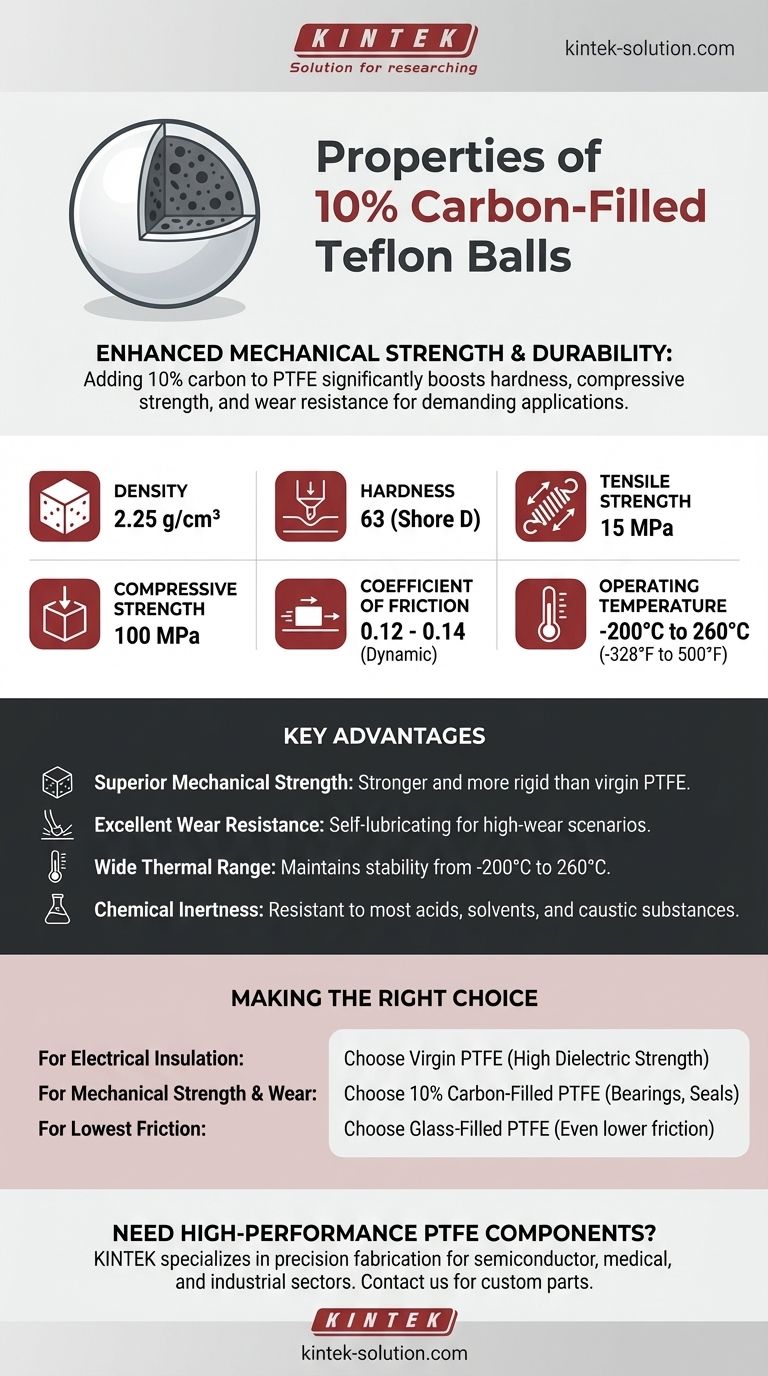
In short, 10% carbon-filled Teflon balls are a high-performance material designed for enhanced mechanical strength and durability. They possess a density of 2.25 g/cm³, a hardness of 63 (Shore D), a tensile strength of 15 MPa, and a high compressive strength of 100 MPa. This composite material maintains Teflon's excellent thermal stability, operating continuously from -200°C up to 260°C (-328°F to 500°F).
The core purpose of adding carbon to Teflon (PTFE) is to significantly increase its hardness, compressive strength, and wear resistance. This creates a material ideal for demanding mechanical applications where unfilled PTFE would be too soft or deform under load.

