In short, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a high-performance fluoropolymer defined by an unmatched combination of properties. It is best known for its extreme chemical inertness, exceptional thermal stability over a wide temperature range, and the lowest coefficient of friction of any known solid material, which gives it its characteristic non-stick, or "slippery," surface.
The core value of PTFE is not any single attribute, but its unique ability to deliver elite performance across multiple domains simultaneously. It is the material of choice for applications where chemical, thermal, and surface properties must not be compromised, though this comes with specific mechanical trade-offs.

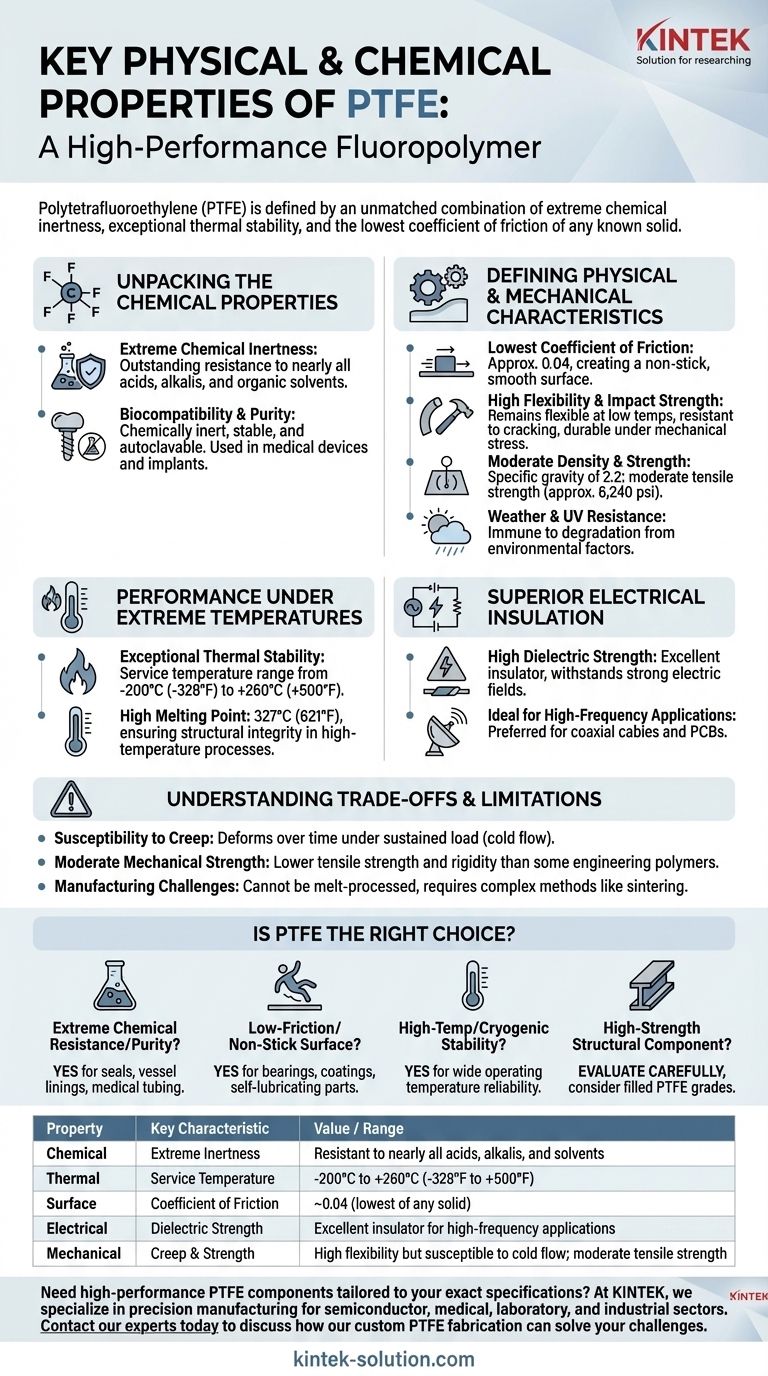
Unpacking the Chemical Properties
PTFE's chemical makeup, a strong carbon-fluorine bond, is the source of its most powerful characteristics. This molecular stability makes it almost universally non-reactive.
Extreme Chemical Inertness
PTFE offers outstanding resistance to nearly all industrial chemicals, including concentrated acids, alkalis, and organic solvents. This makes it an ideal choice for linings, seals, and gaskets in aggressive chemical processing environments.
Biocompatibility and Purity
Because it is chemically inert and stable, PTFE is highly biocompatible. This allows it to be used in medical devices and implants. It is also autoclavable, meaning it can be sterilized with steam, which is critical for medical and laboratory applications.
