In short, the key properties of PTFE that make it ideal for labware are its extreme chemical inertness, its exceptionally wide operational temperature range, and its unique low-friction, non-stick surface. These three characteristics work together to create a material that can withstand the harshest laboratory conditions without degrading or interfering with experimental results.
The core reason PTFE is so trusted in scientific settings is not just its resistance to any single factor, but its unparalleled reliability across a wide spectrum of chemical, thermal, and physical stresses, ensuring the integrity of experiments.

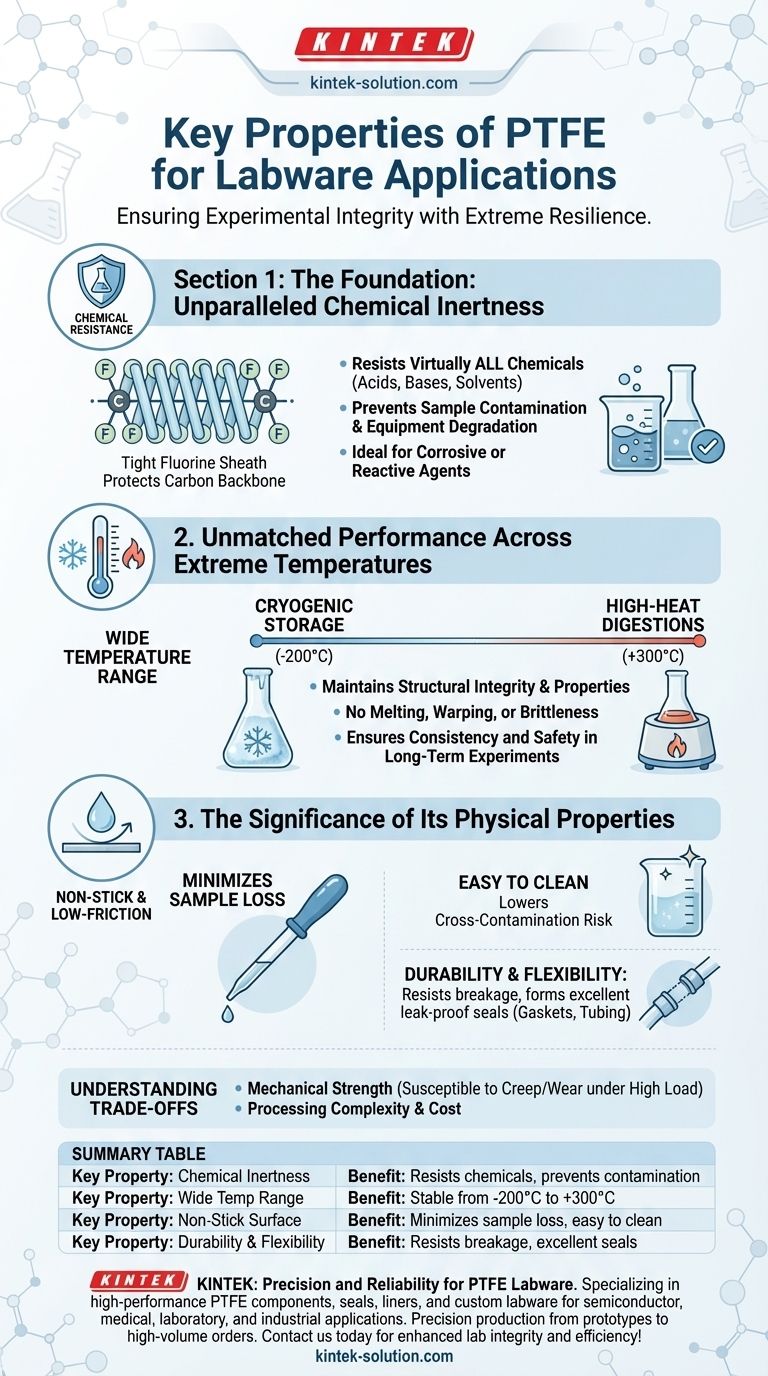
The Foundation: Unparalleled Chemical Inertness
The most legendary quality of Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is its ability to resist chemical attack. This property is not just a feature; it is the primary reason for its widespread adoption in demanding environments.