The Role of Carbon Filler in PTFE
Adding a filler like carbon fundamentally alters the properties of the base Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) polymer. Understanding this relationship is key to selecting the right material.
The Baseline: Unfilled Virgin PTFE
Virgin PTFE is renowned for its extreme chemical inertness and very low coefficient of friction. It is also an exceptional electrical insulator.
However, it is a relatively soft material with lower mechanical and wear resistance compared to other engineering plastics. It can be prone to "creep" or deforming under a sustained load.
The Enhancement: Adding 10% Carbon
The carbon acts as a reinforcing agent within the PTFE matrix. This creates a composite with several critical advantages over the unfilled version.
The primary benefit is a major boost in mechanical properties, making the material far more robust for load-bearing or high-wear scenarios.
Deconstructing the Key Properties
Each technical specification points to a specific real-world performance characteristic.
Mechanical Strength and Hardness
With a compressive strength of 100 MPa and hardness of 63 Shore D, carbon-filled PTFE is significantly stronger and more rigid than virgin PTFE (around 55 Shore D).
This makes it suitable for applications like valve seats, bearings, and seals that operate under pressure. The material is much less likely to deform.
Frictional Characteristics
The dynamic coefficient of friction is 0.12-0.14. While still very low, this is slightly higher than some other PTFE variants, like glass-filled PTFE.
The key benefit here is wear resistance. The carbon filler makes the material self-lubricating, allowing it to withstand abrasion and friction far better than unfilled PTFE.
Thermal Performance
A standout feature is the vast operating temperature range, from -200°C to 260°C (-328°F to 500°F).
The carbon filler also improves thermal conductivity, helping to dissipate heat generated at contact points more effectively than virgin PTFE. This further enhances performance in high-speed or high-load applications.
Chemical Resistance
The PTFE matrix ensures the composite retains exceptional resistance to nearly all industrial acids, solvents, and caustic substances.
This combination of mechanical strength and chemical inertness is what makes this material so valuable in aggressive industrial environments.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No material is perfect for every application. Selecting carbon-filled PTFE involves accepting specific compromises.
Hardness vs. Flexibility
The addition of carbon increases hardness and rigidity, which is a primary goal.
However, this comes at the cost of some flexibility. The elongation at break is 180%, which indicates it can stretch significantly before failing but is less flexible than other PTFE formulations.
Electrical Properties
Virgin PTFE is one of the best electrical insulators available. Carbon, however, is electrically conductive.
Adding carbon filler degrades the insulating properties of PTFE. The resulting composite is more statically dissipative, which can be an advantage in preventing static buildup but makes it unsuitable for high-voltage insulating applications.
Radiation and UV Resistance
Like its unfilled counterpart, carbon-filled PTFE has poor resistance to electromagnetic radiation.
However, it retains PTFE's excellent resistance to degradation from UV light, making it suitable for outdoor exposure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Choosing the correct material formulation is critical to the success and longevity of your component.
- If your primary focus is electrical insulation: Virgin (unfilled) PTFE is the superior choice due to its high dielectric strength.
- If your primary focus is mechanical strength and wear resistance: 10% carbon-filled PTFE is an excellent option for bearings, seals, and components under compressive load.
- If your primary focus is the absolute lowest friction: Glass-filled PTFE often exhibits an even lower coefficient of friction and may be a better alternative.
Ultimately, you should select the material whose properties are most closely aligned with the specific mechanical, thermal, and electrical demands of your application.
Summary Table:
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Density | 2.25 g/cm³ |
| Hardness (Shore D) | 63 |
| Tensile Strength | 15 MPa |
| Compressive Strength | 100 MPa |
| Coefficient of Friction | 0.12 - 0.14 |
| Operating Temperature | -200°C to 260°C (-328°F to 500°F) |
| Elongation at Break | 180% |
Need High-Performance PTFE Components?
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing precision PTFE components, including carbon-filled formulations, for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our custom fabrication services—from prototypes to high-volume orders—ensure you get parts with the exact mechanical strength, wear resistance, and thermal stability your application demands.
Contact us today to discuss your project requirements and get a quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- Why is CNC machining preferred for Teflon parts over other methods? Unlock Precision & Complex Designs
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments



















