric Strength | Excellent electrical insulator |
| Key Limitation | Susceptible to creep and abrasion (soft material) |
Need high-performance PTFE components tailored to your specific challenges?
KINTEK specializes in the precision manufacturing of custom PTFE seals, liners, labware, and more for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether you require prototypes or high-volume orders, our expertise ensures your components leverage PTFE's unique properties while mitigating its limitations.
Contact our experts today to discuss your application and receive a custom solution quote.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Volumetric Flasks for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Use
People Also Ask
- What are the base characteristics of PTFE? Unlocking Extreme Performance in Friction, Temperature, and Chemical Resistance
- What is PTFE commonly known as and what are its unique properties? Unlock Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- What is the working temperature range of PTFE? Master Extreme Heat and Cryogenic Applications
- Why is PTFE suitable for cryogenic or high-temperature applications? Unmatched Thermal Stability from -450°F to 500°F
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications



















