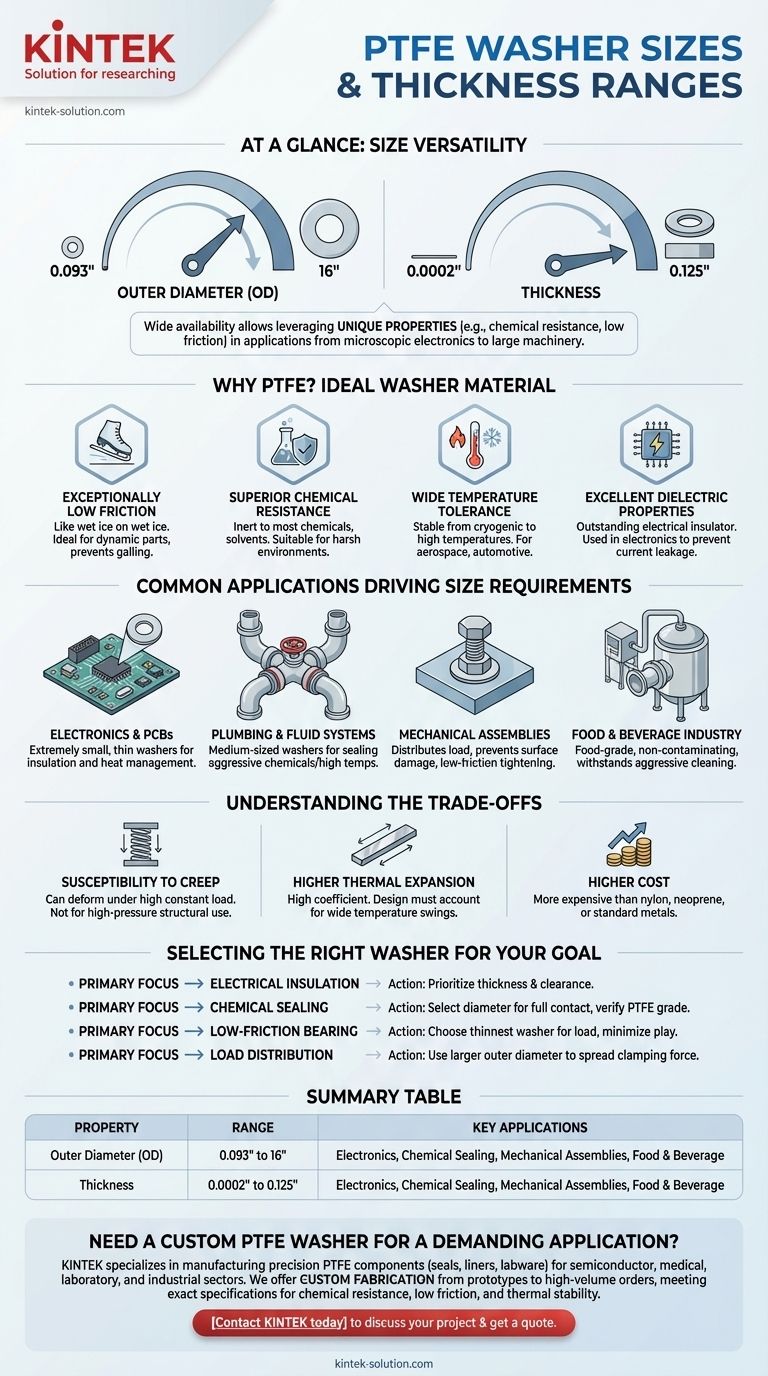
At a glance, PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) washers are available in an exceptionally wide range of standard sizes. You can typically find them with outer diameters from 0.093 to 16 inches and in thicknesses from a remarkably thin 0.0002 inches up to 0.125 inches.
The key takeaway is not just the wide availability of sizes, but understanding that this versatility allows engineers to leverage PTFE's unique properties—like extreme chemical resistance and low friction—in everything from microscopic electronics to large industrial machinery.

What Makes PTFE an Ideal Washer Material?
The demand for such a broad range of washer sizes is driven directly by the unique and powerful properties of the PTFE material itself. It is often chosen when other common materials like steel, nylon, or rubber would fail.
