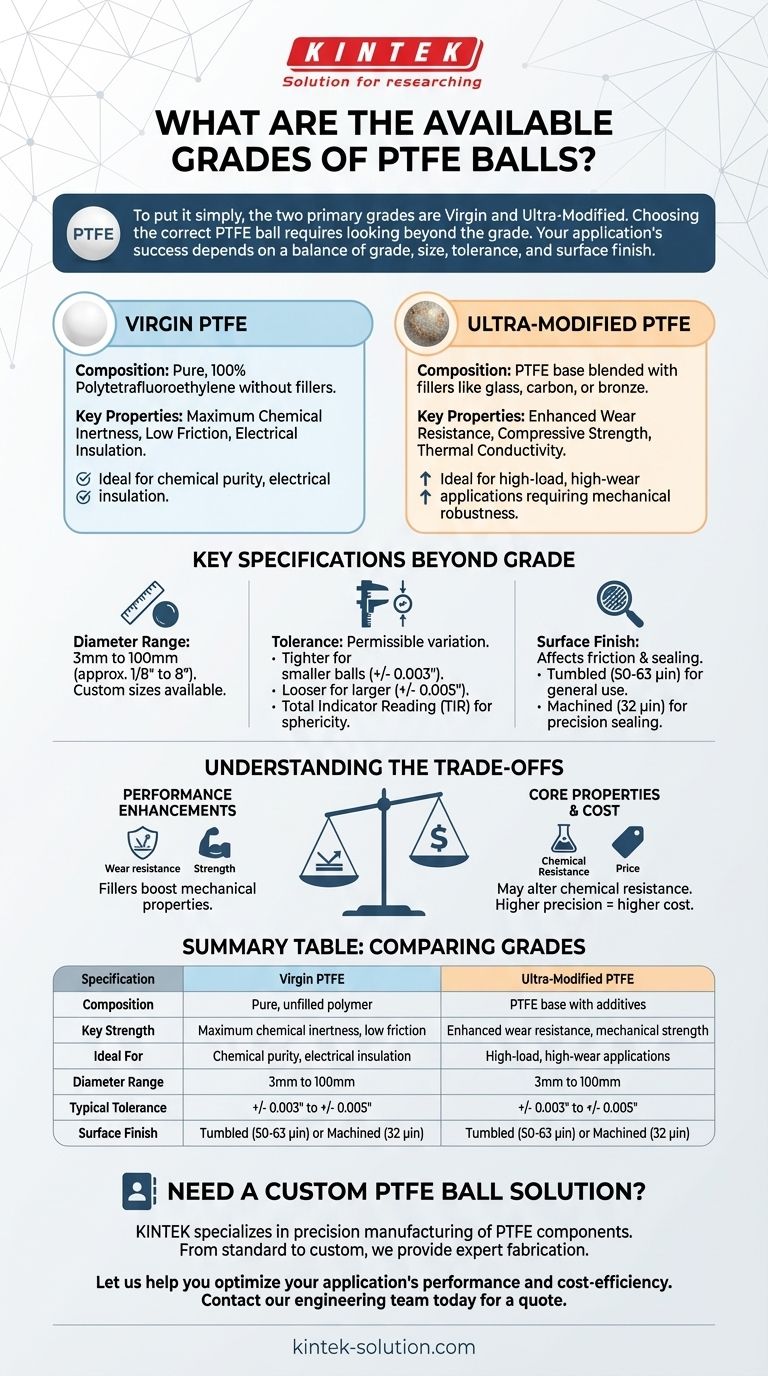
To put it simply, the two primary grades of PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) balls are Virgin and Ultra-Modified. Virgin PTFE is the pure, unfilled polymer known for its exceptional chemical resistance and low friction, while Ultra-Modified grades contain additives to enhance specific mechanical or thermal properties.
Choosing the correct PTFE ball requires looking beyond the material grade. Your application's success depends on a clear understanding of how grade, size, dimensional tolerance, and surface finish work together to meet specific performance demands.

Decoding PTFE Ball Grades
The "grade" of a PTFE ball refers to its material composition. This is the most fundamental choice, as it dictates the ball's inherent chemical and physical properties.
Virgin PTFE
Virgin grade is pure, 100% Polytetrafluoroethylene without any fillers. It represents the baseline for PTFE properties.
This grade is the ideal choice when maximum chemical inertness, low friction, and electrical insulation are the most critical requirements.
