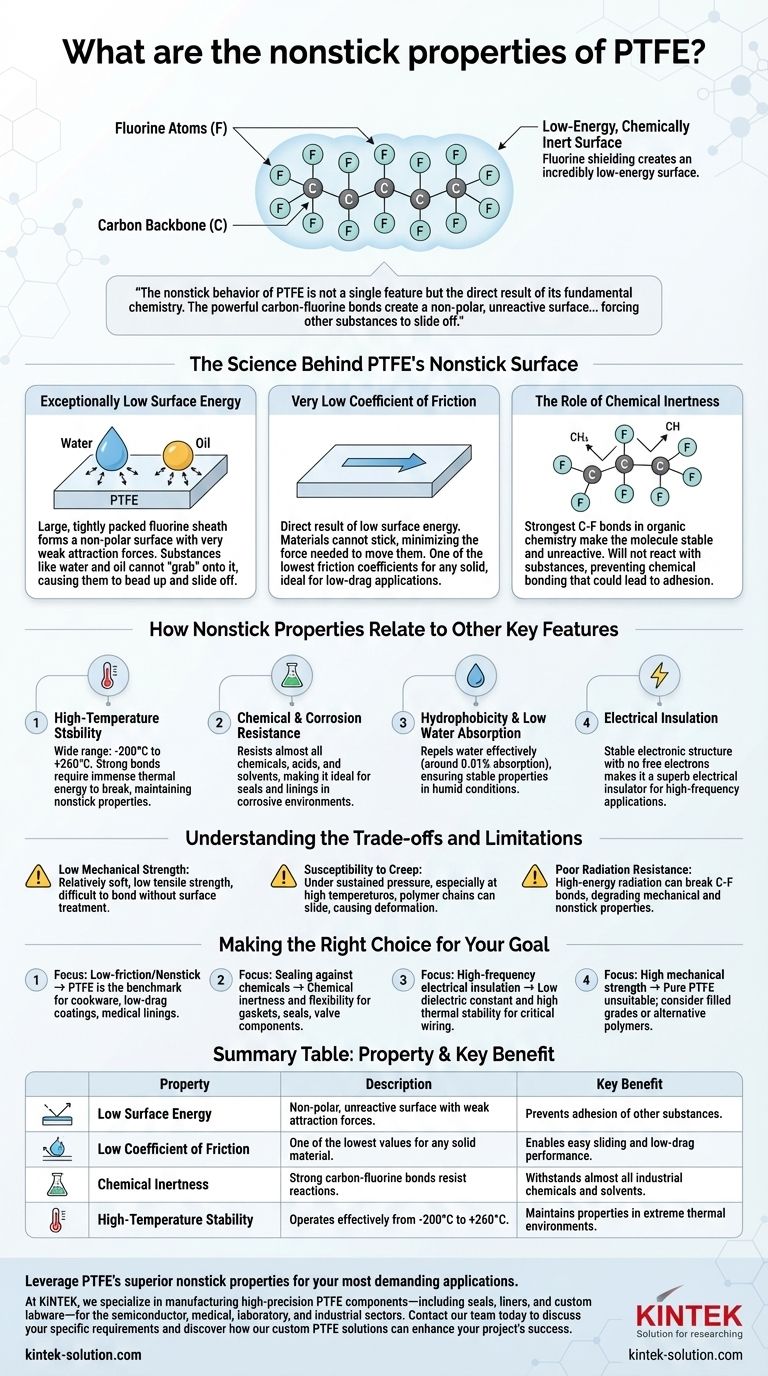
At its core, the exceptional nonstick property of Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) stems from its unique molecular structure. The polymer is composed of a carbon backbone completely shielded by fluorine atoms, which creates an incredibly low-energy, chemically inert surface that other materials simply cannot bond with or adhere to.
The nonstick behavior of PTFE is not a single feature but the direct result of its fundamental chemistry. The powerful carbon-fluorine bonds create a non-polar, unreactive surface with one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid, forcing other substances to slide off.
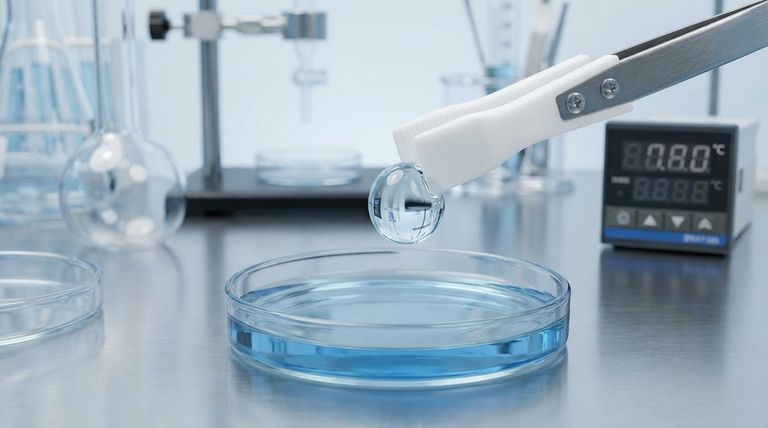

The Science Behind PTFE's Nonstick Surface
To understand PTFE's performance, we must look at the forces at play on a molecular level. Its nonstick nature is a direct consequence of two interconnected properties.
