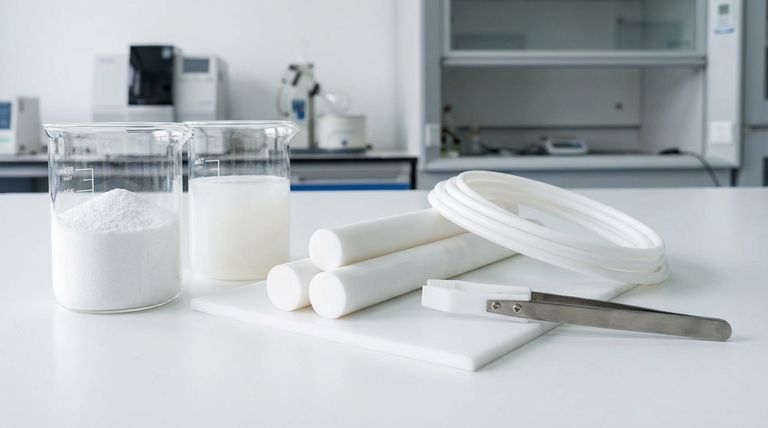
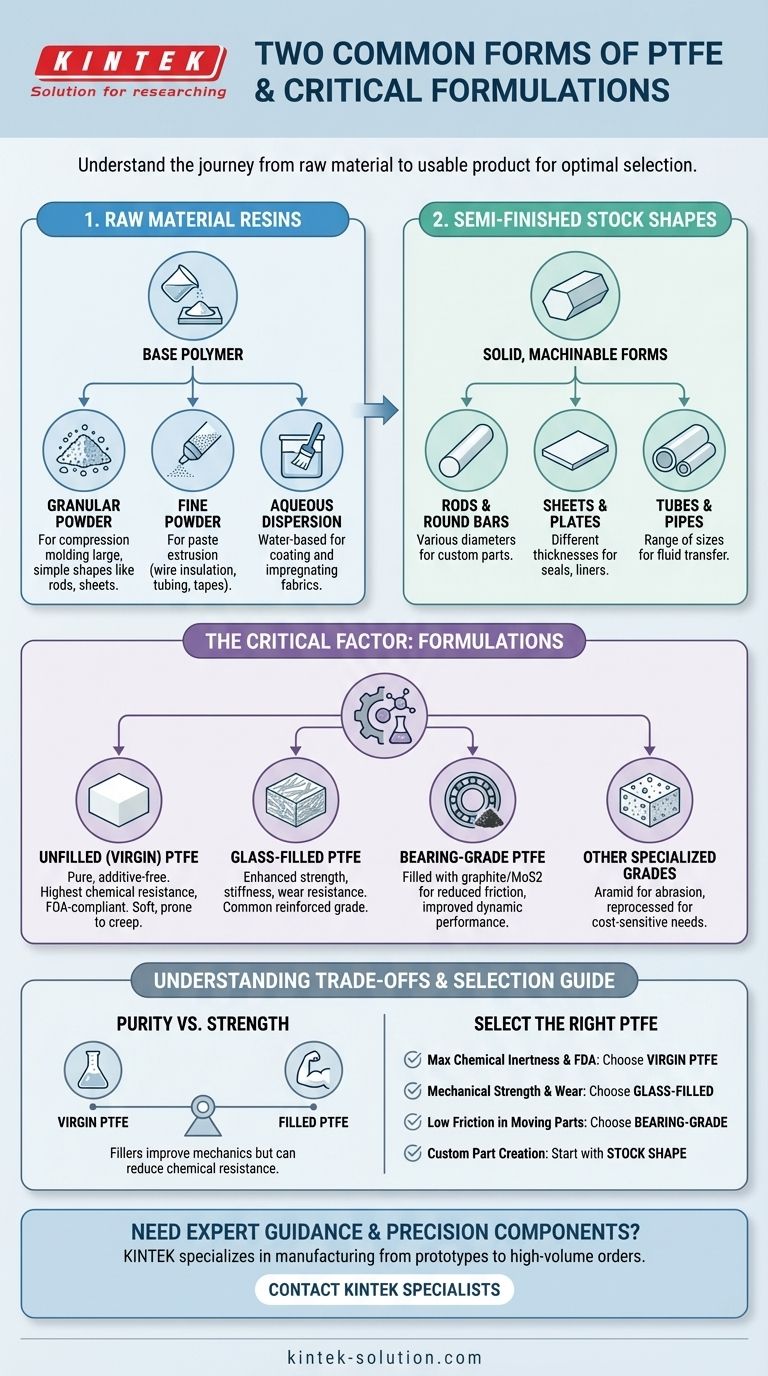
While PTFE can be categorized in several ways, the two most fundamental forms distinguish its state of production: raw material resins and semi-finished stock shapes. Raw materials, such as granular powders and aqueous dispersions, are the base ingredients. Semi-finished shapes like rods, sheets, and tubes are the solid forms created from those resins, ready for machining or use in final parts.
