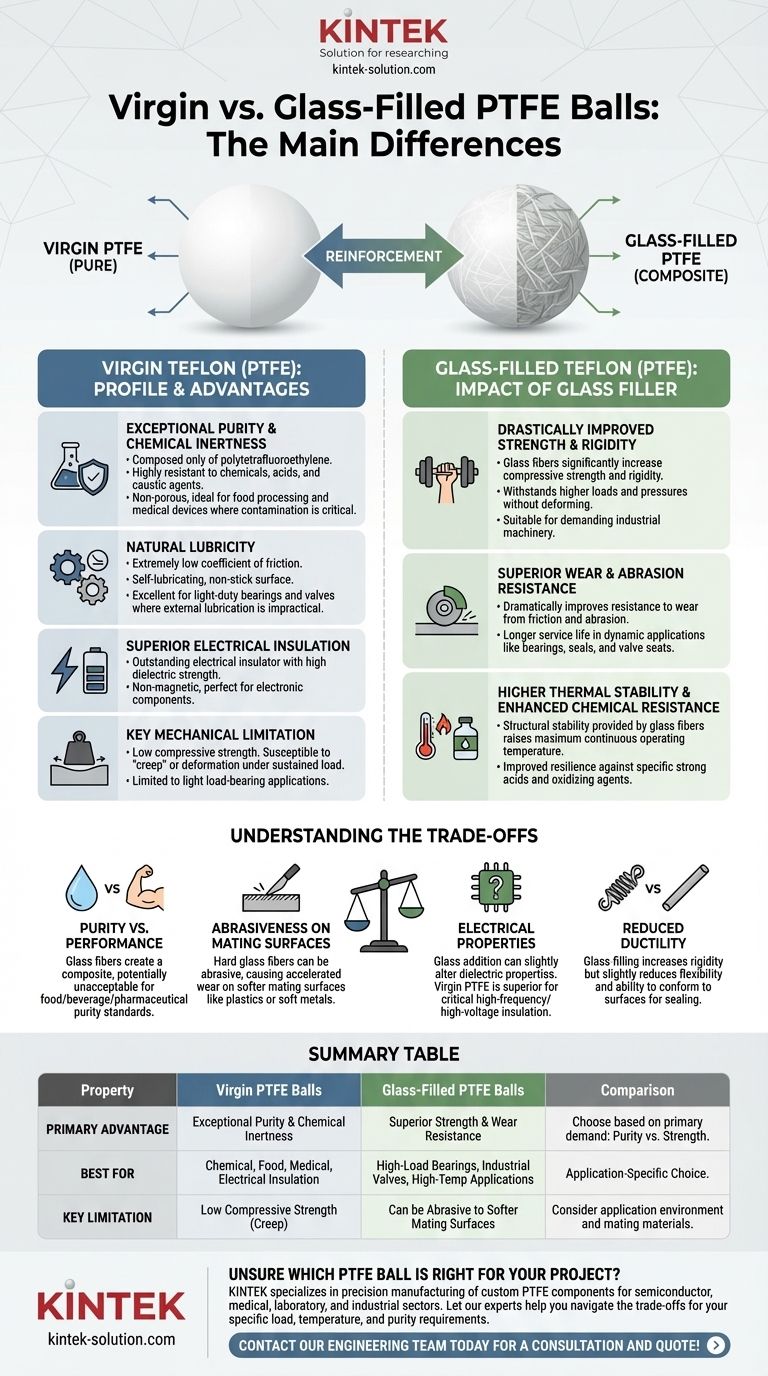
At its core, the primary difference is reinforcement. Virgin Teflon (PTFE) balls are made from pure, unfilled polytetrafluoroethylene, prized for its purity and natural lubricity. Glass-filled Teflon balls are a composite material where glass fibers are added to the PTFE base, dramatically enhancing the material's mechanical strength, wear resistance, and stability under load.
The choice between them is a classic engineering trade-off: select virgin PTFE for its exceptional purity, chemical inertness, and electrical insulation, or choose glass-filled PTFE for its superior strength, wear resistance, and performance in high-load, high-temperature applications.

The Profile of Virgin Teflon (PTFE)
Virgin PTFE is the foundation material, known for a unique set of properties that make it ideal for specific, controlled environments.
### Exceptional Purity and Chemical Inertness
Virgin PTFE is composed of only one ingredient: polytetrafluoroethylene. This purity makes it highly resistant to nearly all chemicals, acids, and caustic agents.
Because it is non-porous and inert, it is a preferred material for applications where contamination is a critical concern, such as in food processing or certain medical devices.
### Natural Lubricity
One of PTFE's most famous characteristics is its extremely low coefficient of friction, giving it a self-lubricating, non-stick surface.
