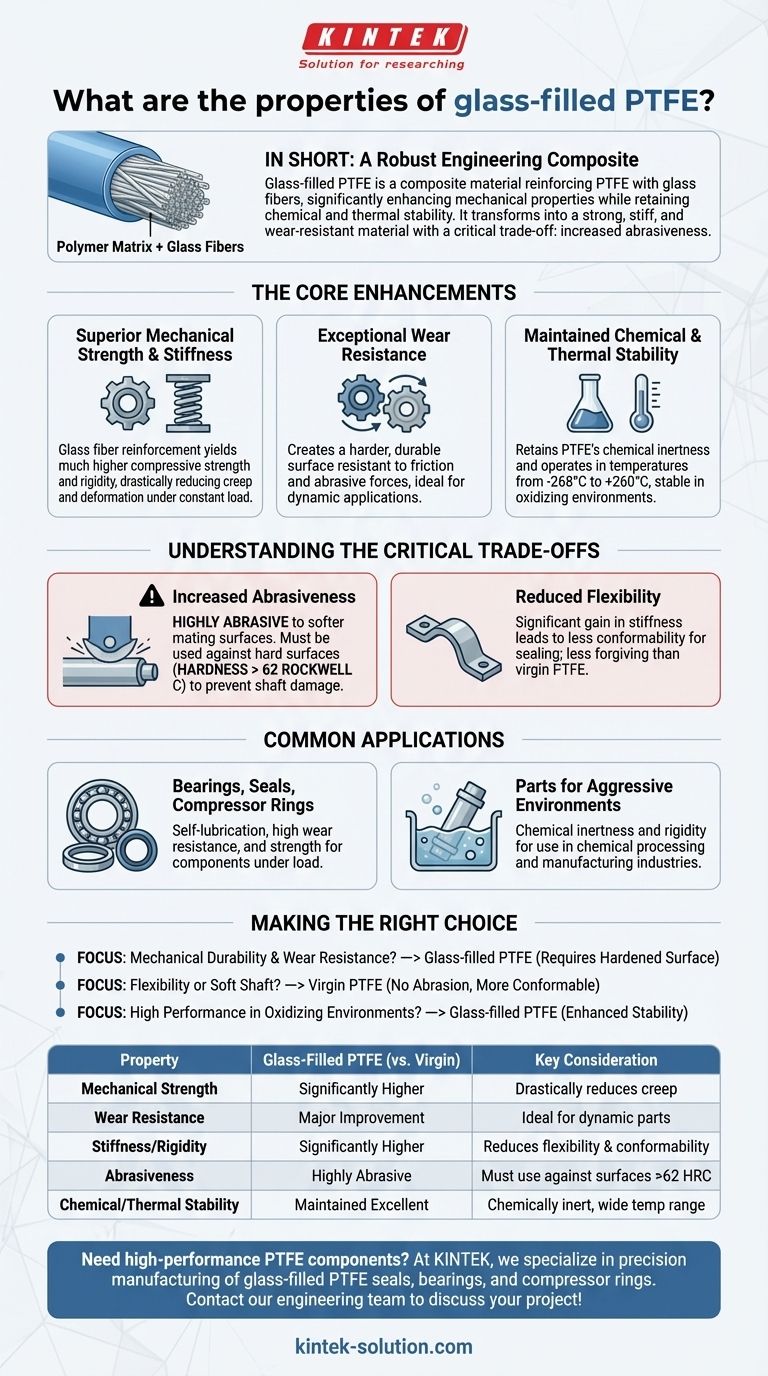
In short, glass-filled PTFE is a composite material that dramatically enhances the mechanical properties of standard PTFE. By reinforcing the polymer matrix with glass fibers, it becomes significantly stronger, stiffer, and more resistant to wear and deformation under load, while retaining PTFE’s excellent chemical and thermal stability.
The core principle to understand is that adding glass fibers transforms PTFE from a soft, compliant polymer into a robust engineering material. This enhancement comes with a critical trade-off: a significant increase in abrasiveness that must be managed in your design.

The Core Enhancements of Glass-Filled PTFE
The addition of glass fibers, typically at a concentration of 25%, fundamentally changes the performance profile of Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE). These changes make it suitable for a new class of demanding applications where virgin PTFE would fail.
