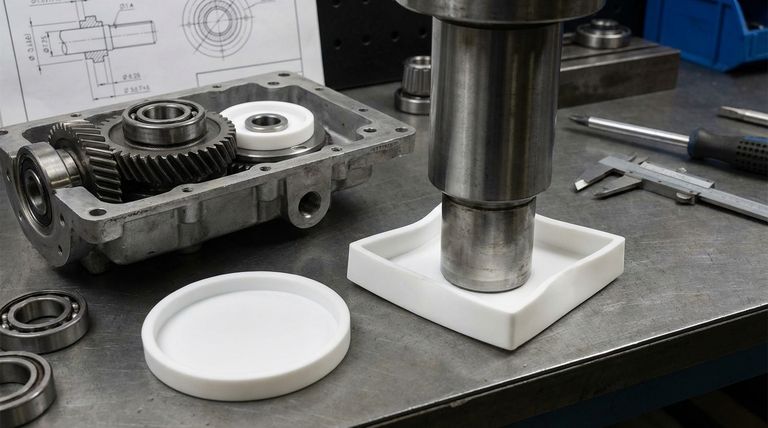
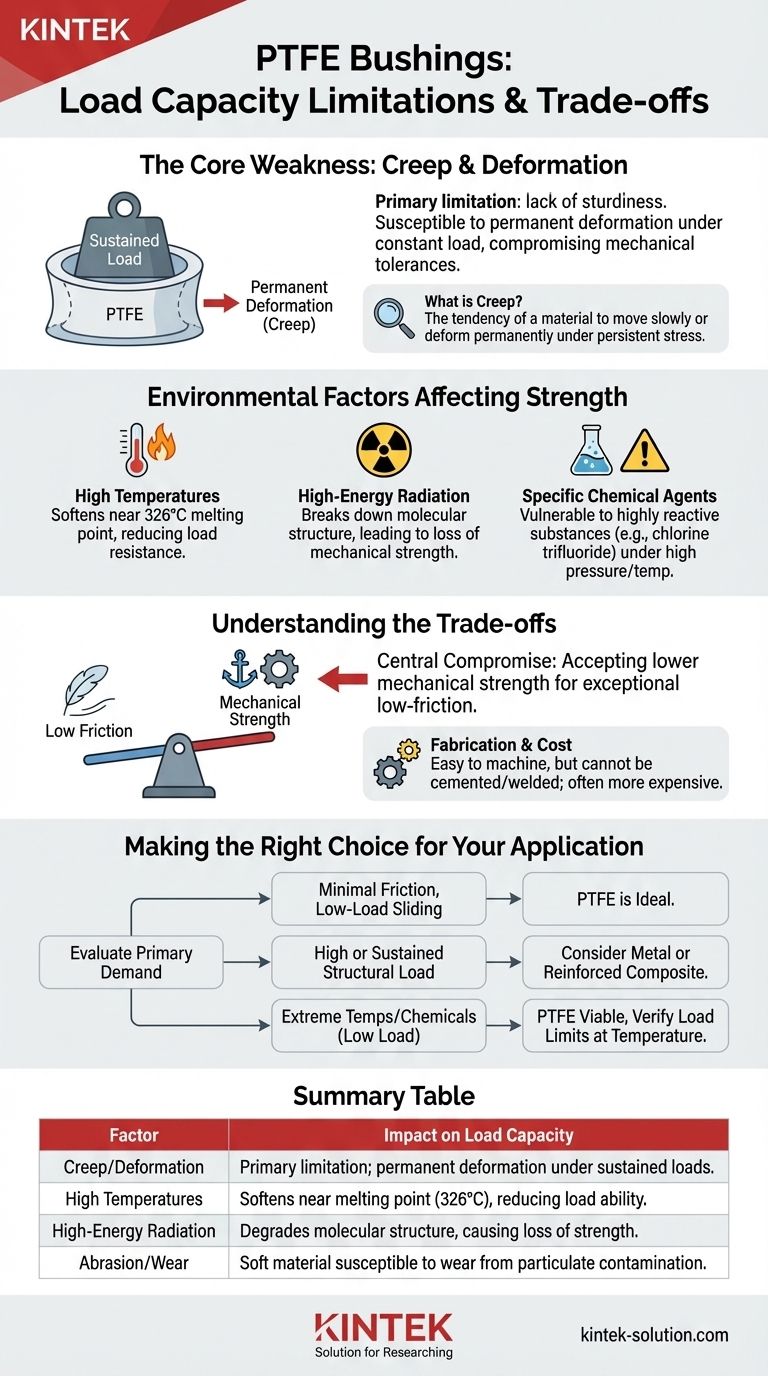
To be direct, the primary load capacity limitation of PTFE bushes is their inherent lack of sturdiness and susceptibility to deformation under pressure. While unmatched for low-friction applications, pure PTFE is a relatively soft material that can "creep" or permanently deform when subjected to a sustained or high load, making it unsuitable for structurally demanding roles.
