At its core, machined Teflon (PTFE) is defined by a unique combination of extreme chemical inertness, an exceptionally low coefficient of friction, and superior electrical insulation. These core properties make it a premier choice for manufacturing critical components like seals, bearings, insulators, and linings across demanding industries such as aerospace, medical, and chemical processing.
Machined Teflon isn't just another plastic; it's a specialized engineering material chosen when performance under extreme chemical, thermal, or electrical stress is non-negotiable. Its value lies in its ability to function reliably where most other materials would fail.

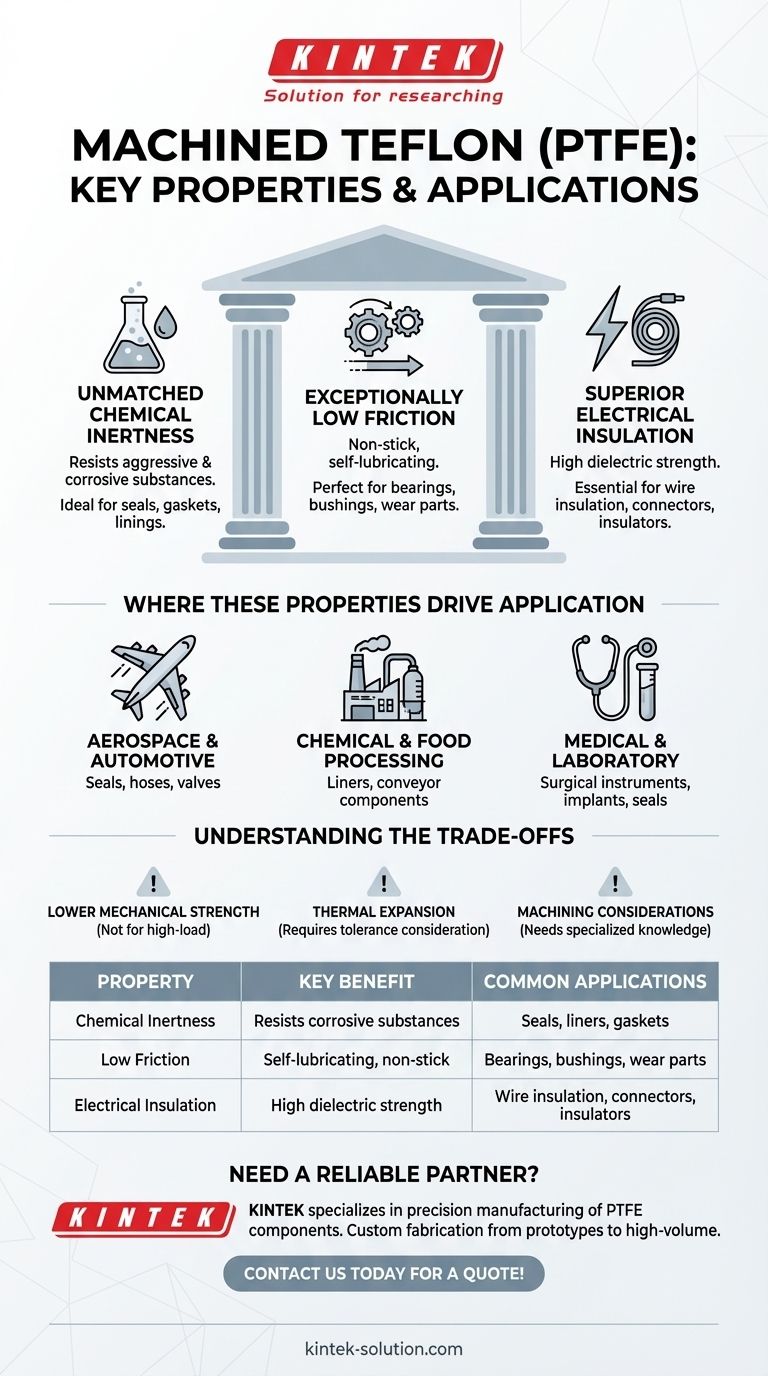
The Three Pillars of Teflon's Performance
To understand why Teflon is specified for such critical roles, we must look at the three properties that set it apart from virtually all other polymers.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
Teflon is famously non-reactive. It can withstand a vast range of aggressive and corrosive substances without degrading.
