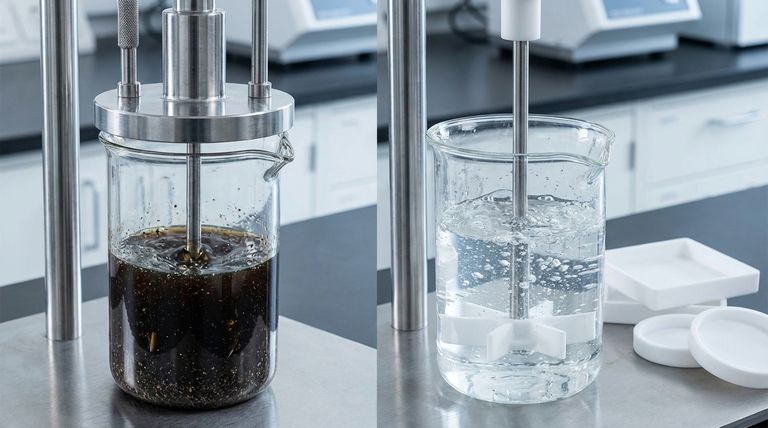
In short, stainless steel impellers are defined by their exceptional mechanical strength and heat resistance. They are engineered to withstand high-speed, demanding applications without significant wear, making them a standard for many physically intensive mixing tasks.
The core decision between a stainless steel impeller and an alternative like PTFE is not about general "durability," but about a specific trade-off: choosing between stainless steel's superior mechanical and thermal strength versus its vulnerability to chemical corrosion.

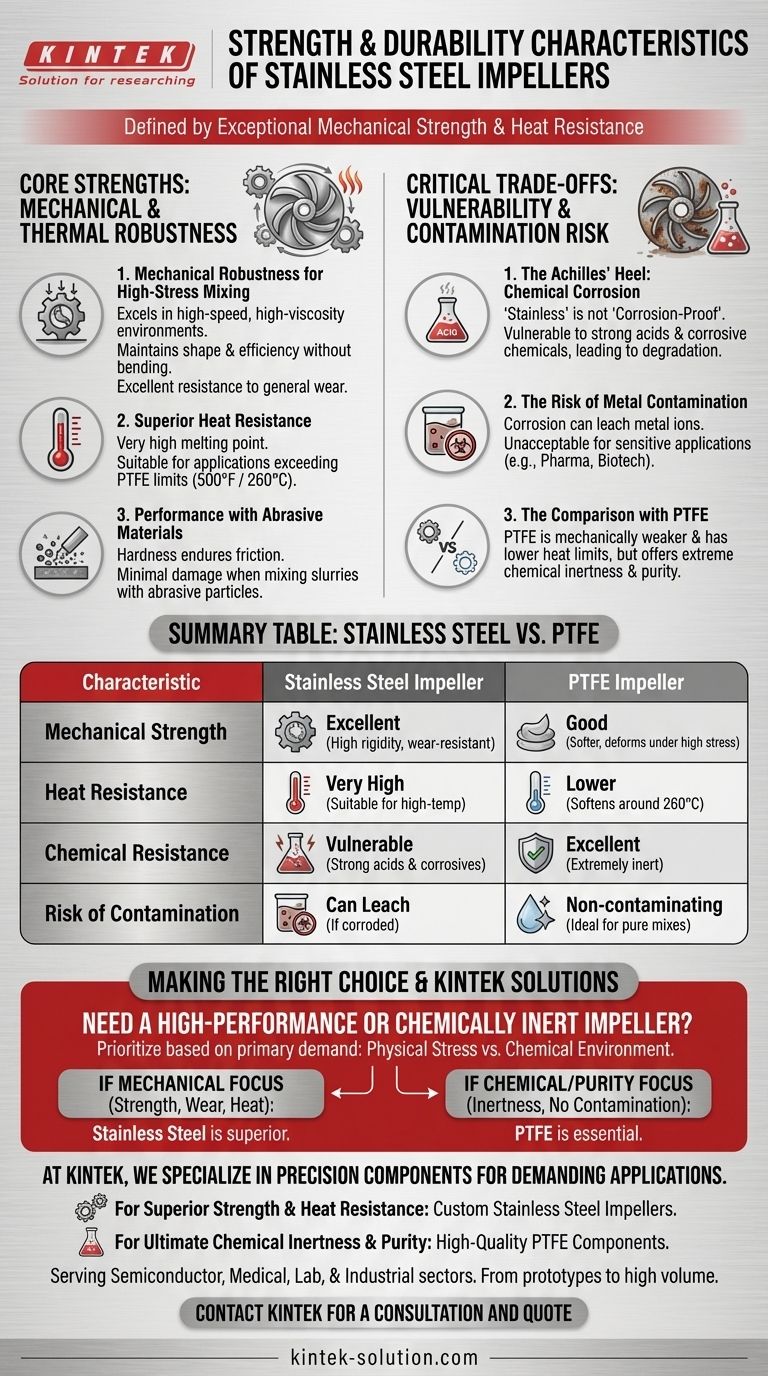
The Core Strengths of Stainless Steel Impellers
Stainless steel is often the default choice for impellers precisely because of its physical robustness. This makes it highly reliable for a wide range of common laboratory and industrial processes.
