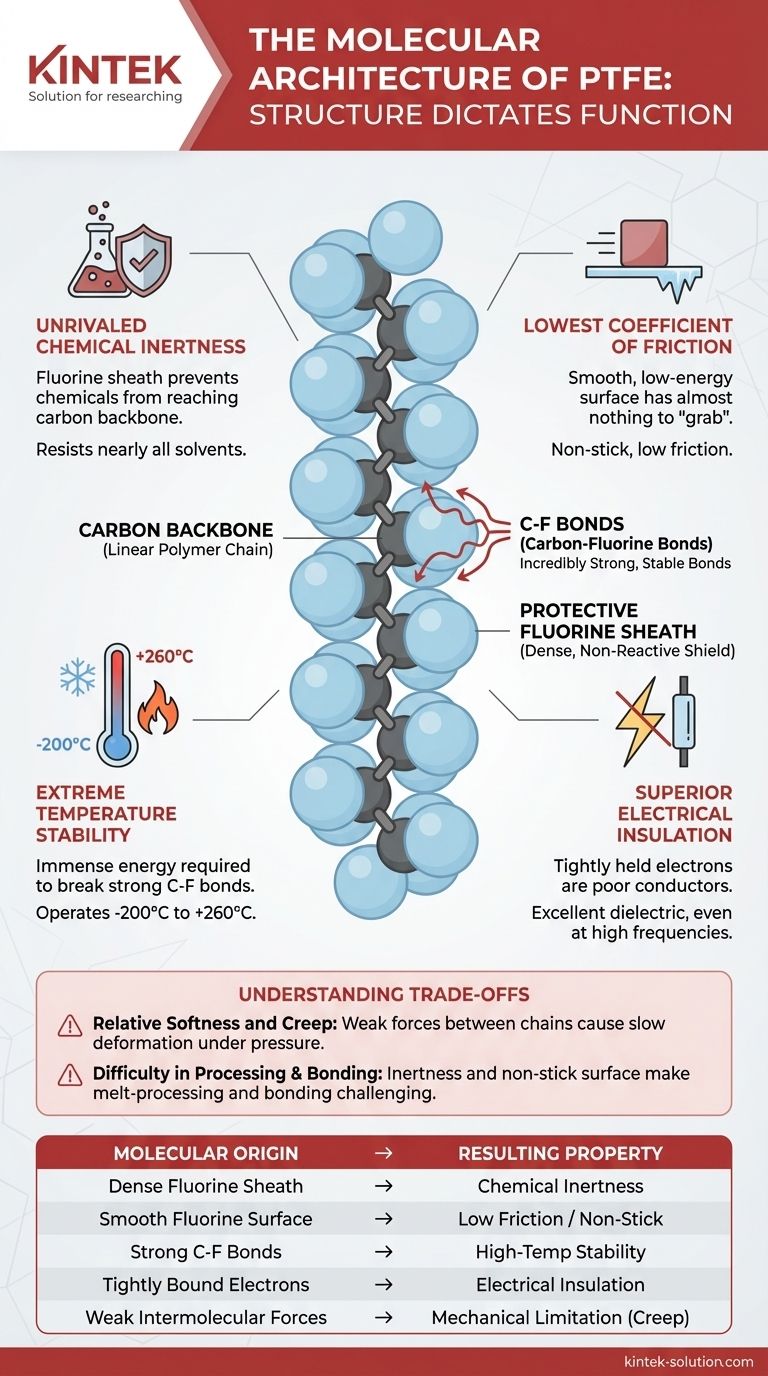
At its core, the molecular structure of Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a long, linear chain of carbon atoms, similar to a simple plastic. However, each carbon atom is completely surrounded by two fluorine atoms, which form a dense, protective, and non-reactive sheath around this carbon backbone. This unique arrangement is directly responsible for PTFE's famous properties.
The key to understanding PTFE is to visualize a simple carbon chain wrapped in a perfect, impenetrable armor of fluorine atoms. This fluorine sheath, held together by incredibly strong carbon-fluorine bonds, is the source of the material's extraordinary chemical inertness, temperature stability, and low-friction surface.

The Anatomy of a PTFE Molecule
To grasp why PTFE behaves the way it does, we must first examine its fundamental components. The simplicity of its design is the source of its complex and valuable characteristics.
The Carbon Backbone
The foundation of a PTFE molecule is a linear polymer chain of carbon-carbon bonds. This is the basic repeating structure, or "backbone," that gives the material its form.
