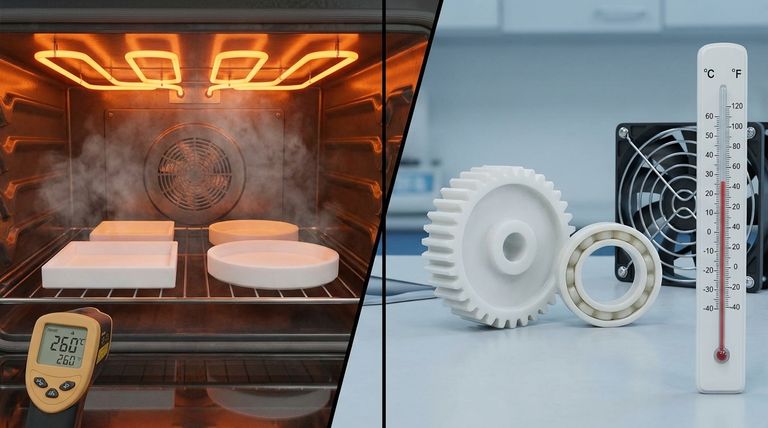
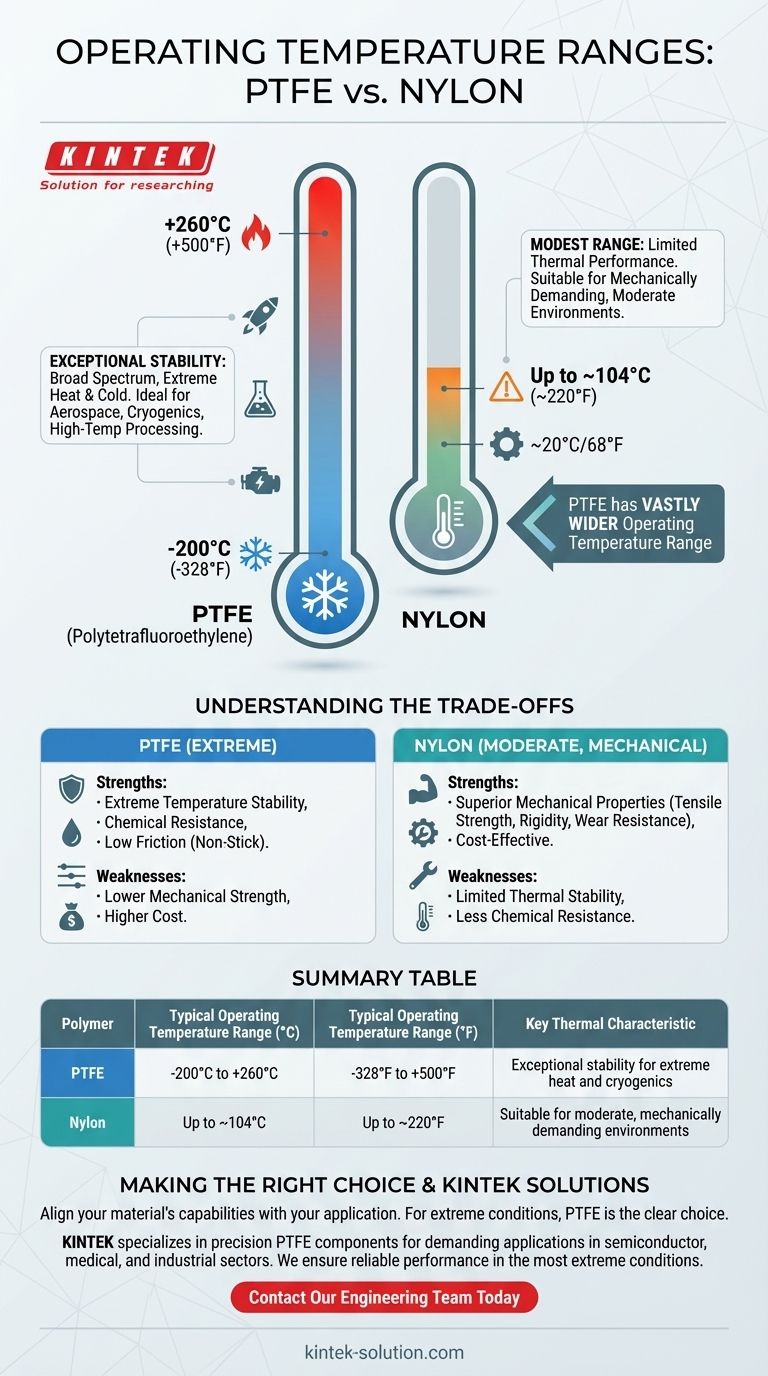
In short, PTFE has a vastly wider operating temperature range than nylon. PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) can reliably operate in environments from approximately -200°C to 260°C (-328°F to 500°F). In stark contrast, nylon's maximum continuous operating temperature is significantly lower, typically around 104°C (220°F), making it unsuitable for high-heat applications where PTFE excels.
