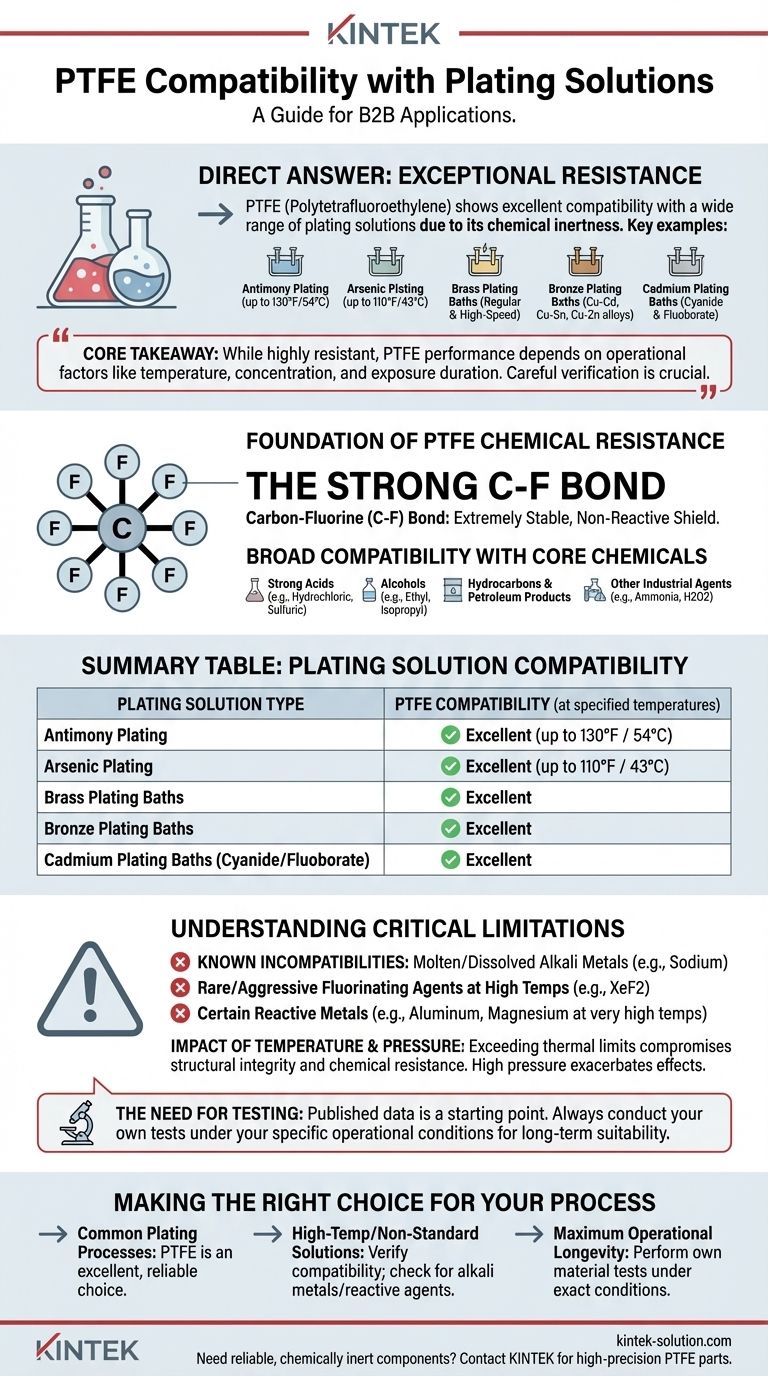
To be direct, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is exceptionally resistant to a wide range of plating solutions due to its chemical inertness. It demonstrates excellent compatibility with antimony, arsenic, brass, bronze, and cadmium plating baths, including both cyanide and fluoborate types. This broad resistance makes it a primary material choice for equipment used in electroplating processes.
The core takeaway is that while PTFE is one of the most chemically resistant polymers available for plating applications, its performance is not absolute. True compatibility depends on specific operational factors like temperature, chemical concentration, and exposure duration, which necessitates careful verification for any critical application.

The Foundation of PTFE's Chemical Resistance
To understand why PTFE is so widely used in plating environments, it's essential to look at its fundamental chemical structure and broad compatibility profile.