The Protective Fluorine Sheath
This is the most critical feature. Each carbon atom in the backbone is bonded to two fluorine atoms. Because fluorine atoms are larger than carbon atoms, they pack tightly together, forming a continuous, uniform, and helical shield around the entire carbon chain.
The carbon-fluorine (C-F) bond is one of the strongest single bonds in organic chemistry. This immense strength is a primary reason for PTFE's stability.
High Molecular Weight and Crystallinity
PTFE molecules are characterized by a very high molecular weight, meaning the polymer chains are extremely long. This contributes to its physical toughness.
The material has a high degree of crystallinity, typically between 50% and 70% depending on processing, which means the long chains align themselves in an orderly, dense structure. By weight, PTFE is theoretically composed of 76% fluorine.
How Structure Dictates Function
Nearly every celebrated property of PTFE can be traced directly back to its molecular structure, particularly the fluorine sheath.
Unrivaled Chemical Inertness
The fluorine sheath provides a formidable barrier. It physically prevents chemicals from reaching and reacting with the vulnerable carbon backbone. Combined with the strength of the C-F bonds, this makes PTFE resistant to nearly all chemicals and solvents.
The Lowest Coefficient of Friction
The surface of the fluorine sheath is exceptionally smooth and has very low surface energy. Molecules have almost nothing to "grab" onto, causing them to slide off effortlessly. This is the mechanism behind its non-stick properties and extremely low friction.
Extreme Temperature Stability
A vast amount of thermal energy is required to break the powerful carbon-fluorine bonds and degrade the molecule. This is why PTFE maintains its properties across a massive temperature range, from –200°C to +260°C.
Superior Electrical Insulation
The electrons in the fluorine atoms are held very tightly, making them poor conductors of electricity. This stability makes PTFE an exceptional dielectric material, or electrical insulator, even at high frequencies and temperatures.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While its molecular structure provides incredible benefits, it also creates inherent limitations that are critical to understand.
Relative Softness and Creep
While the individual molecules are robust, the forces between the separate PTFE chains are relatively weak. This makes the bulk material soft and susceptible to "creep"—a tendency to slowly deform under sustained pressure.
Difficulty in Processing and Bonding
The same chemical inertness that makes PTFE so useful also makes it very difficult to work with. It cannot be easily melt-processed like other plastics, and its non-stick surface makes it nearly impossible to bond to other materials without special surface treatments like chemical etching.
Connecting Structure to Application
Your end goal dictates which aspect of PTFE's molecular structure is most important to your project.
- If your primary focus is chemical resistance: The impenetrable fluorine sheath makes PTFE the default choice for seals, gaskets, and linings used in harsh chemical environments.
- If your primary focus is low friction or non-stick surfaces: The low-energy surface created by the fluorine atoms is directly responsible for its use in non-stick cookware and low-friction bearings.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature electrical insulation: The strength and stability of the carbon-fluorine bond ensure reliable performance for wiring and components in demanding aerospace and industrial applications.
Understanding this elegant molecular architecture is the key to leveraging PTFE's unique capabilities in any application.
Summary Table:
| Key Characteristic | Molecular Origin | Resulting Property |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Inertness | Dense, protective sheath of fluorine atoms | Resists nearly all chemicals and solvents |
| Low Friction / Non-Stick | Smooth, low-energy surface of the fluorine sheath | Excellent release properties and low coefficient of friction |
| High-Temp Stability | Extremely strong carbon-fluorine (C-F) bonds | Stable from -200°C to +260°C |
| Electrical Insulation | Tightly bound electrons in fluorine atoms | Superior dielectric properties, even at high frequencies |
| Mechanical Limitation (Creep) | Weak intermolecular forces between polymer chains | Can deform under sustained pressure |
Ready to leverage PTFE's unique properties for your application?
At KINTEK, we specialize in precision manufacturing of high-performance PTFE components. Our deep understanding of PTFE's molecular structure allows us to produce seals, liners, labware, and custom parts that maximize its benefits—like supreme chemical resistance and thermal stability—for your specific needs in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
We offer custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders, ensuring you get the exact PTFE solution your project requires.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our PTFE components can solve your most challenging application problems.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What is PTFE commonly known as and what type of material is it? A Guide to High-Performance PTFE Properties
- How does PTFE react to common solvents? Discover Its Near-Total Chemical Immunity
- What are the additional properties of PTFE? Beyond Non-Stick: Extreme Chemical, Thermal & Electrical Performance
- What is Teflon and what is its chemical name? Unpacking the Science of PTFE
- What is PTFE and what class of plastics does it belong to? A Guide to High-Performance Fluoropolymers



