Superior Mechanical Strength and Stiffness
Glass fibers act as a powerful reinforcement within the PTFE matrix. This results in a material with much higher compressive strength and rigidity.
This added stiffness drastically reduces creep, which is the tendency of a material to deform slowly over time under a constant load.
Exceptional Wear Resistance
One of the most significant benefits is a major improvement in wear resistance. The glass fibers create a harder, more durable surface that stands up far better to friction and abrasive forces.
This property makes it ideal for dynamic applications like bearings and seals where longevity is critical.
Maintained Chemical and Thermal Stability
Glass-filled PTFE retains the hallmark properties of virgin PTFE. It remains chemically inert in most environments, performing especially well in oxidizing conditions.
It also operates across an extremely wide temperature range, from -268°C to +260°C, ensuring stability in both cryogenic and high-heat applications.
Understanding the Critical Trade-offs
While the benefits are clear, selecting this material without understanding its limitations can lead to catastrophic component failure. The enhancements are not without cost.
Increased Abrasiveness
This is the most critical trade-off. The same glass fibers that improve wear resistance make the material highly abrasive to softer mating surfaces.
Using glass-filled PTFE against a soft metal shaft will quickly destroy the shaft. It should only be used against surfaces with a very high hardness, typically greater than 62 Rockwell C.
Reduced Flexibility
The significant gain in stiffness means a corresponding loss of flexibility. Virgin PTFE is known for its ability to conform to irregular surfaces in sealing applications.
Glass-filled PTFE is much more rigid and less forgiving, a factor that must be considered in the design of components like gaskets or seals requiring high conformability.
Common Applications Driven by These Properties
The unique balance of properties in glass-filled PTFE makes it the material of choice for several key industrial uses where standard plastics and even virgin PTFE are unsuitable.
Bearings, Seals, and Compressor Rings
The combination of self-lubrication (an inherent PTFE trait), high wear resistance, and strength makes it an excellent choice for self-lubricating bearings, gaskets, and piston rings that operate under load.
Parts for Aggressive Environments
Its chemical inertness and rigidity allow it to be used for components in aggressive media applications found in the chemical processing and manufacturing industries.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct material requires aligning its properties with your primary engineering goal.
- If your primary focus is mechanical durability and wear resistance: Glass-filled PTFE is an excellent choice, provided you pair it with a properly hardened mating surface to prevent abrasion.
- If your primary focus is flexibility or use against a soft shaft: Unfilled, virgin PTFE is the superior option, as it will not abrade the mating surface and will conform more easily.
- If your primary focus is high performance in oxidizing environments: The enhanced stability of glass-filled PTFE makes it a reliable and long-lasting solution.
Ultimately, understanding both the strengths and the crucial limitations of glass-filled PTFE is the key to successful engineering design.
Summary Table:
| Property | Glass-Filled PTFE (vs. Virgin PTFE) | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanical Strength | Significantly Higher | Drastically reduces creep (deformation under load) |
| Wear Resistance | Major Improvement | Ideal for dynamic parts like bearings and seals |
| Stiffness/Rigidity | Significantly Higher | Reduces flexibility; less conformable for sealing |
| Abrasiveness | Highly Abrasive | Must be used against hard surfaces (>62 Rockwell C) |
| Chemical/Thermal Stability | Maintained Excellent | Chemically inert, stable from -268°C to +260°C |
Need high-performance PTFE components that stand up to extreme wear and load?
At KINTEK, we specialize in precision manufacturing of glass-filled PTFE components like seals, bearings, and compressor rings for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We understand the critical balance between enhanced performance and managing abrasiveness.
Our experts will work with you to select the right material and design for your application, ensuring longevity and reliability. We offer custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders.
Contact our engineering team today to discuss your project requirements and get a quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- What are the material advantages of machining Teflon? Unlock Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? Unlock Unmatched Performance in Demanding Applications
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- What are the base characteristics of PTFE? Unlocking Extreme Performance in Friction, Temperature, and Chemical Resistance
- What are the primary applications of PTFE fasteners and custom parts? Critical Solutions for Extreme Environments



















