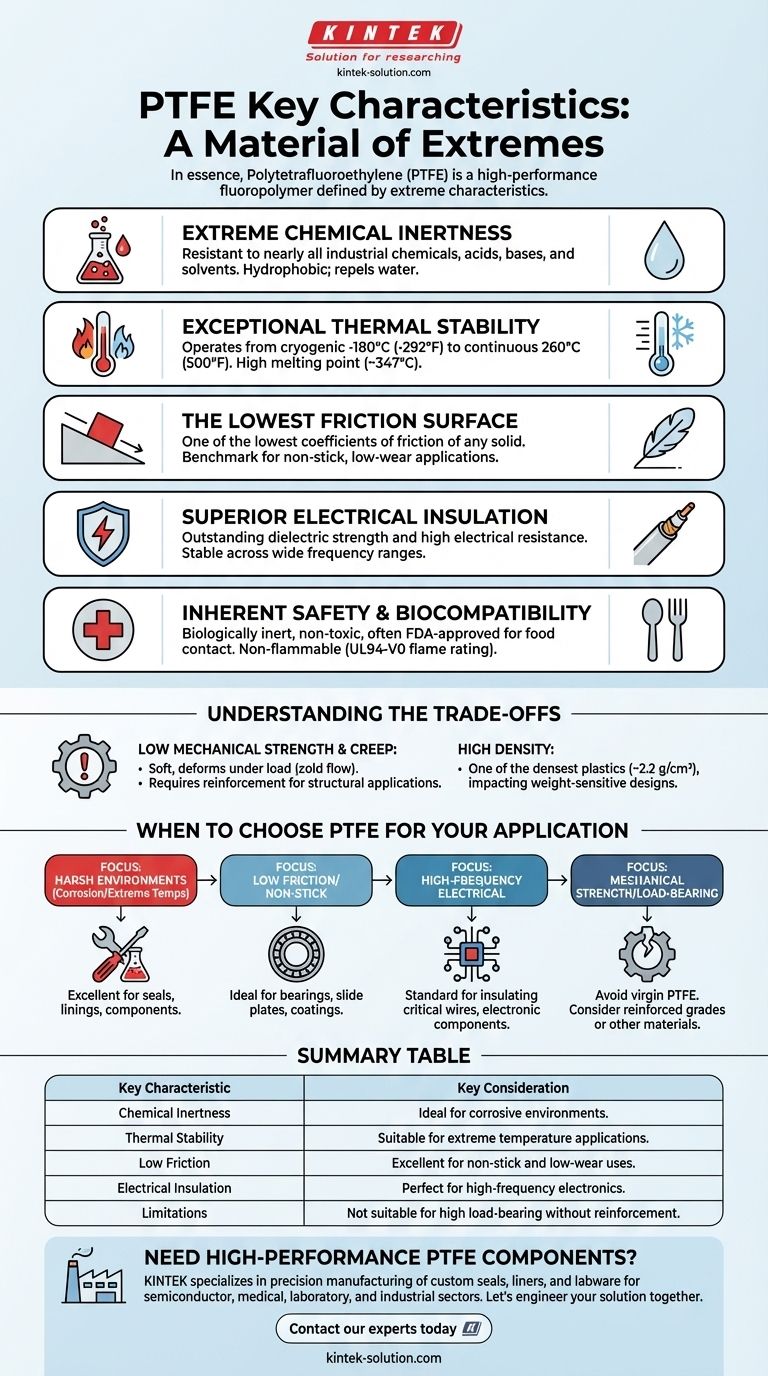
In essence, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a high-performance fluoropolymer defined by a unique combination of extreme characteristics. It is most famous for its exceptional chemical inertness, stability across a vast range of temperatures, superior electrical insulation, and one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any known solid material, making it incredibly non-stick and slippery.
The core takeaway is that PTFE is a material of extremes. It provides unparalleled performance in harsh chemical, thermal, and high-frequency electrical environments where low friction is critical, but this specialization comes at the cost of low mechanical strength, which must be a primary consideration in any design.

Unpacking the Core Properties of PTFE
PTFE's molecular structure—a long chain of carbon atoms completely shielded by fluorine atoms—is the source of its remarkable and highly specialized set of properties.
Extreme Chemical Inertness
The strong carbon-fluorine bonds make PTFE almost universally inert. It is highly resistant to nearly all industrial chemicals, acids, bases, and solvents, even at elevated temperatures.