The Strength of the Carbon-Fluorine Bond
At its core, PTFE is a fluoropolymer. Its structure consists of a long chain of carbon atoms completely surrounded by fluorine atoms.
The carbon-fluorine (C-F) bond is one of the strongest single bonds in organic chemistry. This immense bond strength makes the polymer extremely stable and non-reactive, effectively creating a shield against most corrosive chemicals.
Broad Compatibility with Core Chemicals
The resilience of PTFE isn't limited to a few specific plating solutions. It is rated as excellent against the aggressive chemical components that make up these baths.
This includes common industrial chemicals such as:
- Strong Acids: (e.g., hydrochloric, sulfuric, acetic)
- Alcohols: (e.g., ethyl, methyl, isopropyl)
- Hydrocarbons and Petroleum Products
- Other Industrial Agents: (e.g., ammonia, hydrogen peroxide)
Because PTFE resists these foundational ingredients, it naturally holds up well against the final plating solution mixtures.
Verified Plating Solution Compatibility
Based on material testing, PTFE has demonstrated excellent performance when exposed to several specific plating solutions.
- Antimony Plating (up to 130°F / 54°C)
- Arsenic Plating (up to 110°F / 43°C)
- Brass Plating Baths (both regular and high-speed)
- Bronze Plating Baths (including Cu-Cd, Cu-Sn, and Cu-Zn alloys)
- Cadmium Plating Baths (both cyanide and fluoborate types)
Understanding the Critical Limitations
No material is universally inert. Acknowledging PTFE's limitations is key to preventing equipment failure and ensuring process safety.
Known Chemical Incompatibilities
While the list is short, certain highly reactive substances can attack PTFE.
These include molten or dissolved alkali metals (like sodium), rare and aggressive fluorinating agents at high temperatures (like xenon difluoride), and certain reactive metals like aluminum and magnesium at very high temperatures.
The Impact of Temperature and Pressure
Chemical resistance data is almost always tied to specific temperature ranges. As seen with the antimony and arsenic plating solutions, compatibility can have a defined temperature limit.
Exceeding these thermal limits can compromise PTFE's structural integrity and its ability to resist chemical attack. High pressure can also exacerbate the effects of aggressive chemicals.
Beyond the Data Sheet: The Need for Testing
Published chemical compatibility charts are an indispensable guide, but they are not a guarantee of performance.
Factors like chemical concentration, process temperature, and exposure duration can significantly impact material longevity. The available data is often based on short exposure periods, such as 48 hours, and may not predict performance over weeks or months of continuous service.
Therefore, conducting your own tests under your specific operational conditions is the only way to ensure full compatibility and avoid unexpected failures.
Making the Right Choice for Your Plating Process
Use this guidance to select materials confidently for your specific application.
- If your primary focus is on common plating processes: PTFE is an excellent and highly reliable choice for equipment handling brass, bronze, and cadmium solutions at their typical operating temperatures.
- If you are working with high-temperature or non-standard solutions: You must verify PTFE's compatibility, paying close attention to its known limitations with alkali metals and other reactive agents.
- If your primary focus is ensuring maximum operational longevity: Always treat published data as a starting point and perform your own material tests under your exact process conditions to confirm long-term suitability.
By understanding both its broad capabilities and specific limitations, you can confidently leverage PTFE for reliable performance in demanding plating applications.
Summary Table:
| Plating Solution Type | PTFE Compatibility (at specified temperatures) |
|---|---|
| Antimony Plating | Excellent (up to 130°F / 54°C) |
| Arsenic Plating | Excellent (up to 110°F / 43°C) |
| Brass Plating Baths | Excellent |
| Bronze Plating Baths | Excellent |
| Cadmium Plating Baths (Cyanide/Fluoborate) | Excellent |
Need reliable, chemically inert components for your plating process?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-precision PTFE components—including seals, liners, and custom labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our expertise in custom fabrication ensures you get parts that meet your exact specifications, from prototypes to high-volume orders, guaranteeing compatibility and longevity in your most demanding applications.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific requirements and get a quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Volumetric Flasks for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Use
People Also Ask
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments
- Why is CNC machining preferred for Teflon parts over other methods? Unlock Precision & Complex Designs
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability



