Mechanical Robustness for High-Stress Mixing
Stainless steel impellers excel in high-speed and high-viscosity environments. Their rigidity allows them to maintain their shape and efficiency without bending or fatiguing under heavy loads.
This inherent strength also provides excellent resistance to general wear and tear from prolonged, continuous operation.
Superior Heat Resistance
A key advantage of stainless steel is its very high melting point. This makes it suitable for applications involving significant heat.
In contrast, materials like PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene) begin to lose their structural integrity at much lower temperatures, typically around 500 °F (260 °C).
Performance with Abrasive Materials
The hardness of stainless steel makes it well-suited for mixing slurries or suspensions containing abrasive particles. Softer materials would quickly degrade in these conditions, but stainless steel can endure the friction with minimal damage.
Understanding the Critical Trade-offs
While physically durable, stainless steel is not universally invincible. Its primary weakness is a lack of complete chemical inertness, which is a critical consideration for material selection.
The Achilles' Heel: Chemical Corrosion
The term "stainless" can be misleading; it does not mean corrosion-proof. Certain strong acids and other corrosive chemicals can attack and degrade the steel over time.
This chemical reaction can weaken the impeller's structure, leading to premature failure in environments it is not designed for.
The Risk of Metal Contamination
The most significant consequence of corrosion is not just damage to the equipment, but the potential for leaching metal contaminants into the mixture.
For sensitive applications in fields like pharmaceuticals, biotech, or food science, this type of contamination is unacceptable and can compromise the integrity of an entire batch or experiment.
The Comparison with PTFE
This is where the choice becomes clear. While PTFE is mechanically weaker and has a lower temperature limit, its primary advantage is its extreme chemical inertness. It is the material of choice when purity and resistance to corrosive agents are the top priorities.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct impeller material requires you to prioritize the primary demand of your specific process—its physical stress or its chemical environment.
- If your primary focus is mechanical performance: Stainless steel is the superior choice for high-speed, high-viscosity, or abrasive mixing due to its strength and wear resistance.
- If your primary focus is chemical inertness: A material like PTFE is essential when working with highly corrosive chemicals or when avoiding metal contamination is critical.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature mixing: Stainless steel is the necessary option, especially for applications that exceed the thermal limits of polymers like PTFE.
Ultimately, choosing the right impeller is about precisely matching the material's capabilities to the unique chemical and physical demands of your work.
Summary Table:
| Characteristic | Stainless Steel Impeller | PTFE Impeller |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanical Strength | Excellent (High rigidity, wear-resistant) | Good (Softer, can deform under high stress) |
| Heat Resistance | Very High (Suitable for high-temp applications) | Lower (Softens around 260°C / 500°F) |
| Chemical Resistance | Vulnerable to strong acids & corrosive chemicals | Excellent (Extremely inert, ideal for corrosive agents) |
| Risk of Contamination | Can leach metal ions if corroded | Non-contaminating, ideal for pure mixes |
| Best For | High-speed, high-viscosity, abrasive, high-temperature mixing | Chemically aggressive environments, purity-critical applications |
Need a High-Performance or Chemically Inert Impeller?
Selecting the right impeller material is critical to your process's success. At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing precision components, including custom impellers, for the most demanding applications.
- For Superior Strength & Heat Resistance: Our stainless steel impellers are engineered for high-speed, high-viscosity, and abrasive mixing tasks.
- For Ultimate Chemical Inertness & Purity: We manufacture high-quality PTFE components that resist even the most aggressive chemicals, ensuring zero contamination.
We serve the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors with custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders. Let us help you optimize your mixing process.
Contact KINTEK today for a consultation and quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- PTFE Chemical Solvent Sampling Spoon
- PTFE Deep Evaporating Dishes Customizable Laboratory and Industrial Solutions
People Also Ask
- What are the base characteristics of PTFE? Unlocking Extreme Performance in Friction, Temperature, and Chemical Resistance
- Why is PTFE suitable for cryogenic or high-temperature applications? Unmatched Thermal Stability from -450°F to 500°F
- What are some common applications of machined PTFE? Leverage its Unique Properties for Demanding Applications
- What is PTFE commonly known as and what are its unique properties? Unlock Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- What are the primary applications of PTFE fasteners and custom parts? Critical Solutions for Extreme Environments



















