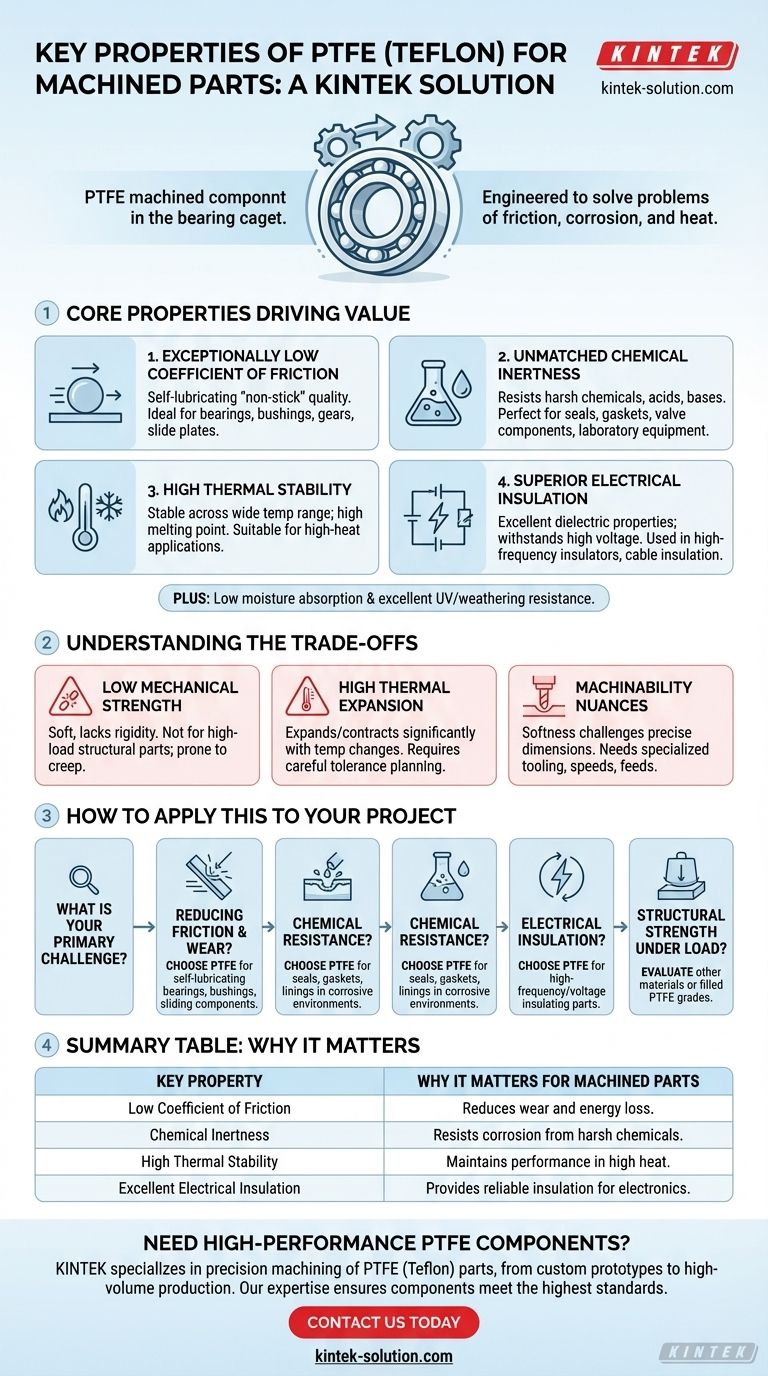
At its core, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), commonly known by the trade name Teflon, is suitable for machined parts due to a unique combination of four key properties: an exceptionally low coefficient of friction, near-total chemical inertness, high-temperature stability, and excellent electrical insulation. These characteristics allow it to perform reliably in demanding environments where most other materials would degrade or fail.
The decision to machine a part from PTFE is rarely about mechanical strength. Instead, it is a strategic choice for applications requiring extreme slipperiness, chemical resistance, and thermal stability—a material engineered to solve problems of friction, corrosion, and heat.

The Core Properties Driving PTFE's Value
To understand why PTFE is so frequently specified, we must examine the specific properties that make it a uniquely capable engineering plastic.