This chemical stability is why it's a go-to material for seals, gaskets, and linings in the chemical processing and aerospace industries, where components are constantly exposed to harsh fluids.
Exceptionally Low Friction
Teflon has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid material known, giving it its renowned non-stick and self-lubricating qualities.
This makes it ideal for bearings, bushings, and wear parts. In these applications, it reduces energy loss and eliminates the need for external lubricants, which is crucial in clean environments like food processing or hard-to-service machinery.
Superior Electrical Insulation
Teflon possesses a very high dielectric strength and a low dissipation factor, making it an outstanding electrical insulator.
Its insulating properties remain stable even at high temperatures and frequencies. This reliability makes it indispensable for wire insulation, connectors, and insulators in electronics and aerospace applications.
Where These Properties Drive Application
The combination of these core strengths allows machined Teflon to solve specific problems across a wide range of advanced industries.
In Aerospace and Automotive
In these sectors, reliability is paramount. Teflon is used for seals and hoses that handle aggressive fuels and hydraulic fluids.
Its wear resistance and low friction are leveraged in valves and bearings, while its insulating properties protect critical electrical systems from extreme temperature swings.
In Chemical and Food Processing
Here, purity and non-reactivity are the primary concerns. Teflon's inertness ensures it won't contaminate the products it touches.
Its non-stick surface makes it perfect for liners, seals, and conveyor components that require frequent, easy cleaning and must prevent material buildup.
In Medical and Laboratory Settings
Teflon is often selected for its biocompatibility and chemical stability. It will not react with bodily fluids or sensitive laboratory reagents.
This makes it a trusted material for surgical instruments, medical tubing, implants, and seals in scientific equipment where material integrity is critical.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No material is perfect. To use Teflon effectively, it's crucial to understand its limitations.
Lower Mechanical Strength
Teflon is a relatively soft material with low tensile strength compared to other engineering plastics. It is not suitable for high-load structural components.
Under sustained pressure, it can be susceptible to "creep," or slow deformation over time. This must be accounted for in component design.
Thermal Expansion
The material has a relatively high coefficient of thermal expansion. Engineers must factor this into designs that involve tight tolerances and will operate across a wide range of temperatures.
Machining Considerations
While machinable, Teflon's softness and thermal properties require specialized knowledge, sharp tooling, and specific techniques to achieve precise dimensions without causing deformation or internal stress.
Making the Right Choice for Your Project
Choosing Teflon is a decision driven by the specific demands of your application.
- If your primary focus is chemical resistance and purity: Teflon is an ideal choice for seals, liners, and components in corrosive or sanitary environments.
- If your primary focus is low friction and self-lubrication: It excels in applications for bearings, bushings, and sliding parts where external lubricants are impractical.
- If your primary focus is high-performance electrical insulation: Its dielectric properties make it a superior material for insulators, especially at high frequencies or wide temperature ranges.
- If your primary focus is high mechanical load or structural integrity: You should evaluate harder plastics or metals, as Teflon's relative softness is its key limitation.
By understanding both its unique strengths and its practical limitations, you can leverage machined Teflon to solve some of engineering's most demanding challenges.
Summary Table:
| Property | Key Benefit | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Inertness | Resists corrosive substances | Seals, liners, gaskets |
| Low Friction | Self-lubricating, non-stick | Bearings, bushings, wear parts |
| Electrical Insulation | High dielectric strength | Wire insulation, connectors, insulators |
Need a reliable partner for your machined Teflon components?
KINTEK specializes in precision manufacturing of PTFE components (seals, liners, labware, and more) for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We combine expert knowledge of Teflon's properties with custom fabrication services—from prototypes to high-volume orders—to deliver parts that perform reliably in your most demanding applications.
Contact us today to discuss your project requirements and get a quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the base characteristics of PTFE? Unlocking Extreme Performance in Friction, Temperature, and Chemical Resistance
- What is PTFE commonly known as and what are its unique properties? Unlock Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? Unlock Unmatched Performance in Demanding Applications
- Why is PTFE suitable for cryogenic or high-temperature applications? Unmatched Thermal Stability from -450°F to 500°F
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications



















