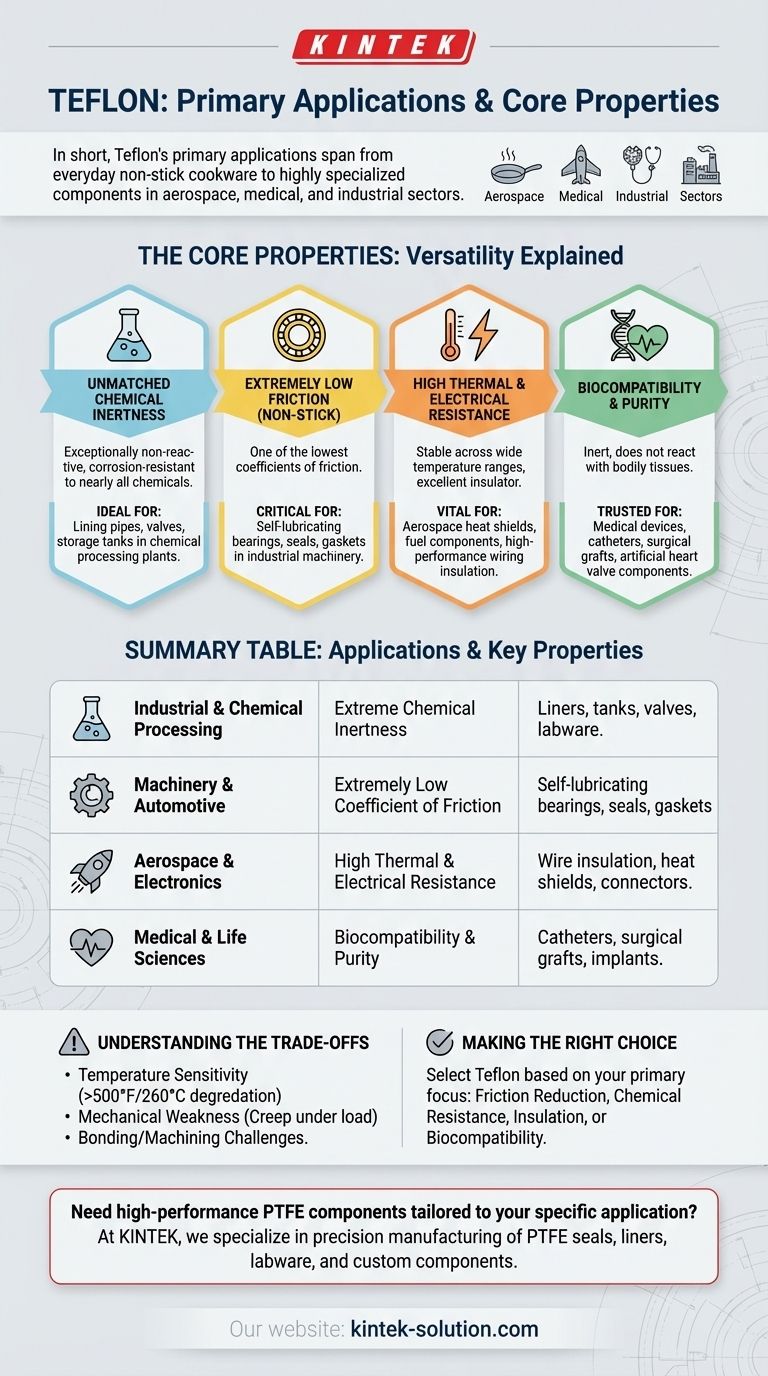
In short, Teflon's primary applications span from everyday non-stick cookware to highly specialized components in the aerospace, medical, and industrial sectors. Its use is incredibly diverse, including electrical wire insulation, chemically-resistant linings for pipes and tanks, low-friction bearings and seals, and even biocompatible medical implants.
The true value of Teflon (PTFE) isn't in a single application, but in its unique combination of three core properties: extreme chemical inertness, a remarkably low coefficient of friction, and high thermal stability. Understanding these properties is the key to understanding its widespread use.

