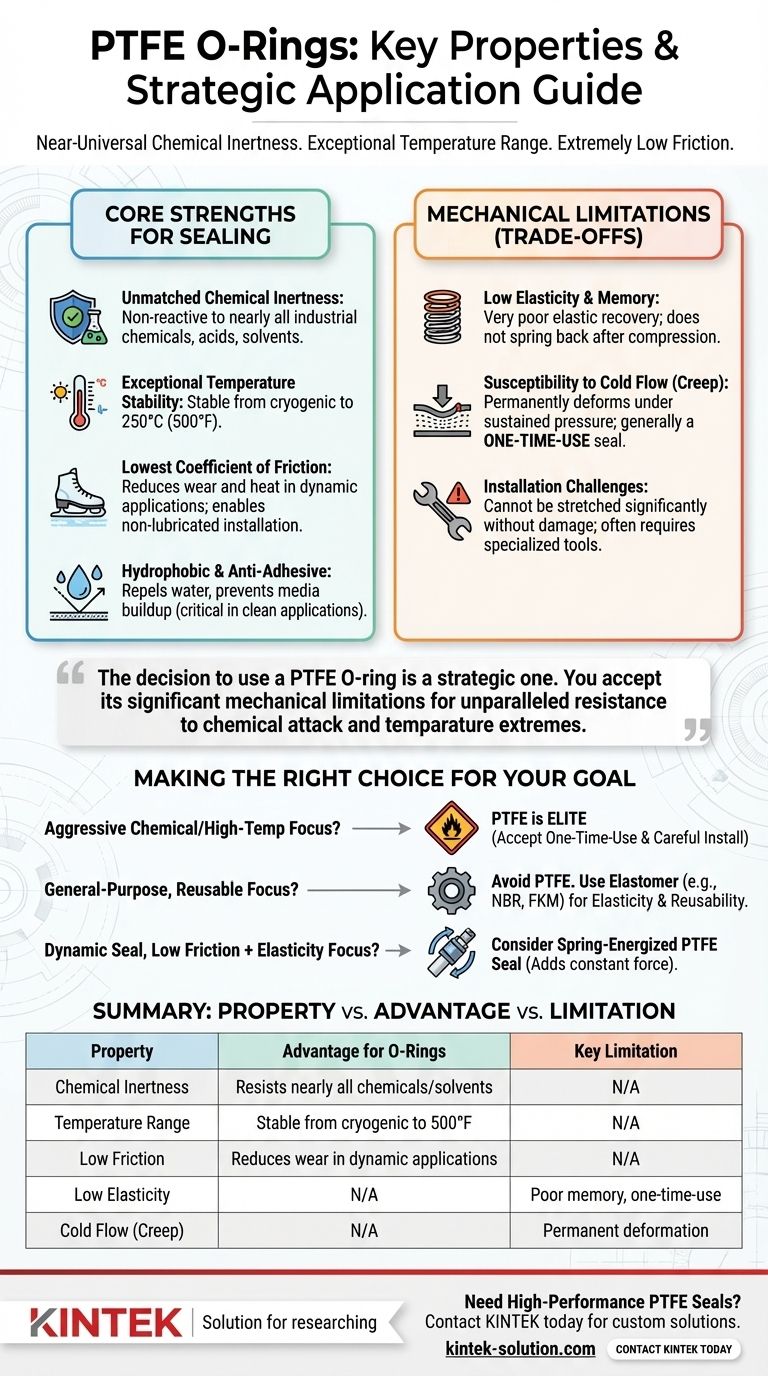
At its core, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is chosen for O-rings when performance in extreme environments is non-negotiable. Its primary properties are near-universal chemical inertness, an exceptionally wide operating temperature range, and an extremely low coefficient of friction. These traits allow it to function where common elastomer seals would quickly degrade and fail.
The decision to use a PTFE O-ring is a strategic one. You are choosing a material that offers unparalleled resistance to chemical attack and temperature extremes, but you must accept its significant mechanical limitations, namely its low elasticity and tendency to permanently deform under pressure.

The Core Strengths of PTFE for Sealing
To understand if PTFE is the right choice, we must first examine the specific properties that make it a high-performance sealing material.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
PTFE is non-reactive and inert to nearly all industrial chemicals, acids, and solvents.
This universal resistance prevents the O-ring from swelling, hardening, or degrading, ensuring the integrity of the seal when exposed to aggressive media.
Exceptional Temperature Stability
PTFE maintains its properties across a vast temperature range, from cryogenic lows to highs of around 250°C (500°F).
Where traditional rubber O-rings would become brittle or melt, PTFE remains stable and functional, making it essential for high-temperature processes.
The Lowest Coefficient of Friction
PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any known solid material, often compared to wet ice on wet ice.
This property reduces wear and heat generation in dynamic applications (like rotating shafts) and allows for easier, non-lubricated installation in static seals.
Hydrophobic and Anti-Adhesive Nature
The material is hydrophobic, meaning it repels water and does not absorb moisture.
Its anti-adhesive, or non-stick, surface also prevents process media from building up on the seal, which is critical in food, medical, and semiconductor applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs: The Mechanical Limitations
The unique strengths of PTFE are balanced by critical mechanical weaknesses. Ignoring these trade-offs is a common cause of seal failure.
Low Elasticity and Memory
Unlike rubber elastomers, PTFE has very poor elastic memory.
It does not spring back to its original shape effectively after being compressed. This can compromise its ability to maintain a consistent sealing force if flanges shift or vibrate.
Susceptibility to Cold Flow (Creep)
Under sustained pressure, PTFE will permanently deform, a phenomenon known as "cold flow" or "creep."
This is why PTFE O-rings are generally considered one-time-use seals. Once compressed and seated, they take a permanent set and will not reseal effectively if the joint is disassembled.
Installation Challenges
The low elasticity makes installation more difficult than with rubber O-rings.
PTFE seals cannot be stretched significantly over components without causing permanent damage. Specialized installation tools and careful handling are often required, especially for closed grooves.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct O-ring material requires matching its properties to the demands of your application.
- If your primary focus is sealing in aggressive chemical or high-temperature environments: PTFE is an elite choice, provided you can accommodate a one-time-use seal with careful installation.
- If your primary focus is a general-purpose, reusable seal for a standard application: Avoid PTFE. A standard elastomer like Nitrile (NBR) or Viton™ (FKM) will provide the necessary elasticity and reusability.
- If your primary focus is a dynamic seal requiring both low friction and elasticity: A standard PTFE O-ring may not suffice. Consider a spring-energized PTFE seal, which incorporates a metal spring to provide the constant force that the PTFE material lacks.
Understanding these distinct properties empowers you to select the right seal for the right application, ensuring reliability and performance.
Summary Table:
| Property | Advantage for O-Rings | Key Limitation |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Inertness | Resists nearly all chemicals, acids, and solvents | N/A |
| Temperature Range | Stable from cryogenic to 500°F (260°C) | N/A |
| Low Friction | Reduces wear in dynamic applications | N/A |
| Low Elasticity | N/A | Poor memory, one-time-use seal |
| Cold Flow (Creep) | N/A | Permanent deformation under pressure |
Need a High-Performance PTFE Seal for Your Application?
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing precision PTFE components, including O-rings, seals, and custom fabrications for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our expertise ensures your seals meet the exact demands of your environment, from aggressive chemicals to extreme temperatures.
We provide solutions from prototypes to high-volume orders, prioritizing precision and performance.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific sealing requirements and get a custom solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech



















