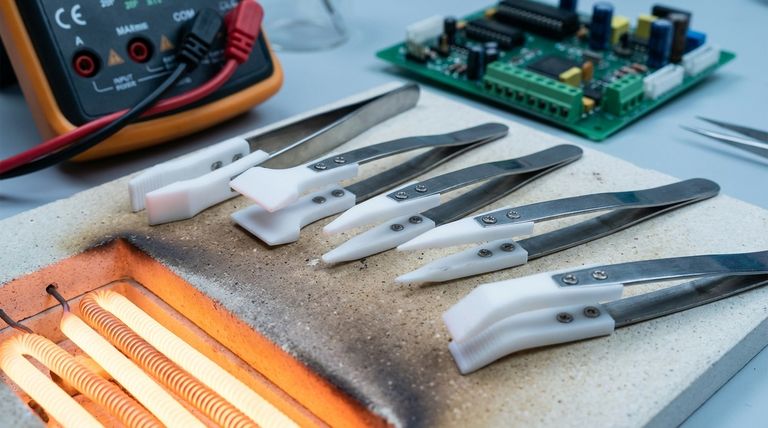
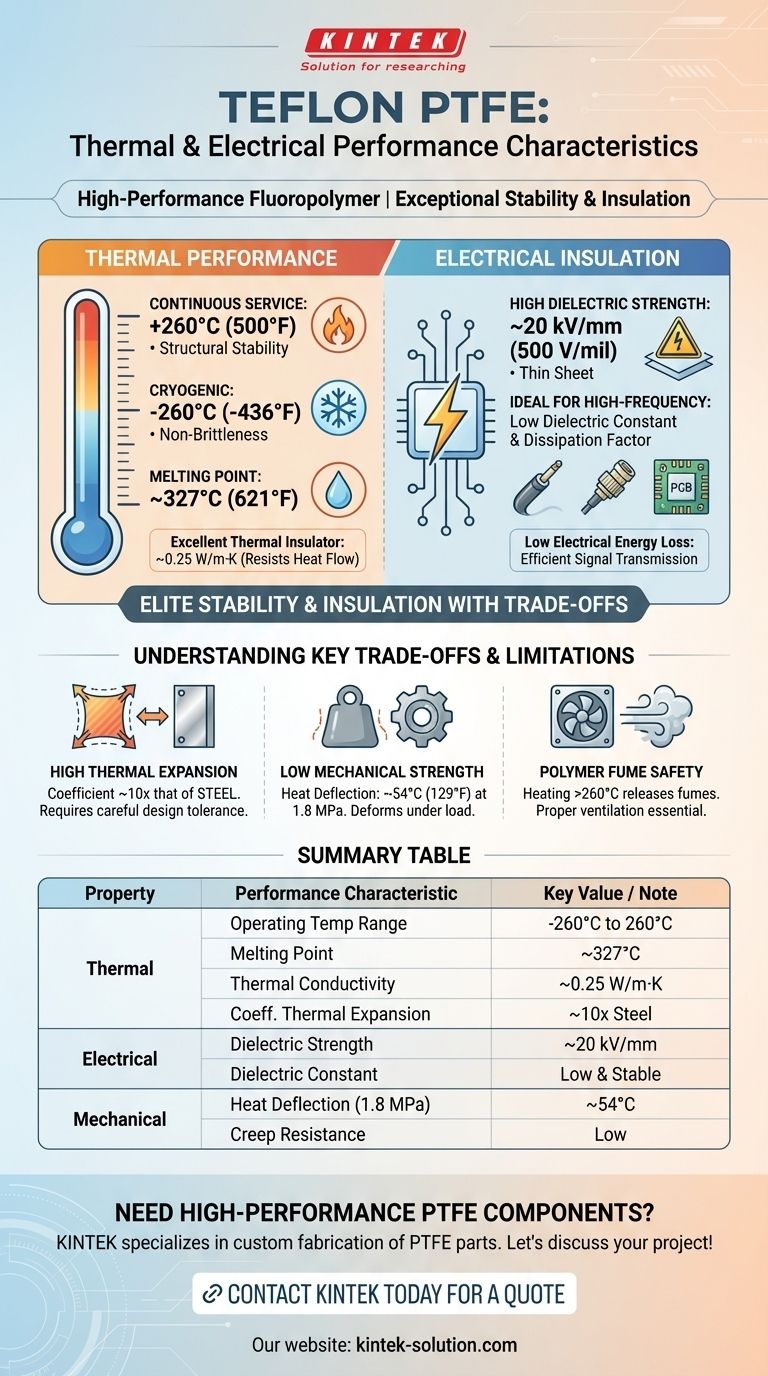
In short, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a high-performance fluoropolymer known for its exceptional thermal stability and outstanding electrical insulation. It maintains its properties across an extremely wide temperature range, from cryogenic conditions at -260°C (-436°F) up to a continuous service temperature of 260°C (500°F), and possesses a very high dielectric strength, making it a premier material for demanding applications.