This property is ideal for light-duty bearings, check valves, and any application where external lubrication is impractical or undesirable.
### Superior Electrical Insulation
As a pure polymer, virgin PTFE is an outstanding electrical insulator with a high dielectric strength.
This, combined with its non-magnetic nature, makes it a top choice for insulating components in electronic and electrical equipment.
### Key Mechanical Limitations
The primary drawback of virgin PTFE is its relative softness and low compressive strength.
It is susceptible to "creep" or deformation under a sustained load, which limits its use to light load-bearing applications.
The Impact of Glass Filler
Adding glass fibers transforms the performance profile of PTFE, creating a much more robust engineering material.
### Drastically Improved Strength and Rigidity
The glass fibers act as a reinforcing agent, significantly increasing the material's compressive strength and rigidity.
This enhancement allows glass-filled PTFE balls to withstand much higher loads and pressures without deforming, making them suitable for demanding industrial machinery.
### Superior Wear and Abrasion Resistance
Glass-filling dramatically improves the material's resistance to wear from friction and abrasion.
This results in a much longer service life in dynamic applications like bearings, seals, and valve seats that experience continuous movement.
### Higher Thermal Stability
While virgin PTFE has a high melting point, it begins to soften and deform under load at much lower temperatures.
Glass fibers provide structural stability, raising the material's maximum continuous operating temperature and making it more reliable in high-heat environments.
### Enhanced Chemical Resistance
Although virgin PTFE is already highly resistant, the addition of glass can improve its resilience against specific chemicals, particularly strong acids and oxidizing agents.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing glass-filled PTFE is not a simple upgrade; it involves specific compromises that must be considered for your application.
### Purity vs. Performance
The most obvious trade-off is purity. The presence of glass fibers makes the material a composite, which may not be acceptable for applications with strict purity standards, such as in the food, beverage, or pharmaceutical industries.
### Abrasiveness on Mating Surfaces
The hard glass fibers can be more abrasive than pure PTFE. If a glass-filled ball is used against a softer mating surface, such as a plastic or soft metal seat, it may cause accelerated wear on that component over time.
### Electrical Properties
While still a very good insulator, the addition of glass can slightly alter the dielectric properties of PTFE. For the most critical high-frequency or high-voltage electrical insulation applications, virgin PTFE remains the superior choice.
### Reduced Ductility
Virgin PTFE is known for its excellent ductility and flexibility, which makes it an exceptional sealing material that conforms well to surfaces. Glass-filling increases rigidity but slightly reduces this flexibility.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision should be driven entirely by the primary demands of your specific use case.
- If your primary focus is electrical insulation or material purity: Choose virgin PTFE for its unmatched dielectric properties and inert, single-material composition.
- If your primary focus is withstanding high loads or resisting mechanical wear: Choose glass-filled PTFE for its superior compressive strength and durability.
- If your primary focus is creating a low-friction seal for a soft mating surface: Choose virgin PTFE to prevent abrasion and take advantage of its natural lubricity and ductility.
- If your primary focus is performance in a high-temperature, high-pressure industrial valve: Choose glass-filled PTFE for its enhanced stability under thermal and mechanical stress.
By understanding that adding glass is a strategic reinforcement, you can confidently select the material that provides the precise performance your application requires.
Summary Table:
| Property | Virgin PTFE Balls | Glass-Filled PTFE Balls |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Advantage | Exceptional Purity & Chemical Inertness | Superior Strength & Wear Resistance |
| Best For | Chemical, Food, Medical, Electrical Insulation | High-Load Bearings, Industrial Valves, High-Temp Applications |
| Key Limitation | Low Compressive Strength (Creep) | Can be Abrasive to Softer Mating Surfaces |
Unsure which PTFE ball is right for your project? KINTEK specializes in the precision manufacturing of custom PTFE components, including seals, liners, and labware for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our experts can help you navigate the trade-offs between virgin and glass-filled PTFE to select the optimal material for your specific load, temperature, and purity requirements. We deliver from prototypes to high-volume orders with a focus on precision and performance.
Contact our engineering team today for a consultation and quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- How do PTFE balls contribute to reduced maintenance costs? Extend Component Life and Cut Downtime
- In which industries are Teflon (PTFE) balls commonly used? Key Applications & Benefits
- What temperature range can Teflon (PTFE) balls withstand? -200°C to +260°C Performance Guide
- What are the available grades of PTFE balls? Choose the Right Grade for Your Application
- What are the advantages of PTFE balls over metals or alloys? Superior Chemical & Friction Resistance



















