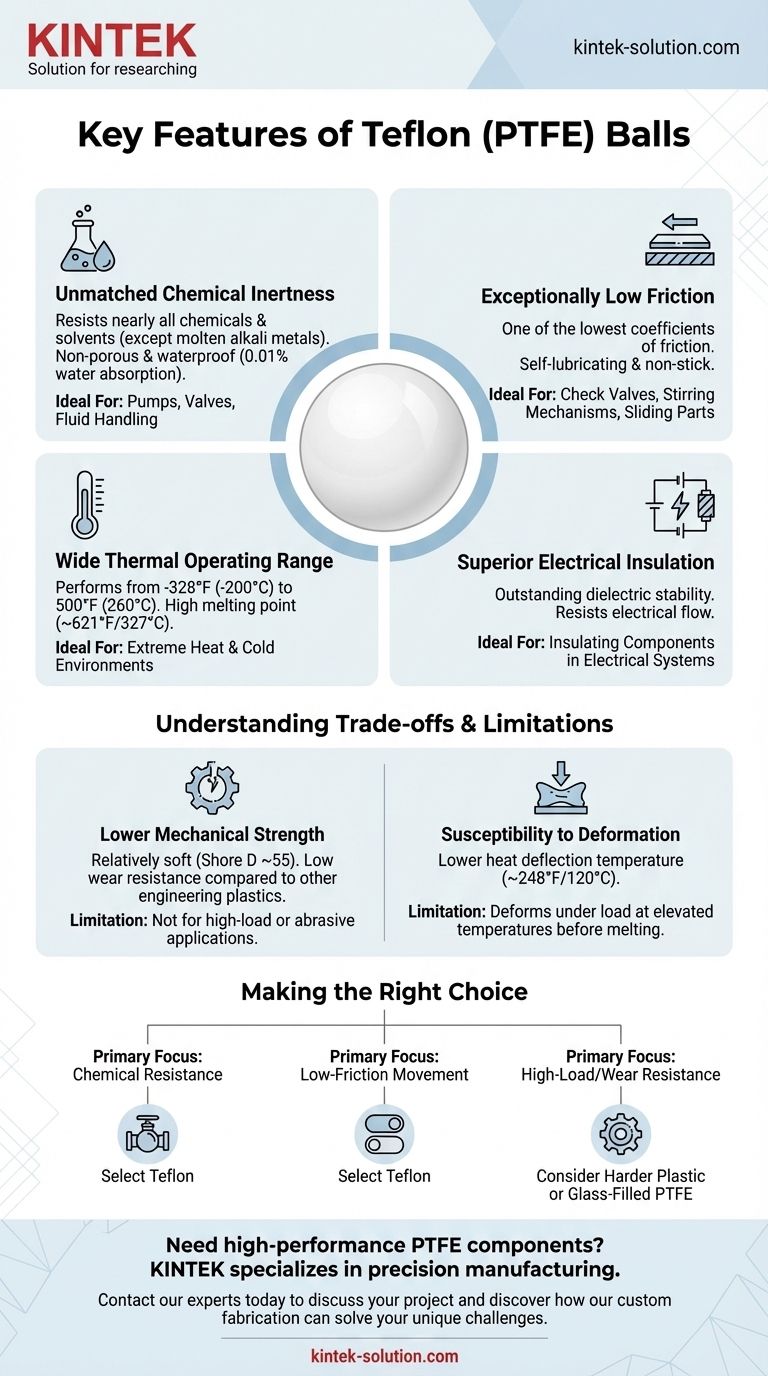
In short, Teflon (PTFE) balls are defined by four primary features: exceptional chemical resistance, an extremely low coefficient of friction, stability across a wide temperature range, and excellent electrical insulation. These properties make them a highly specialized material for demanding environments where other plastics would fail.
The core takeaway is that Teflon's unique combination of chemical, thermal, and electrical resistance makes it an elite material for specific applications. However, this performance comes with a significant trade-off: it is a soft material with lower mechanical strength and wear resistance compared to other engineering plastics.

