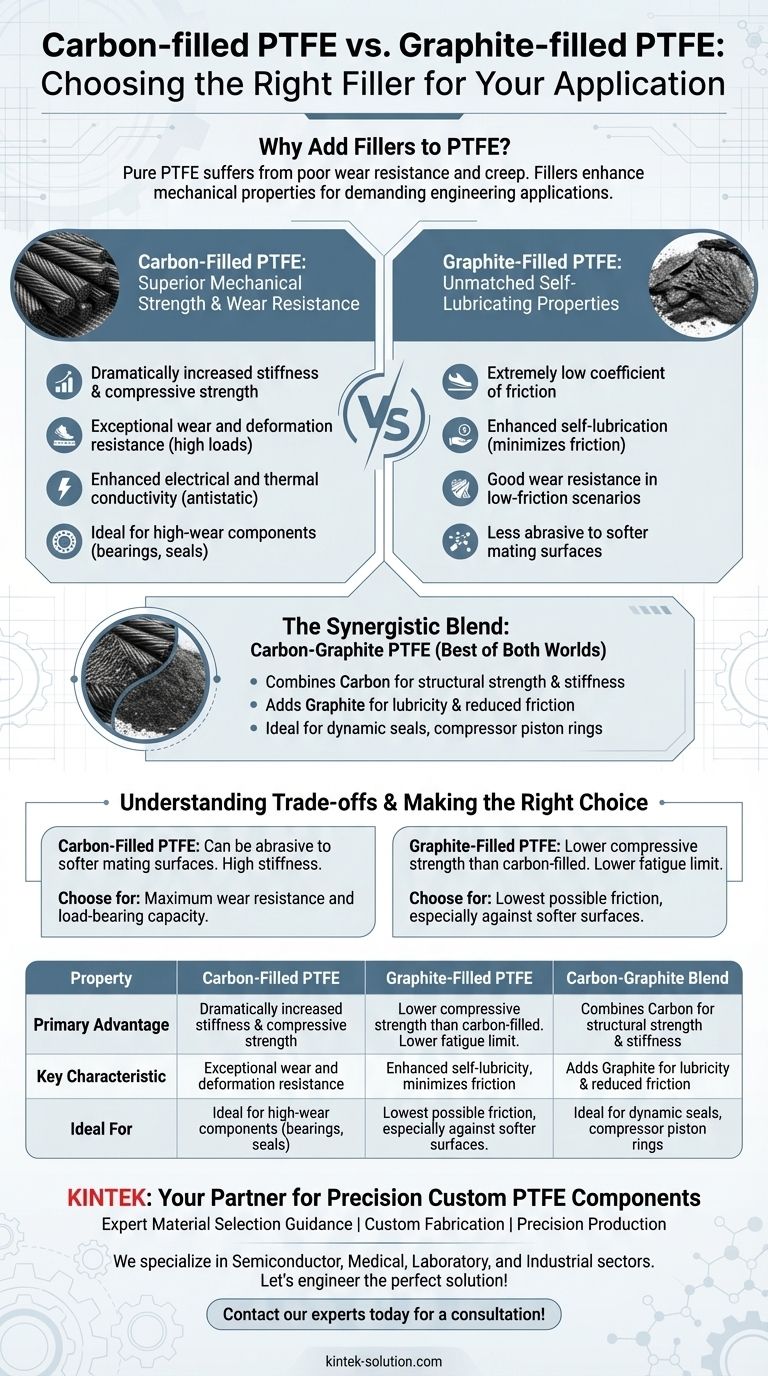
At a fundamental level, carbon-filled PTFE is chosen for its superior mechanical strength and wear resistance, while graphite-filled PTFE is selected for its enhanced self-lubricating properties and lower friction. Though they share similar operating temperatures and chemical resistance, their primary functions differ. Carbon provides stiffness and durability, whereas graphite provides lubricity.
The choice between carbon and graphite as a filler for PTFE is not about which is "better," but which property is more critical for your specific application. Carbon excels in high-load, high-wear environments, while graphite excels in low-friction scenarios.

Why Add Fillers to PTFE?
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is renowned for its chemical inertness and low friction. However, in its pure or "virgin" state, it suffers from poor wear resistance and a tendency to deform under load, a phenomenon known as "creep."
Fillers are added to enhance its mechanical properties. By compounding PTFE with materials like carbon or graphite, we create a composite material that retains PTFE's core benefits while significantly improving its performance in demanding engineering applications.
Analyzing Carbon-Filled PTFE
Superior Mechanical Strength and Wear Resistance
Adding carbon fiber (typically up to 35% by weight) dramatically increases the stiffness, compressive strength, and hardness of PTFE.