The core difference is not just numerical; it's functional. PTFE is a specialty polymer engineered for extreme thermal stability, both hot and cold. Nylon is a workhorse engineering plastic valued for its mechanical properties within a much more conventional temperature range.

A Tale of Two Polymers: Thermal Performance
Your choice between PTFE and nylon is fundamentally dictated by the thermal demands of your application. One is built for extremes, while the other is designed for moderate, mechanically demanding environments.
PTFE's Exceptional Temperature Range
PTFE maintains its properties across an incredibly broad spectrum of temperatures. Its effective service range is generally accepted as -200°C to +260°C (-328°F to +500°F).
This stability makes it a default choice for applications involving cryogenic fluids, high-temperature processing, aerospace components, and demanding automotive systems.
The Source of PTFE's Stability
This thermal resilience stems from the powerful carbon-fluorine bonds that make up its molecular structure. These bonds are exceptionally strong and stable, requiring a great deal of thermal energy to disrupt.
Nylon's More Modest Range
Nylon's thermal performance is much more limited. It has a typical maximum continuous operating temperature of around 104°C (220°F).
Beyond this point, nylon will begin to lose its structural integrity and mechanical properties, making it unsuitable for applications that experience significant heat.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Temperature is only one part of the material selection equation. Choosing the right polymer requires balancing thermal needs with mechanical and economic realities.
Mechanical Strength vs. Thermal Stability
While PTFE dominates in temperature resistance, nylon often possesses superior mechanical properties at room temperature. It typically has better tensile strength, rigidity, and wear resistance.
If your application operates in a moderate climate and requires high durability against friction or impact, nylon is frequently the better choice.
The Impact of Cost
PTFE is a specialty material, and its manufacturing process is more complex than nylon's. Consequently, PTFE is almost always a more expensive material.
Choosing PTFE for an application that doesn't require its extreme temperature range is often an unnecessary expense.
Application Environment
Beyond temperature, consider the chemical environment. PTFE is famously inert and possesses a very low coefficient of friction (it's non-stick). This makes it invaluable for seals, gaskets, and linings in corrosive environments.
Nylon, while robust, does not share this level of chemical resistance or low-friction characteristic.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct material requires a clear understanding of your primary operational goal.
- If your primary focus is extreme temperature stability: PTFE is the clear and unambiguous choice for performance in both high-heat and cryogenic conditions.
- If your primary focus is mechanical strength and cost-effectiveness: Nylon is the superior and more economical option for general-purpose parts in moderate temperature environments.
- If your primary focus is chemical resistance or a non-stick surface: PTFE's unique properties make it the ideal selection, often justifying its higher cost.
By aligning your material's capabilities with your application's specific demands, you ensure both operational success and economic efficiency.
Summary Table:
| Polymer | Typical Operating Temperature Range (°C) | Typical Operating Temperature Range (°F) | Key Thermal Characteristic |
|---|---|---|---|
| PTFE | -200°C to +260°C | -328°F to +500°F | Exceptional stability for extreme heat and cryogenics |
| Nylon | Up to ~104°C | Up to ~220°F | Suitable for moderate, mechanically demanding environments |
Need High-Performance PTFE Components for Demanding Applications?
Selecting the right polymer is critical for your project's success. KINTEK specializes in manufacturing precision PTFE components—including seals, liners, and custom labware—for industries where thermal stability, chemical resistance, and non-stick properties are paramount.
We serve the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors with custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders. Let our expertise ensure your components perform reliably in the most extreme conditions.
Contact our engineering team today to discuss your specific requirements and receive a quote.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? Unlock Unmatched Performance in Demanding Applications
- What are the material advantages of machining Teflon? Unlock Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- What are the primary applications of PTFE fasteners and custom parts? Critical Solutions for Extreme Environments
- What are the base characteristics of PTFE? Unlocking Extreme Performance in Friction, Temperature, and Chemical Resistance
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications



