While PTFE offers elite thermal stability and electrical insulation that few materials can match, its practical application hinges on understanding its key trade-offs: high thermal expansion and low mechanical strength, especially under load.

Unpacking the Thermal Performance
PTFE's reputation is built on its ability to perform reliably in extreme thermal conditions. This performance is not defined by a single metric but by a combination of distinct properties.
Exceptionally Wide Operating Temperature
PTFE has one of the widest operating temperature ranges of any polymer. It remains functional and avoids becoming brittle at cryogenic temperatures as low as -260°C (-436°F).
At the upper end, it provides a continuous service temperature of 260°C (500°F), maintaining its structural integrity and chemical inertness without degrading.
High Melting Point and Stability
The crystalline melting point of PTFE is approximately 327°C (621°F). This high threshold is a primary reason for its excellent thermal stability.
Below its service limit, it experiences virtually no thermal degradation, ensuring predictable performance in high-heat environments.
Excellent Thermal Insulation
PTFE is an effective thermal insulator, meaning it resists the flow of heat. Its thermal conductivity is very low, around 0.25 W/m·K.
This property makes it ideal for applications where you need to prevent heat transfer between components.
Defining the Electrical Insulation Capabilities
Alongside its thermal characteristics, PTFE is one of the best electrical insulators available. Its performance is critical for applications from high-voltage wiring to high-frequency electronics.
High Dielectric Strength
Dielectric strength measures a material's ability to withstand a strong electric field without breaking down. PTFE exhibits an excellent dielectric strength of approximately 500 volts per mil, which translates to 20 kV/mm.
This means a very thin sheet of PTFE can insulate against a very high voltage, making it invaluable for compact electronic components.
Ideal for High-Frequency Applications
PTFE maintains its excellent insulating properties across a wide range of frequencies. Its low dielectric constant and extremely low dissipation factor mean that very little electrical energy is lost as heat when alternating currents pass through it.
This makes it a go-to material for high-frequency applications, including coaxial cable insulation, RF connectors, and printed circuit boards (PCBs).
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
No material is perfect. To use PTFE effectively, you must design around its inherent mechanical and physical limitations, which become more pronounced at higher temperatures.
High Coefficient of Thermal Expansion
PTFE expands and contracts significantly with changes in temperature. Its coefficient of thermal expansion is roughly 10 times that of steel.
This must be accounted for in designs with tight tolerances, especially when PTFE parts are mated with metal components, to avoid stress, warping, or failure.
Low Mechanical Strength and Creep
PTFE is a relatively soft material. It is susceptible to creep, which is the tendency to slowly deform under a constant mechanical load.
Its heat deflection temperature, as low as 54°C (129°F) under a load of 1.8 MPa, highlights this softness. For structural applications, especially at elevated temperatures, unfilled PTFE is often unsuitable.
Polymer Fume Safety
While exceptionally stable within its service range, heating PTFE above 260°C (500°F) can cause it to release fumes that may lead to a temporary flu-like condition known as polymer fume fever. Proper ventilation is essential in any application where overheating is possible.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting PTFE depends entirely on whether its unique strengths align with your primary design goal.
- If your primary focus is electrical insulation: PTFE is an industry-standard choice, especially for high-voltage or high-frequency systems where low signal loss is critical.
- If your primary focus is performance in extreme temperatures: PTFE's vast operating range is a key benefit, but you must engineer your design to accommodate its high thermal expansion.
- If your primary focus is a structural component under mechanical load: Unfilled PTFE is likely the wrong material due to its softness and tendency to creep; consider using filled PTFE grades or a different high-performance polymer.
By understanding both its exceptional insulating properties and its inherent mechanical trade-offs, you can confidently leverage PTFE in the most demanding applications.
Summary Table:
| Property | Performance Characteristic | Key Value / Note |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal | Operating Temperature Range | -260°C to 260°C (-436°F to 500°F) |
| Melting Point | ~327°C (621°F) | |
| Thermal Conductivity | ~0.25 W/m·K (Excellent Insulator) | |
| Coefficient of Thermal Expansion | ~10x that of steel | |
| Electrical | Dielectric Strength | ~20 kV/mm |
| Dielectric Constant & Dissipation Factor | Low and stable, ideal for high-frequency use | |
| Mechanical Limitation | Heat Deflection Temperature (under load) | ~54°C (129°F) at 1.8 MPa |
| Creep Resistance | Low; deforms under sustained load |
Need High-Performance PTFE Components for Your Critical Application?
Understanding PTFE's properties is the first step; obtaining precision-manufactured components that leverage these strengths is the next. KINTEK specializes in custom fabricating PTFE seals, liners, labware, and other critical parts for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
We help you navigate the trade-offs of PTFE to deliver components that meet your exact requirements for thermal stability, electrical insulation, and chemical resistance—from prototypes to high-volume production.
Let's discuss your project requirements and how our expertise can ensure your application's success.
Contact KINTEL Today for a Quote
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- Why is CNC machining preferred for Teflon parts over other methods? Unlock Precision & Complex Designs
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech



