Defining the Physical & Mechanical Characteristics
While its chemical resilience is legendary, PTFE's physical properties are what enable its use in a vast range of mechanical and industrial applications.
The Lowest Coefficient of Friction
PTFE has a coefficient of friction of approximately 0.04, the lowest of any solid. This creates an incredibly smooth, non-stick surface ideal for low-wear bearings, gears, and non-stick coatings on cookware and industrial equipment.
High Flexibility and Impact Strength
Even at very low temperatures, PTFE remains highly flexible and resistant to cracking. It also possesses high impact strength, making it a durable material that can withstand significant mechanical stress without fracturing.
Moderate Density and Strength
PTFE is a relatively dense polymer with a specific gravity of 2.2. Its tensile strength is moderate, around 6,240 psi, meaning it is tough but not typically used for high-load structural applications on its own.
Weather and UV Resistance
The material is virtually immune to degradation from environmental factors like UV radiation and weathering. This ensures exceptional long-term performance in outdoor applications without becoming brittle or discolored.
Performance Under Extreme Temperatures
Few polymers can match PTFE's ability to perform reliably across such a vast spectrum of temperatures.
Exceptional Thermal Stability
PTFE maintains its properties over a very wide service temperature range, from cryogenic conditions at -200°C (-328°F) up to a continuous operating temperature of +260°C (500°F).
High Melting Point
With a high melting point of 327°C (621°F), PTFE far exceeds the thermal limits of most conventional plastics, ensuring its structural integrity in high-temperature processes.
Superior Electrical Insulation
PTFE is an exceptional electrical insulator, making it a critical component in the electronics and telecommunications industries.
High Dielectric Strength
Its high dielectric strength means it can withstand a strong electric field without breaking down. This property makes it perfect for insulating high-voltage wiring and components.
Ideal for High-Frequency Applications
Because it has excellent dielectric properties, PTFE is a preferred material for insulating high-frequency coaxial cables and manufacturing printed circuit boards (PCBs) used in radio frequency applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
To use PTFE effectively, it is critical to recognize its limitations. Its unique strengths are balanced by specific weaknesses that can be deal-breakers for certain applications.
Susceptibility to Creep
PTFE is prone to creep, or cold flow. Under a sustained compressive load, the material will slowly deform over time. This must be accounted for in the design of seals and structural parts.
Moderate Mechanical Strength
While durable, PTFE is not a high-strength plastic. It has lower tensile strength and rigidity compared to engineering polymers like PEEK or nylon, making it unsuitable for applications requiring high structural integrity.
Manufacturing Challenges
PTFE cannot be melt-processed using conventional techniques like injection molding. It must be processed through more complex methods like compression molding and sintering, which can increase manufacturing costs and design constraints.
Is PTFE the Right Choice for Your Application?
Choosing PTFE depends entirely on prioritizing its elite characteristics while respecting its mechanical limits.
- If your primary focus is extreme chemical resistance or purity: PTFE is an unparalleled choice for seals, vessel linings, and medical tubing where reactivity cannot be tolerated.
- If your primary focus is a low-friction, non-stick surface: It is the definitive material for high-performance bearings, self-lubricating parts, and advanced coatings.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature or cryogenic stability: Its incredibly wide operating temperature range ensures reliability where nearly all other polymers would fail.
- If your primary focus is a high-strength structural component: You should carefully evaluate its tendency to creep and consider alternative materials or filled PTFE grades to enhance mechanical properties.
By understanding both its exceptional capabilities and its practical limitations, you can leverage PTFE to solve some of the most demanding engineering challenges.
Summary Table:
| Property | Key Characteristic | Value / Range |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical | Extreme Inertness | Resistant to nearly all acids, alkalis, and solvents |
| Thermal | Service Temperature | -200°C to +260°C (-328°F to +500°F) |
| Surface | Coefficient of Friction | ~0.04 (lowest of any solid) |
| Electrical | Dielectric Strength | Excellent insulator for high-frequency applications |
| Mechanical | Creep & Strength | High flexibility but susceptible to cold flow; moderate tensile strength |
Need high-performance PTFE components tailored to your exact specifications?
At KINTEK, we specialize in the precision manufacturing of PTFE seals, liners, labware, and custom components. Whether you require prototypes or high-volume orders for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, or industrial sectors, we deliver solutions that leverage PTFE's elite properties while expertly managing its limitations.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our custom PTFE fabrication can solve your most demanding engineering challenges.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability
- Why is CNC machining preferred for Teflon parts over other methods? Unlock Precision & Complex Designs



