This property also makes it hydrophobic, meaning it repels water and water-based substances, preventing moisture absorption.
Exceptional Thermal Stability
PTFE operates effectively across an incredibly broad temperature range, from cryogenic lows of -180°C (-292°F) up to continuous service temperatures of 260°C (500°F).
It maintains high flexural strength and flexibility even at very low temperatures and possesses a high melting point of around 347°C (657°F), ensuring stability in demanding heat applications.
The Lowest Friction Surface
PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid material, making it the benchmark for non-stick and low-wear applications.
This inherent lubricity is why it's used for everything from non-stick cookware coatings to self-lubricating bearings and seals.
Superior Electrical Insulation
This material is an outstanding electrical insulator with high dielectric strength and high electrical resistance.
Its electrical properties are remarkably stable across wide frequency and temperature ranges, making it an ideal choice for high-frequency applications like coaxial cable insulation.
Inherent Safety and Biocompatibility
PTFE is biologically inert, non-toxic, and often FDA-approved for food contact applications, making it safe for use in food processing and medical devices.
Furthermore, it is non-flammable and has a UL94-V0 flame rating, meaning it resists ignition and does not promote flame spread.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While its specialized properties are exceptional, PTFE is not a universally ideal material. Understanding its limitations is critical for successful implementation.
Low Mechanical Strength
The most significant trade-off of using PTFE is its relatively low mechanical strength, rigidity, and creep resistance, especially when compared to other engineering plastics.
It is soft and can deform under load, a characteristic known as creep or cold flow. This limits its use in applications that require high structural integrity or load-bearing capabilities without reinforcement.
High Density
PTFE is one of the densest plastics, with a density of up to 2.2 g/cm³.
This high density can be a disadvantage in applications where minimizing weight is a primary design goal.
When to Choose PTFE for Your Application
Selecting PTFE is about matching its unique strengths to the specific demands of your project. Use this as a guide to your decision-making.
- If your primary focus is survival in harsh environments: PTFE is an excellent choice for seals, linings, and components exposed to corrosive chemicals or extreme temperatures.
- If your primary focus is low friction or non-stick surfaces: It is the ideal material for high-performance bearings, slide plates, and coatings where minimal friction is essential.
- If your primary focus is high-frequency electrical performance: Its stable dielectric properties make it the standard for insulating critical wires, cables, and electronic components.
- If your primary focus is mechanical strength or load-bearing: You should avoid using virgin PTFE and instead consider reinforced grades or an entirely different material.
Ultimately, leveraging PTFE successfully means designing to its unparalleled thermal, chemical, and frictional strengths while accommodating its inherent mechanical softness.
Summary Table:
| Key Characteristic | Description | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Inertness | Resistant to nearly all chemicals, acids, and solvents. Hydrophobic. | Ideal for corrosive environments. |
| Thermal Stability | Operates from -180°C to 260°C. High melting point (347°C). | Suitable for extreme temperature applications. |
| Low Friction | One of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid. | Excellent for non-stick and low-wear uses. |
| Electrical Insulation | Superior dielectric strength, stable across frequencies and temperatures. | Perfect for high-frequency electronics. |
| Limitations | Low mechanical strength, prone to creep, and high density. | Not suitable for high load-bearing applications without reinforcement. |
Need High-Performance PTFE Components?
PTFE's unique properties make it the ideal material for demanding applications in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. However, designing with it requires expert knowledge to leverage its strengths and mitigate its limitations.
KINTEK specializes in the precision manufacturing of PTFE components—including custom seals, liners, and labware. We work with you from prototype to high-volume production to ensure your parts excel in harsh chemical, thermal, and electrical environments.
Let's engineer your solution together. Contact our experts today for a consultation on your specific requirements.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Volumetric Flasks for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Use
People Also Ask
- What is PTFE commonly known as and what are its unique properties? Unlock Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- What are the key benefits of PTFE in custom fabrication? Unlock Performance in Extreme Conditions
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? Unlock Unmatched Performance in Demanding Applications
- What are the base characteristics of PTFE? Unlocking Extreme Performance in Friction, Temperature, and Chemical Resistance
- What are the material advantages of machining Teflon? Unlock Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance



