Exceptionally Low Friction
PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid material, often compared to wet ice on wet ice. This makes it an ideal choice for dynamic applications where parts must slide or rotate against each other without galling or seizing.
Superior Chemical Resistance
PTFE is chemically inert and resistant to nearly all industrial chemicals, solvents, and corrosive agents. This allows it to be used for sealing and spacing in harsh environments, from chemical processing plants to laboratory equipment.
Wide Temperature Tolerance
This material maintains its properties across a vast temperature range, remaining stable in cryogenic conditions and in continuous use at high temperatures. This stability is critical for applications in aerospace, automotive, and industrial processing.
Excellent Dielectric Properties
PTFE is an outstanding electrical insulator, making it a critical component in electronics. Its ability to resist high voltages and prevent current leakage is why tiny, thin washers are frequently used on circuit boards and in connectors.
Common Applications Driving Size Requirements
The specific dimensions of a PTFE washer are directly tied to its function in a given assembly. The broad size availability reflects its use across many industries.
Electronics and PCBs
In electronics, extremely small and thin washers are used to insulate components like transistors and connectors from the circuit board or chassis, preventing short circuits while managing heat.
Plumbing and Fluid Systems
Medium-sized washers are essential for creating seals in pipes, valves, and fittings, especially those carrying aggressive chemicals or operating at high temperatures where a typical rubber gasket would degrade.
Mechanical Assemblies
In mechanical systems, PTFE washers are used to distribute the load from a screw or bolt over a delicate surface, such as plastic or a painted panel. Their low-friction nature also prevents damage during tightening.
Food and Beverage Industry
Because PTFE is available in food-grade formulations and can withstand aggressive cleaning agents and high temperatures, it is commonly used in processing equipment to ensure sanitary, non-contaminating connections.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, PTFE is not the solution for every problem. Its limitations are as important to understand as its strengths.
Susceptibility to Creep
PTFE is a relatively soft material and can deform or "creep" over time, especially under high, constant compressive loads. It is not suitable for high-pressure structural applications where maintaining precise torque is critical.
Higher Thermal Expansion
Compared to metals, PTFE has a high coefficient of thermal expansion. In applications with wide temperature swings, this must be accounted for in the design to avoid loosening or excessive stress on the assembly.
Higher Cost
Specialty materials come at a higher cost. PTFE washers are generally more expensive than their counterparts made from nylon, neoprene, or standard metals.
Selecting the Right Washer for Your Goal
Your final choice depends entirely on the primary problem you are trying to solve.
- If your primary focus is electrical insulation: Prioritize the correct thickness and ensure the washer provides sufficient clearance between conductive components.
- If your primary focus is chemical sealing: Select a diameter that ensures full contact with the sealing surfaces and verify the PTFE grade is suitable for the specific chemicals involved.
- If your primary focus is a low-friction bearing surface: Choose the thinnest washer possible that can withstand the load to minimize play in the assembly.
- If your primary focus is distributing load on a delicate surface: Use a washer with a larger outer diameter to spread the clamping force over a wider area, preventing damage.
Ultimately, the vast range of available PTFE washer sizes ensures you can find a precise fit for nearly any application that demands its elite performance characteristics.
Summary Table:
| Property | Range |
|---|---|
| Outer Diameter (OD) | 0.093" to 16" |
| Thickness | 0.0002" to 0.125" |
| Key Applications | Electronics, Chemical Sealing, Mechanical Assemblies, Food & Beverage |
Need a custom PTFE washer for a demanding application?
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing precision PTFE components, including seals, liners, and labware, for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We offer custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders, ensuring your parts meet exact specifications for chemical resistance, low friction, and thermal stability.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your project requirements and get a quote.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? Unlock Unmatched Performance in Demanding Applications
- What are the base characteristics of PTFE? Unlocking Extreme Performance in Friction, Temperature, and Chemical Resistance
- What is PTFE commonly known as and what are its unique properties? Unlock Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- What are the material advantages of machining Teflon? Unlock Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- Why is PTFE suitable for cryogenic or high-temperature applications? Unmatched Thermal Stability from -450°F to 500°F



