Exceptionally Low Coefficient of Friction
PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid material, giving it a characteristic "non-stick" or self-lubricating quality.
This makes it an ideal choice for components that must slide or rotate against other parts with minimal energy loss and wear.
Common applications leveraging this property include bearings, bushings, gears, and slide plates in mechanical systems.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
PTFE is non-reactive and resists degradation from the vast majority of industrial chemicals, acids, and bases.
This inertness ensures the material maintains its integrity even when in constant contact with corrosive substances.
As a result, it is heavily used for seals, gaskets, valve components, and laboratory equipment in the chemical and processing industries.
High Thermal Stability
PTFE parts remain stable and functional across a wide temperature range, with a relatively high melting point for a polymer.
This allows it to be used in high-temperature applications without losing its critical properties. It is also resistant to becoming brittle at low temperatures.
Superior Electrical Insulation
PTFE is an outstanding electrical insulator with excellent dielectric properties, meaning it does not conduct electricity and can withstand high voltages.
This characteristic is critical in the aerospace and electronics industries for parts like high-frequency insulators, cable insulation, and spacers.
Resistance to Environmental Factors
Beyond these primary traits, PTFE has very low moisture absorption, making it highly effective in wet or humid environments.
It also exhibits excellent resistance to weathering and degradation from UV light, ensuring long-term durability in outdoor applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While its properties are exceptional, PTFE is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is critical for successful application.
Low Mechanical Strength
PTFE is a relatively soft material. While it has high impact strength, it lacks the rigidity and tensile strength of other engineering plastics or metals.
Under a sustained load, especially at elevated temperatures, PTFE parts can be prone to "creep" or permanent deformation. It is not suitable for high-load structural components.
High Thermal Expansion
PTFE has a higher coefficient of thermal expansion than many other engineering materials.
This means it expands and contracts significantly with temperature changes, a factor that must be carefully accounted for when machining parts to tight tolerances.
Machinability Nuances
While PTFE is soft and easy to cut, its softness and thermal properties can make holding precise dimensions challenging without specialized techniques.
Proper tooling, speeds, and feeds are required to prevent material deformation and ensure an accurate final part.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Your choice of material must align directly with the primary challenge your component needs to overcome.
- If your primary focus is reducing friction and wear: PTFE is an elite choice for creating self-lubricating bearings, bushings, and sliding components.
- If your primary focus is chemical resistance: Use PTFE for seals, gaskets, and linings that will be exposed to corrosive chemicals.
- If your primary focus is electrical insulation: PTFE is a top-tier material for high-frequency and high-voltage insulating parts.
- If your primary focus is structural strength under load: You should evaluate other materials or consider filled grades of PTFE, as unfilled PTFE will likely deform.
Ultimately, selecting PTFE is a deliberate choice for its unique performance envelope, not as a general-purpose structural plastic.
Summary Table:
| Key Property | Why It Matters for Machined Parts |
|---|---|
| Low Coefficient of Friction | Creates self-lubricating parts like bearings and bushings that reduce wear and energy loss. |
| Chemical Inertness | Resists corrosion from harsh chemicals, ideal for seals, gaskets, and labware. |
| High Thermal Stability | Maintains performance across a wide temperature range, suitable for high-heat environments. |
| Excellent Electrical Insulation | Provides reliable insulation for high-voltage and high-frequency electronic components. |
Need high-performance PTFE components for your project?
At KINTEK, we specialize in precision machining of PTFE (Teflon) parts—from custom prototypes to high-volume production. Whether you're in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, or industrial sector, our expertise ensures your components meet the highest standards for chemical resistance, low friction, and thermal stability.
Contact us today to discuss your specific requirements and get a quote for your next project!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What challenges arise when machining PTFE (Teflon)? Overcome Softness, Heat, and Instability
- What industrial benefits do PTFE-machined parts offer? Achieve Peak Performance in Demanding Applications
- What fabrication services are available for PTFE? Shearing, Stamping, Laser Cutting, Molding & Machining
- What chemical processing applications involve PTFE-machined parts? Essential Components for Corrosive & High-Purity Systems
- What finishing techniques are effective for machined Teflon parts? Achieve Functional Performance and Dimensional Stability



