Why Teflon is So Versatile: The Core Properties
The reason Teflon appears in so many unrelated industries is that its fundamental characteristics solve critical engineering challenges. Different applications leverage different aspects of its unique chemical makeup.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
Teflon is exceptionally non-reactive and resistant to corrosion from nearly all chemicals.
This property makes it an ideal material for lining pipes, valves, and storage tanks in chemical processing plants. It's also used for laboratory equipment that must withstand highly corrosive substances without degrading.
Extremely Low Friction (Non-Stick)
Teflon has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any known solid material, giving it its famous "non-stick" quality.
While this is best known in cookware, its most critical use is in industrial machinery. It is used to create self-lubricating bearings, seals, and gaskets that reduce wear and improve efficiency in engines and other moving parts.
High Thermal and Electrical Resistance
Teflon maintains its stability across a wide range of temperatures and is an excellent electrical insulator.
This combination is vital in the aerospace industry, where it's used in heat shields and fuel system components. Its dielectric properties also make it a primary choice for insulating high-performance wiring and cables, from consumer electronics to automotive systems.
Biocompatibility and Purity
The inert nature of Teflon means it does not react with bodily tissues, making it highly biocompatible.
This allows it to be used safely inside the human body for medical devices such as catheters, surgical grafts, and even components for artificial heart valves.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No material is perfect, and relying on Teflon requires an understanding of its limitations. Being aware of these trade-offs is critical for proper application.
Temperature Sensitivity
While Teflon has high heat resistance, it begins to degrade at temperatures above 500°F (260°C). Overheating can release fumes, a primary concern in cookware applications.
Mechanical Weakness
Teflon is a relatively soft material. It is not suitable for high-load structural components, as it can deform under pressure (a phenomenon known as "creep").
Bonding and Machining Challenges
The very non-stick properties that make Teflon useful also make it extremely difficult to bond to other materials using conventional adhesives. It requires special surface preparation techniques.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting Teflon is about matching its specific strengths to the primary problem you need to solve.
- If your primary focus is reducing friction: Teflon is an elite choice for non-stick coatings, self-lubricating bearings, and low-wear seals.
- If your primary focus is chemical resistance: It is the go-to material for lining containers, pipes, and laboratory equipment exposed to corrosive agents.
- If your primary focus is insulation: Its thermal and electrical stability makes it ideal for high-performance wiring, connectors, and aerospace components.
- If your primary focus is biocompatibility: Its inert nature makes it a trusted material for medical implants and devices that require contact with human tissue.
Ultimately, Teflon's value comes from its ability to perform reliably where other materials fail.
Summary Table:
| Application Category | Key Teflon (PTFE) Property Leveraged | Common Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Industrial & Chemical Processing | Extreme Chemical Inertness | Liners for pipes, tanks, valves; labware |
| Machinery & Automotive | Extremely Low Coefficient of Friction | Self-lubricating bearings, seals, gaskets |
| Aerospace & Electronics | High Thermal & Electrical Resistance | Wire insulation, heat shields, connectors |
| Medical & Life Sciences | Biocompatibility & Purity | Catheters, surgical grafts, implants |
Need high-performance PTFE components tailored to your specific application?
At KINTEK, we specialize in the precision manufacturing of PTFE seals, liners, labware, and custom components. Whether you're in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, or industrial sector, we can help you leverage Teflon's unique properties to solve your most challenging design problems—from prototypes to high-volume production.
Contact our experts today to discuss your project requirements and discover how our custom PTFE solutions can benefit you.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Volumetric Flasks for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Use
People Also Ask
- Why are PTFE vials considered environmentally friendly? Reduce Lab Waste with Durable Reusables
- What are the unique properties of PTFE that make it commercially valuable? Unlock Unmatched Performance
- What are the common characteristics of Teflon? Unlocking Extreme Chemical and Thermal Resistance
- What makes the PTFE bottle durable? Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Stability for Demanding Applications
- Why is chemical compatibility important when choosing a PTFE-coated septum? Avoid Sample Contamination and Data Loss



