Why It Resists Virtually Everything
PTFE's inertness is a direct result of its molecular structure. It consists of a long chain of carbon atoms, but each carbon is completely sheathed by highly electronegative fluorine atoms.
This tight, helical "fluorine sheath" protects the vulnerable carbon-carbon backbone from attack by almost all chemicals, including aggressive acids, bases, and organic solvents.
The Practical Impact in the Lab
This chemical resistance is critical for lab work. It ensures that the labware itself does not react with the substances it holds, preventing both sample contamination and equipment degradation.
This makes PTFE the material of choice for containers, stir bars, and tubing used with highly corrosive or reactive agents where purity is paramount.
Unmatched Performance Across Extreme Temperatures
Beyond its chemical resilience, PTFE demonstrates remarkable stability across a vast range of temperatures, making it suitable for experiments involving both intense heating and deep cooling.
From Cryogenics to High Heat
PTFE maintains its structural integrity and properties over a temperature range of approximately -200°C (-390°F) to +300°C (+570°F).
This allows it to be used safely for applications ranging from cryogenic storage to high-temperature digestions, a versatility few other polymers can offer.
Ensuring Consistency and Safety
This thermal stability means the material will not melt, warp, or become brittle under conditions that would cause other plastics to fail. This reliability is crucial for the consistency of long-term experiments and the safety of lab personnel.
The Significance of Its Physical Properties
PTFE's physical characteristics provide further practical advantages that simplify lab work and improve the accuracy of results.
The Non-Stick, Low-Friction Surface
PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid, giving it an exceptionally slick and non-stick surface.
For labware like beakers and petri dishes, this minimizes the amount of sample that adheres to the surface, reducing loss during transfers. It also makes the equipment remarkably easy to clean, lowering the risk of cross-contamination between experiments.
Durability and Sealing
While not as rigid as glass, PTFE is highly durable, flexible, and does not break easily. This resilience reduces the risk of costly and dangerous breakage.
Its flexibility also allows it to form excellent seals, making it an ideal material for stopcocks, gaskets, and tubing connectors where a leak-proof fit is essential.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No material is perfect, and a complete technical understanding requires acknowledging PTFE's limitations.
Mechanical Strength and Creep
PTFE is a relatively soft material. Under high mechanical loads, especially at elevated temperatures, it can be susceptible to "creep" (slow deformation) and surface wear. It is not suitable for high-load structural applications.
Processing and Cost
The same properties that make PTFE so resilient—its high melting point and chemical inertness—also make it more difficult and costly to process and manufacture into complex shapes compared to more common polymers.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting PTFE is a decision to prioritize chemical and thermal resilience above all else.
- If your primary focus is handling highly corrosive agents: PTFE's chemical inertness is its most critical feature, ensuring no reaction or sample contamination.
- If your primary focus is applications with extreme temperature cycling: Its vast thermal range from -200°C to +300°C guarantees stability where other materials would fail.
- If your primary focus is quantitative analysis and sample purity: The non-stick surface minimizes sample loss and simplifies cleaning, reducing the risk of cross-contamination.
Ultimately, choosing PTFE labware is an investment in the reliability and integrity of your work.
Summary Table:
| Key Property | Benefit in Labware Applications |
|---|---|
| Chemical Inertness | Resists virtually all acids, bases, and solvents; prevents contamination and degradation. |
| Wide Temperature Range | Stable from -200°C to +300°C; suitable for cryogenics to high-heat processes. |
| Non-Stick, Low-Friction Surface | Minimizes sample loss, easy to clean, reduces cross-contamination. |
| Durability & Flexibility | Resists breakage and forms excellent seals for leak-proof connections. |
Need PTFE labware that guarantees precision and reliability? KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-performance PTFE components—including seals, liners, and custom labware—for semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial applications. We deliver precision production and custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders. Contact us today to discuss how our PTFE solutions can enhance your lab's integrity and efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Volumetric Flasks for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Use
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- What are the key benefits of PTFE in custom fabrication? Unlock Performance in Extreme Conditions
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- Why is PTFE suitable for cryogenic or high-temperature applications? Unmatched Thermal Stability from -450°F to 500°F
- What is PTFE commonly known as and what are its unique properties? Unlock Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? Unlock Unmatched Performance in Demanding Applications



















