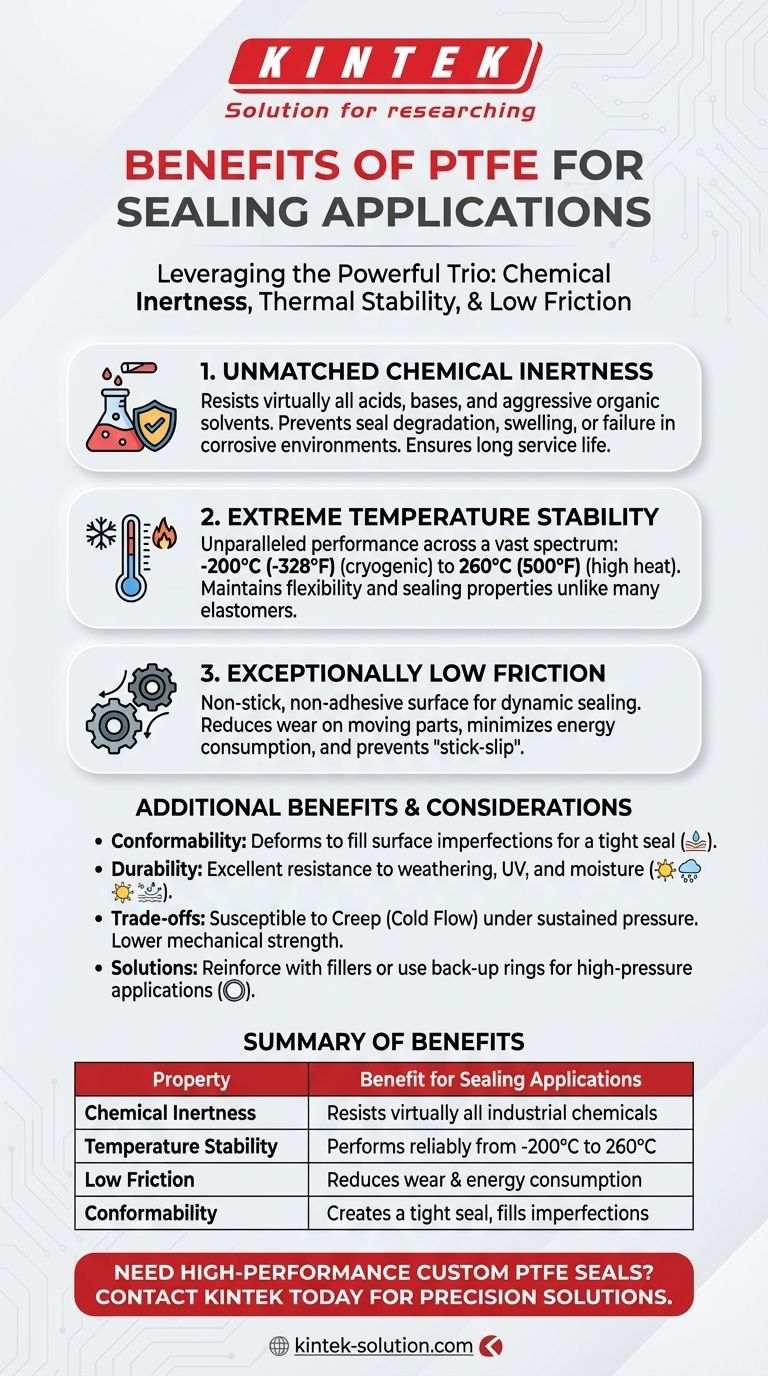
The primary benefits of using PTFE for sealing applications stem from its unique combination of three core properties: exceptional chemical resistance, an incredibly wide operating temperature range, and an extremely low coefficient of friction. This powerful trio makes Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) a definitive material choice for preventing leaks and ensuring operational integrity in the most demanding industrial environments, from chemical processing to aerospace.
The true value of PTFE isn't just one single benefit, but how its unique molecular structure delivers a combination of chemical inertness, thermal stability, and a low-friction surface. This allows it to solve sealing challenges where most conventional elastomers would quickly fail.