Exceptionally Low Surface Energy
The fluorine atoms bonded to the carbon chain are large and tightly packed, forming a protective "sheath." This sheath is electronically stable and non-polar, meaning it exhibits very weak attraction forces to other molecules.
Because adhesion requires some form of molecular attraction, substances like water, oil, and adhesives find nothing to "grab" onto, causing them to bead up and slide off easily.
Very Low Coefficient of Friction
This "slipperiness" is a direct result of its low surface energy. When materials cannot stick to a surface, the force required to move them across it is minimal.
PTFE possesses one of the lowest coefficients of friction known for any solid material, which is why it is used not only for nonstick coatings but also for high-performance bearings and low-friction industrial parts.
The Role of Chemical Inertness
The bond between carbon and fluorine is one of the strongest in organic chemistry. This makes the PTFE molecule remarkably stable and unreactive, or chemically inert.
It will not react with substances it contacts, preventing chemical bonding that could lead to adhesion. This inertness is why PTFE can withstand nearly all industrial chemicals and solvents.
How Nonstick Properties Relate to Other Key Features
The same molecular structure that creates PTFE's nonstick surface is also responsible for its other valuable industrial characteristics. Understanding this connection is key to leveraging the material effectively.
High-Temperature Stability
The immense strength of the carbon-fluorine bonds requires significant thermal energy to break. This allows PTFE to operate effectively in a very wide temperature range, typically from -200°C to +260°C, without degrading its nonstick properties.
Chemical and Corrosion Resistance
Its chemical inertness makes PTFE resistant to almost all chemicals, acids, and solvents. This makes it an ideal material for seals, gaskets, and linings in corrosive environments.
Hydrophobicity and Low Water Absorption
The non-polar surface that repels other materials is especially effective at repelling water. This results in extremely low water absorption (around 0.01%), ensuring its properties remain stable even in humid environments.
Electrical Insulation
The stable electronic structure of the C-F bonds means there are no free electrons to conduct electricity. This makes PTFE a superb electrical insulator with a high dielectric strength, ideal for high-frequency applications and wire coatings.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
No material is perfect. The same properties that make PTFE uniquely nonstick also introduce important limitations that must be considered in any engineering application.
Low Mechanical Strength
PTFE is a relatively soft material with low tensile strength and hardness. Its nonstick nature also makes it difficult to bond to other substrates without special surface treatments like chemical etching.
Susceptibility to Creep
Under sustained pressure, especially at elevated temperatures, the polymer chains can slide past one another. This phenomenon, known as creep, can cause the material to deform over time.
Poor Radiation Resistance
While resistant to UV light, high-energy radiation (like gamma rays) can break the strong carbon-fluorine bonds. This process degrades the polymer, compromising its mechanical and nonstick properties.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting a material requires aligning its properties with your primary objective. PTFE is an outstanding choice for specific applications but is not a universal solution.
- If your primary focus is a low-friction or nonstick surface: PTFE is the industry benchmark for applications like cookware, low-drag coatings, and medical device linings.
- If your primary focus is sealing against aggressive chemicals: Its chemical inertness and flexibility make it a superior choice for gaskets, seals, and valve components in chemical processing.
- If your primary focus is high-frequency electrical insulation: PTFE's low dielectric constant and high thermal stability make it ideal for coating critical wiring and electronic components.
- If your primary focus is high mechanical strength or abrasion resistance: Pure PTFE is likely unsuitable; you should consider filled PTFE grades or alternative high-performance polymers.
Ultimately, leveraging PTFE successfully depends on understanding that its celebrated nonstick surface is a direct outcome of its fundamental chemical stability.
Summary Table:
| Property | Description | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Low Surface Energy | Non-polar, unreactive surface with weak attraction forces. | Prevents adhesion of other substances. |
| Low Coefficient of Friction | One of the lowest values for any solid material. | Enables easy sliding and low-drag performance. |
| Chemical Inertness | Strong carbon-fluorine bonds resist reactions. | Withstands almost all industrial chemicals and solvents. |
| High-Temperature Stability | Operates effectively from -200°C to +260°C. | Maintains properties in extreme thermal environments. |
Leverage PTFE's superior nonstick properties for your most demanding applications. At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-precision PTFE components—including seals, liners, and custom labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether you need prototypes or high-volume production, our expertise ensures optimal performance and reliability. Contact our team today to discuss your specific requirements and discover how our custom PTFE solutions can enhance your project's success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech



