Ultra-Modified PTFE
Ultra-Modified grades consist of a PTFE base blended with fillers like glass, carbon, or bronze. These additives are introduced to improve specific characteristics.
For example, glass fillers can enhance wear resistance and compressive strength, while carbon can increase thermal conductivity. These grades are selected when an application demands more mechanical robustness than virgin PTFE can offer.
Key Specifications Beyond Grade
Once you've determined the appropriate grade, you must define the physical characteristics of the ball to ensure it fits and functions correctly within your assembly.
Diameter and Sizing
PTFE balls are available in a wide range of sizes, typically from 3mm to 100mm (or approximately 1/8" to 8").
While many common sizes are available from stock, large quantities or non-standard diameters can often be made-to-order for specific production needs.
Dimensional Tolerances
Tolerance defines the permissible limit of variation in a ball's diameter and roundness. This is a critical factor for precision applications like check valves or bearings.
As a general rule, smaller balls can be manufactured to tighter tolerances (e.g., +/- 0.003 inch). Larger balls often have slightly looser standard tolerances (e.g., +/- 0.005 inch).
Precision is also measured by Total Indicator Reading (TIR), which quantifies the ball's sphericity or roundness. A lower TIR value indicates a more perfectly spherical ball.
Surface Finish
The surface finish affects both the friction characteristics and the sealing capability of the ball.
A tumbled finish (around 50-63 microinches) is a standard, cost-effective option suitable for many general-purpose uses. A smoother machined finish (around 32 microinches) is specified for applications requiring a more precise surface for sealing or low-torque movement.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Every specification choice involves a balance between performance and cost. Understanding these trade-offs is key to avoiding over-engineering and unnecessary expense.
Cost vs. Precision
Higher precision comes at a price. Tighter dimensional tolerances and smoother, machined surface finishes require more manufacturing steps and increase the final cost of the ball.
Performance Enhancements vs. Core Properties
While fillers in Ultra-Modified grades boost properties like wear resistance, they can slightly alter the core characteristics of PTFE. For example, some fillers may subtly reduce the material's overall chemical resistance compared to the virgin grade.
This trade-off requires you to clearly identify the single most important performance characteristic for your specific application.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Use your primary engineering goal to guide your final specification.
- If your primary focus is chemical purity or biocompatibility: Specify Virgin PTFE, as it contains no additives.
- If your primary focus is mechanical strength or wear resistance: Select an Ultra-Modified grade with a filler designed for those properties.
- If your primary focus is precision flow control or sealing: Demand tight dimensional tolerances, a low TIR, and a machined surface finish.
- If your primary focus is general-purpose use at a low cost: A standard Virgin PTFE ball with a tumbled finish and standard tolerances is likely sufficient.
By carefully considering each of these factors, you can specify a PTFE ball that delivers reliable performance without unnecessary cost.
Summary Table:
| Specification | Virgin PTFE | Ultra-Modified PTFE |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Pure, unfilled polymer | PTFE base with additives (e.g., glass, carbon) |
| Key Strength | Maximum chemical inertness, low friction | Enhanced wear resistance, mechanical strength |
| Ideal For | Chemical purity, electrical insulation | High-load, high-wear applications |
| Diameter Range | 3mm to 100mm (custom sizes available) | 3mm to 100mm (custom sizes available) |
| Typical Tolerance | +/- 0.003" to +/- 0.005" | +/- 0.003" to +/- 0.005" |
| Surface Finish | Tumbled (50-63 µin) or Machined (32 µin) | Tumbled (50-63 µin) or Machined (32 µin) |
Need a Custom PTFE Ball Solution?
KINTEK specializes in the precision manufacturing of PTFE components, including seals, liners, and labware for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether you require a standard Virgin PTFE ball or a custom Ultra-Modified grade engineered for specific mechanical, thermal, or chemical demands, we provide expert fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders.
Let us help you optimize your application's performance and cost-efficiency. Contact our engineering team today to discuss your project requirements and receive a quote.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are PTFE balls made of and what are their key properties? Unlock Superior Chemical & Thermal Performance
- What are the common applications of PTFE balls? Leverage Unmatched Chemical Resistance & Low Friction
- What materials are used for PTFE balls? A Guide to Virgin PTFE vs. Filled Composites
- What are the key features of Teflon balls? Unlock Superior Performance in Demanding Environments
- What temperature range can PTFE balls withstand? Unlock Extreme Thermal Stability from -200°C to 260°C



