The Defining Characteristics of PTFE Balls
To determine if Teflon is the right material for your project, it's essential to understand the practical implications of its core properties.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
Teflon is famously inert, meaning it resists reacting with nearly all industrial chemicals, solvents, and caustic agents. The only known substances that can chemically attack it are molten alkali metals.
This high level of resistance is complemented by its non-porous and waterproof nature. With a water absorption rate of just 0.01% over 24 hours, it is an ideal choice for components in fluid handling systems.
Exceptionally Low Friction
Teflon possesses one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid material, giving it a distinct "non-stick" quality.
This characteristic makes PTFE balls self-lubricating. They are excellent for applications requiring smooth, low-resistance movement without external lubricants, such as in check valves or stirring mechanisms.
Wide Thermal Operating Range
This material performs reliably in both extreme heat and cold. It maintains excellent flexibility at low temperatures and has a high melting point of around 621°F (327°C).
For practical applications, the continuous operating temperature can range from as low as -328°F (-200°C) to 500°F (260°C), particularly for filled grades.
Superior Electrical Insulation
PTFE is an outstanding electrical insulator with very good dielectric stability.
Its ability to resist the flow of electricity makes it a valuable material for insulating components in electrical devices and systems where high temperatures or chemical exposure are also a concern.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While its strengths are significant, Teflon is not a universally superior material. Acknowledging its limitations is critical for successful application.
Lower Mechanical Strength
The primary drawback of virgin PTFE is its low mechanical and wear resistance compared to other plastics like Nylon or PEEK. It is a relatively soft material with a Shore D hardness of around 55.
This softness means it can be easily scratched and is generally unsuitable for high-load or abrasive applications where structural integrity and durability are the top priorities.
Susceptibility to Deformation
While the melting point is high, its heat deflection temperature—the point at which it deforms under a specified load—is much lower, at around 248°F (120°C).
This means that in applications involving both heat and mechanical stress, the ball may deform long before it begins to melt.
Material Enhancements
To counteract its mechanical weaknesses, Teflon is often modified with fillers like glass or carbon. For example, a 25% glass-filled PTFE offers increased hardness, compressive strength, and a higher continuous operating temperature, though it may alter other properties like the friction coefficient.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right material depends entirely on the primary demands of your project.
- If your primary focus is chemical resistance: Teflon is an excellent choice for components in pumps, valves, and bearings that handle aggressive or corrosive fluids.
- If your primary focus is low-friction movement: It is ideal for non-load-bearing applications like check valves, toggle switches, and other sliding mechanisms.
- If your primary focus is high-load or wear resistance: Standard Teflon is likely unsuitable, and you should consider a harder plastic or a glass-filled PTFE variant.
Ultimately, Teflon's value lies in its ability to perform reliably where other materials simply cannot survive.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Key Benefit | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Inertness | Resists nearly all industrial chemicals and solvents. | Pumps, valves, and fluid handling systems. |
| Low Coefficient of Friction | Self-lubricating and non-stick. | Check valves, stirring mechanisms, and sliding parts. |
| Wide Thermal Range | Operates from -328°F to 500°F (-200°C to 260°C). | High and low-temperature environments. |
| Electrical Insulation | Excellent dielectric stability. | Electrical components exposed to heat or chemicals. |
| Limitation: Mechanical Strength | Softer than other plastics; consider filled grades for wear resistance. | Low-load applications; avoid high-stress or abrasive uses. |
Need high-performance PTFE components tailored to your exact specifications?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing precision PTFE components—including seals, liners, labware, and custom balls—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether you require a prototype or a high-volume order, our expertise ensures you get the right material solution for your demanding application.
Contact our experts today to discuss your project and discover how our custom fabrication can solve your unique challenges.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- What are the overall advantages of using PTFE balls in fluid management systems? Enhance Reliability & Efficiency
- How do PTFE balls contribute to reduced maintenance costs? Extend Component Life and Cut Downtime
- In which industries are Teflon (PTFE) balls commonly used? Key Applications & Benefits
- What are the key chemical properties of PTFE balls? Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Stability
- What are the available grades of PTFE balls? Choose the Right Grade for Your Application



