The distinction between PTFE forms goes well beyond raw material versus finished product. The critical decision lies in selecting the right formulation (e.g., virgin, glass-filled) and the correct stock shape (e.g., rod, sheet) to meet the specific mechanical, thermal, and chemical demands of your application.

From Raw Material to Usable Product
Understanding how Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is produced provides clarity on its available forms. The journey starts with a basic polymer resin and ends with a solid object ready for a specific function.
The Foundational Forms: Raw Resins
Before it becomes a solid part, PTFE exists as a bulk polymer. The primary commercial forms at this stage are:
- Granular Powder: A type of resin used in compression molding to create large, simple shapes like rods, tubes, and sheets.
- Fine Powder: A smaller particle size resin used in a paste extrusion process, often to create wire insulation, tubing, and tapes.
- Aqueous Dispersion: A water-based suspension of PTFE particles, used for coating and impregnating materials like fiberglass to create PTFE fabrics.
The Intermediate Forms: Semi-Finished Shapes
Most engineers and fabricators interact with PTFE in its semi-finished state. These are solid stock shapes created from raw resins, intended to be machined into final components.
Common shapes include:
- Rods/Round Bars
- Sheets/Plates
- Tubes/Pipes
These shapes are produced through processes like compression molding or extrusion and are available in a vast range of diameters and thicknesses.
The Critical Factor: PTFE Formulations
Simply choosing a shape is not enough. The most important decision involves selecting the correct formulation or grade. The properties of PTFE can be dramatically altered by adding fillers.
Unfilled (Virgin) PTFE
This is pure, additive-free PTFE. It is known for being extremely soft and formable, offering the highest chemical resistance and electrical insulation. It is the only grade suitable for FDA-compliant applications.
Glass-Filled PTFE
By adding glass fibers, the formulation gains significantly enhanced strength, stiffness, and wear resistance. This is one of the most common reinforced grades of PTFE.
Bearing-Grade PTFE
These formulations are compounded with fillers like graphite or molybdenum disulfide. The goal is to reduce friction and improve performance in dynamic, high-temperature applications like bearings and seals.
Other Specialized Grades
The versatility of PTFE allows for other formulations, including those combined with aramid fibers for abrasion resistance or reprocessed grades made from recycled material for less critical, cost-sensitive applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting the right PTFE requires balancing its inherent strengths and weaknesses. The choice of form and formulation always involves a compromise.
The Purity vs. Strength Dilemma
Virgin PTFE offers unmatched chemical inertness but suffers from poor mechanical strength and a tendency to deform under load (a phenomenon known as "creep").
The Compromise of Fillers
Adding fillers like glass dramatically improves mechanical properties but can reduce the overall chemical resistance of the material. Fillers can also be abrasive to softer mating surfaces in dynamic applications.
The Machining Challenge
PTFE's softness, while beneficial for sealing, makes it challenging to machine to extremely tight tolerances. Its high coefficient of thermal expansion also means that part dimensions can change significantly with temperature fluctuations.
Selecting the Right PTFE for Your Application
Your end goal dictates the ideal form and formulation. Use these guidelines to make a clear choice.
- If your primary focus is maximum chemical inertness and FDA compliance: Choose virgin (unfilled) PTFE for its unmatched purity.
- If your primary focus is mechanical strength and wear resistance: Select a glass-filled or other reinforced formulation.
- If your primary focus is low friction in moving parts: Opt for a bearing-grade PTFE, often filled with graphite or other solid lubricants.
- If your primary focus is creating a custom part: Start with a semi-finished stock shape (rod, sheet, tube) in the appropriate formulation for machining.
Understanding these layers—from raw resin to final formulation—is the key to leveraging PTFE's unique properties effectively.
Summary Table:
| PTFE Form | Key Characteristics | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Raw Resins (Granular/Fine Powder, Aqueous Dispersion) | Base polymer material for molding/extrusion/coating. | Manufacturing stock shapes, wire insulation, fabric coatings. |
| Semi-Finished Shapes (Rods, Sheets, Tubes) | Solid, machinable forms made from resins. | Fabricating custom seals, liners, labware, and components. |
Need the Right PTFE Form for Your Project?
Choosing between virgin PTFE for maximum chemical resistance or a glass-filled grade for superior strength is critical to your component's performance. KINTEK specializes in manufacturing precision PTFE components (seals, liners, labware, etc.) for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
We provide expert guidance on material selection and offer custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders. Let us help you optimize your application.
Contact our specialists today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the general characteristics of PTFE? Master Extreme Performance with This High-Performance Polymer
- How does graphite-filled PTFE compare to carbon-filled PTFE? Choose the Right Filler for Your Application
- What is the hardness of PTFE on the Shore scale? A Guide to Its Softness and Performance
- What industries commonly use Teflon material? Unlocking Versatility Across Sectors
- What types of plating solutions are compatible with PTFE? A Guide to Maximizing Chemical Resistance
- How is Teflon classified in terms of plastic types? A Guide to Thermoplastic Fluoropolymers
- What are the key properties of PTFE? A Guide to Its High-Performance Versatility
- What raw materials are used to synthesize PTFE? From Fluorspar to High-Performance Polymer



