The Core Properties Driving PTFE's Performance
PTFE's effectiveness as a sealing material is a direct result of its unique molecular structure: a long chain of carbon atoms completely shielded by fluorine atoms. The powerful carbon-fluorine bond is the source of its remarkable stability.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
PTFE is virtually inert to almost all industrial chemicals, including strong acids, bases, and aggressive organic solvents. This prevents the seal from degrading, swelling, or failing when exposed to corrosive media, ensuring a long and reliable service life.
Extreme Temperature Stability
This material offers unparalleled performance across a vast temperature spectrum, remaining effective from cryogenic conditions at -200°C (-328°F) up to high-heat applications at 260°C (500°F). Unlike many elastomers that become brittle in the cold or degrade in heat, PTFE maintains its flexibility and sealing properties.
Exceptionally Low Friction
PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid material, giving it a non-stick, non-adhesive surface. In dynamic sealing applications, this property is critical for reducing wear on moving parts, minimizing energy consumption, and preventing the "stick-slip" phenomenon.
Physical Malleability and Durability
PTFE is a relatively soft material that deforms under pressure to fill microscopic imperfections between mating surfaces. This conformability creates an exceptionally tight and reliable seal. It also exhibits excellent resistance to weathering, UV radiation, and moisture, making it suitable for long-term outdoor or exposed applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While its properties are exceptional, PTFE is not without its limitations. Acknowledging these trade-offs is key to successful application and design.
Susceptibility to Creep (Cold Flow)
The same softness that allows PTFE to conform so well also makes it susceptible to creep, or "cold flow." Under sustained high pressure, especially in static applications, the material can slowly deform permanently, potentially compromising the seal over time.
The Need for Reinforcement
To counteract creep and improve mechanical strength, pure PTFE is often enhanced with fillers like glass, carbon, or bronze. For high-pressure scenarios, PTFE seals are frequently paired with harder back-up rings (often made of PEEK) to provide structural support and prevent extrusion.
Lower Mechanical Strength
Compared to engineered plastics or metals, PTFE has lower tensile strength and abrasion resistance. In applications with significant abrasive media or high mechanical stress, a filled grade of PTFE or a different material may be a more appropriate choice.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right seal requires matching the material's properties to the application's primary demands.
- If your primary focus is handling aggressive chemicals: PTFE is an ideal first choice due to its near-universal chemical inertness, which prevents material degradation.
- If your primary focus is operating in extreme temperatures: PTFE's stability from cryogenic levels to over 260°C makes it superior to nearly all elastomeric seals.
- If your primary focus is reducing friction in dynamic seals: PTFE's non-stick surface and low coefficient of friction will minimize wear, heat buildup, and energy loss.
- If your primary focus is high-pressure static sealing: Use a filled grade of PTFE or design the seal with back-up rings to mitigate its natural tendency for cold flow.
Ultimately, understanding both PTFE's core strengths and its inherent limitations allows you to leverage it as a powerful problem-solving tool for the most demanding sealing environments.
Summary Table:
| Property | Benefit for Sealing Applications |
|---|---|
| Chemical Inertness | Resists virtually all industrial chemicals, preventing degradation. |
| Temperature Stability | Performs reliably from -200°C to 260°C, unlike many elastomers. |
| Low Coefficient of Friction | Reduces wear and energy consumption in dynamic applications. |
| Conformability | Deforms to fill surface imperfections, creating a tight seal. |
Need a reliable seal for extreme conditions? KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-performance, custom PTFE components like seals, liners, and labware for the semiconductor, medical, and industrial sectors. We deliver precision-engineered solutions from prototypes to high-volume orders to ensure your equipment's integrity and longevity. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Customizable PTFE Crucibles for Laboratory and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the primary applications of PTFE fasteners and custom parts? Critical Solutions for Extreme Environments
- What are the base characteristics of PTFE? Unlocking Extreme Performance in Friction, Temperature, and Chemical Resistance
- What is the working temperature range of PTFE? Master Extreme Heat and Cryogenic Applications
- What is PTFE commonly known as and what are its unique properties? Unlock Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- What are some common applications of machined PTFE? Leverage its Unique Properties for Demanding Applications



