The core trade-off with PTFE is accepting lower mechanical strength in exchange for its exceptional low-friction, chemical resistance, and wide temperature tolerance. Its load capacity is defined more by its resistance to deformation than its ultimate breaking strength.

The Core Weakness: Susceptibility to Creep and Deformation
The main reason PTFE bushes are not used in high-load scenarios is their poor resistance to a phenomenon known as creep. This is the central limiting factor you must consider.
What is "Creep"?
Creep is the tendency of a solid material to move slowly or deform permanently under the influence of persistent mechanical stresses.
Unlike metal bushings that might bend or break under extreme load, a PTFE bushing can slowly change shape under even a moderate but constant load over time.
This deformation compromises mechanical tolerances and can lead to premature failure of the assembly.
The Impact on Load-Bearing Applications
Because PTFE lacks rigidity, it is not a suitable choice for applications where maintaining precise dimensions under pressure is critical.
It is designed for sliding, not for structurally supporting significant weight. This makes it a poor substitute for metal bushings in high-pressure or heavy-duty machinery.
Environmental Factors Affecting Strength
While known for their resilience, certain environmental conditions can further degrade the already limited load-bearing capabilities of PTFE.
High Temperatures
PTFE has an excellent operational temperature range but will begin to lose its mechanical properties and soften as it approaches its melting point of 326°C.
This softening effect significantly reduces its ability to resist deformation under load.
High-Energy Radiation
PTFE has poor resistance to high-energy radiation, which can cause its molecular structure to break down. This degradation leads to a loss of mechanical strength and overall integrity.
Specific Chemical Agents
While famous for its chemical inertness, PTFE is vulnerable to a few rare and highly reactive substances.
These include agents like chlorine trifluoride and elementary fluorine, especially under high pressure and temperature, which can compromise the material.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting PTFE is a conscious decision to prioritize certain characteristics over others. Understanding these trade-offs is key to using the material correctly.
Strength vs. Low Friction
This is the central compromise. You are choosing a material with one of the lowest coefficients of friction available at the direct expense of mechanical strength and rigidity.
Fabrication and Cost
PTFE machines easily, which allows for precise shaping. However, it cannot be cemented or welded, limiting some assembly methods.
It is also generally more expensive than many other common polymers, which is a factor in mass production.
Abrasion and Wear
The softness that makes PTFE susceptible to creep also makes it sensitive to abrasion. In environments with hard particulate contamination, a PTFE bushing can wear more quickly than a harder metal alternative.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To determine if a PTFE bushing is appropriate, you must evaluate the primary demand of your design.
- If your primary focus is minimal friction in a low-load, sliding application: PTFE is an excellent and often ideal choice.
- If your primary focus is supporting a high or sustained structural load: You must consider a more rigid material, such as a metal bushing or a reinforced composite polymer.
- If your application involves extreme temperatures or harsh chemicals (but low loads): PTFE remains a strong contender, but you must verify the load is well within its deformation limits at the target temperature.
Choosing the right bushing means matching the material's inherent strengths to your application's specific demands.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on Load Capacity |
|---|---|
| Creep/Deformation | Primary limitation; PTFE permanently deforms under sustained loads. |
| High Temperatures | Softens near melting point (326°C), further reducing load-bearing ability. |
| High-Energy Radiation | Degrades molecular structure, causing loss of mechanical strength. |
| Abrasion/Wear | Soft material is susceptible to wear from particulate contamination. |
Need High-Performance PTFE Components That Balance Low Friction with Reliability?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing precision PTFE components—including seals, liners, and labware—for demanding industries like semiconductor, medical, and laboratory equipment. We understand the critical balance between PTFE's low-friction benefits and its mechanical limitations.
We provide:
- Custom Fabrication: From prototypes to high-volume orders, we engineer solutions tailored to your specific load, temperature, and chemical requirements.
- Expert Guidance: Our team helps you select or design the right component to avoid failure from creep or deformation.
- Quality Assurance: Precision production ensures consistent performance and longevity.
Let us help you optimize your application. Contact our experts today for a consultation on your PTFE component needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What is the working temperature range of PTFE? Master Extreme Heat and Cryogenic Applications
- What are the base characteristics of PTFE? Unlocking Extreme Performance in Friction, Temperature, and Chemical Resistance
- What are the key benefits of PTFE in custom fabrication? Unlock Performance in Extreme Conditions
- What are the material advantages of machining Teflon? Unlock Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications



