This makes carbon-filled PTFE exceptionally resistant to wear and deformation, especially under high loads and pressures. It has superior fatigue resistance compared to graphite-filled alternatives.
Enhanced Thermal and Electrical Conductivity
Virgin PTFE is an excellent electrical and thermal insulator. The addition of carbon makes the material electrically conductive, creating excellent antistatic properties.
This is critical in applications where the buildup of static electricity is a risk. It also improves thermal conductivity, helping to dissipate heat from sealing or bearing surfaces more effectively.
Common Applications
Due to its strength and conductivity, carbon-filled PTFE is ideal for high-wear components like sliding profiles, bearings, and seals that operate under significant load or where static discharge is a concern.
Analyzing Graphite-Filled PTFE
Unmatched Self-Lubricating Properties
Graphite is an excellent solid lubricant. When blended into PTFE, its flaky particle structure creates a material with an extremely low coefficient of friction.
This enhanced lubricity is graphite's primary advantage, making it highly effective in applications where minimizing friction is the top priority.
Good Wear Resistance for Low-Friction Needs
Graphite-filled PTFE offers good wear characteristics, but this is primarily a result of its low-friction nature rather than high mechanical strength.
It is particularly effective at preventing wear on softer mating surfaces, as it is less abrasive than carbon fiber.
The Role of Blends
Graphite is often used in combination with other fillers, like carbon or glass, to achieve a balance of properties. A common and highly effective blend combines the strength of carbon with the lubricity of graphite.
The Synergistic Blend: Carbon-Graphite PTFE
The Best of Both Worlds
A popular formulation, such as 23% carbon with 2% graphite, leverages the strengths of both fillers. The carbon provides the structural backbone, offering stiffness and wear resistance.
The small amount of graphite enhances lubricity, reducing friction and making the material more forgiving on softer shaft materials.
The Go-To for Demanding Seals
This blend is a standard choice for components like piston rings, rider rings, and rod packing in industrial compressors and general-purpose rotary shaft seals. It provides a robust, low-friction sealing solution that resists extrusion and performs well in dry, water, and steam environments.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Abrasiveness on Mating Surfaces
Carbon fiber is inherently harder and can be more abrasive than graphite. In applications with softer mating surfaces, such as aluminum or some stainless steels, pure carbon-filled PTFE can cause increased wear on the shaft.
Fatigue and Load Limitations
Graphite-filled PTFE lacks the high compressive strength and fatigue resistance of its carbon-filled counterpart. It is not the ideal choice for high-load static seals or dynamic applications with significant pressure spikes.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
- If your primary focus is maximum wear resistance and load-bearing capacity: Choose a carbon-filled PTFE for its superior stiffness and strength.
- If your primary focus is the lowest possible friction, especially against a softer mating surface: Choose a graphite-filled PTFE for its exceptional self-lubricating properties.
- If you need balanced performance for dynamic seals (e.g., rotary shafts, compressors): A carbon-graphite blend is often the optimal choice, delivering both durability and low friction.
By understanding the distinct role of each filler, you can engineer the precise performance characteristics your application demands.
Summary Table:
| Property | Carbon-Filled PTFE | Graphite-Filled PTFE | Carbon-Graphite Blend |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Advantage | Superior Mechanical Strength & Wear Resistance | Enhanced Self-Lubrication & Lower Friction | Balanced Performance (Strength + Lubricity) |
| Key Characteristic | Stiff, Durable, Electrically Conductive | Very Low Coefficient of Friction | Excellent for Dynamic Seals |
| Ideal For | High-Load Bearings, Sliding Parts, Anti-Static Seals | Low-Friction Applications, Softer Mating Surfaces | Compressor Piston Rings, Rotary Shaft Seals |
Still Unsure Which PTFE Composite is Right for Your Project?
KINTEK specializes in the precision manufacturing of custom PTFE components, including carbon-filled, graphite-filled, and blended formulations. We help engineers in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors select the ideal material to enhance performance, reduce wear, and extend component life.
We provide:
- Expert Material Selection Guidance: Leverage our deep knowledge to choose the perfect filler for your specific load, friction, and environmental requirements.
- Custom Fabrication: From prototypes to high-volume production, we manufacture seals, liners, labware, and more to your exact specifications.
- Precision Production: We prioritize quality and consistency to ensure every component delivers reliable performance.
Let's engineer the perfect solution for your application. Contact our experts today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the primary applications of PTFE fasteners and custom parts? Critical Solutions for Extreme Environments
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? Unlock Unmatched Performance in Demanding Applications
- What are the material advantages of machining Teflon? Unlock Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- What are the key benefits of PTFE in custom fabrication? Unlock Performance in Extreme Conditions



















