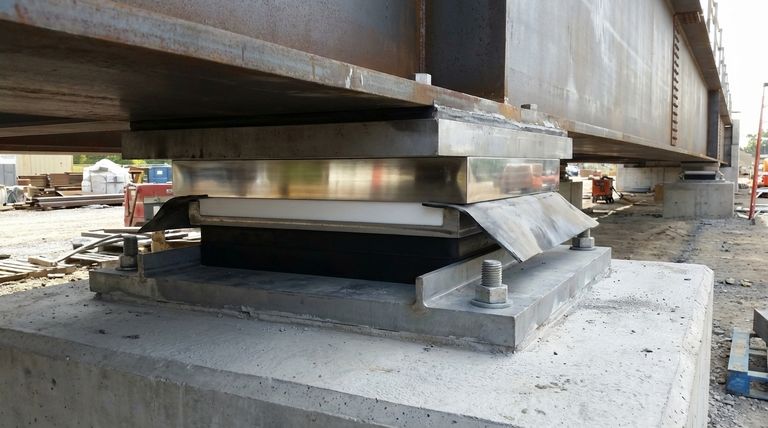
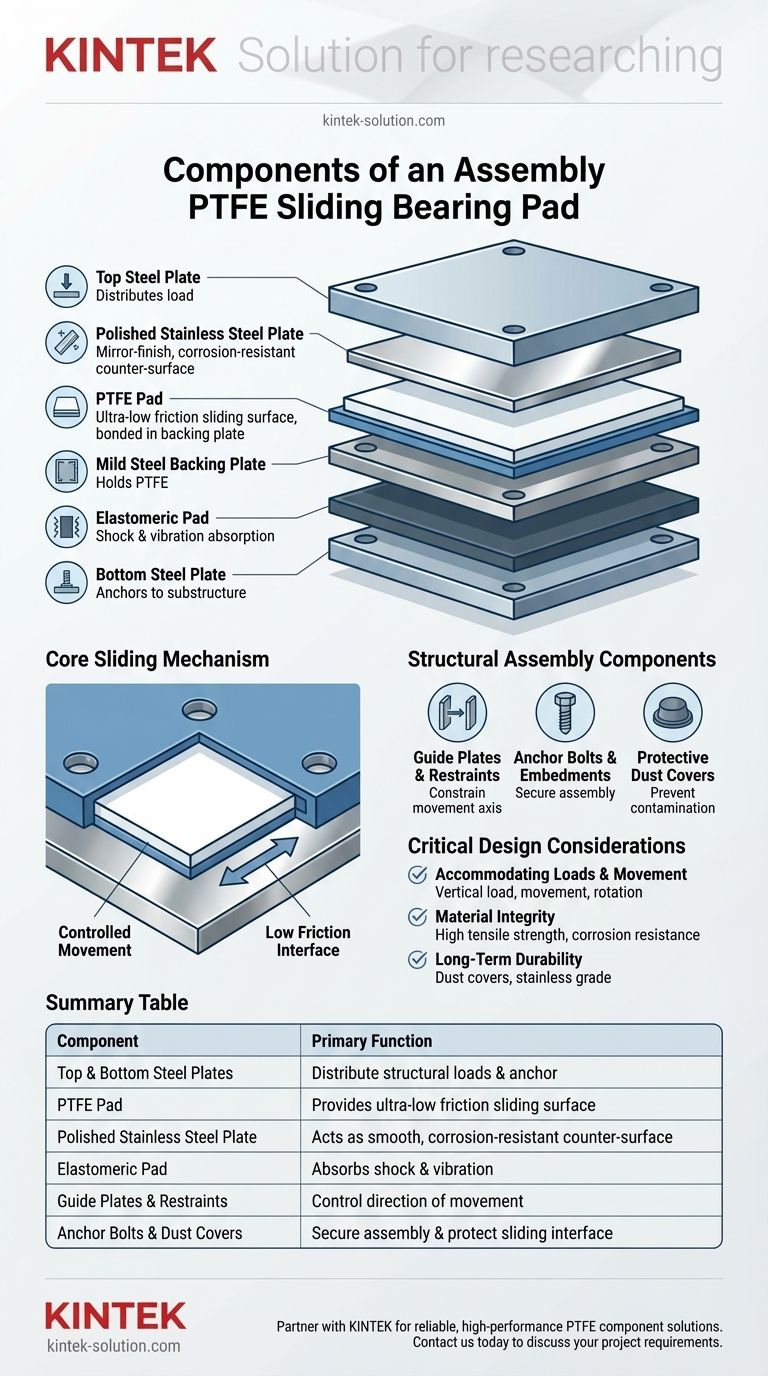
At its core, an assembly PTFE sliding bearing pad is a system of layered components designed for a single purpose: to safely transfer enormous loads while allowing for controlled, low-friction movement. A complete assembly typically includes a top steel plate, a polished stainless steel plate, the PTFE (polytetrafluoroethylene) pad itself, a bottom steel plate, and often guide plates, anchor bolts, and protective dust covers.
A PTFE sliding bearing is more than just a low-friction surface; it's an engineered assembly where each component—from the steel backing plates to the protective covers—plays a critical role in managing structural loads, accommodating movement, and ensuring long-term durability.

Deconstructing the Core Sliding Mechanism
The heart of the bearing is the interface that allows for movement. This is almost always a combination of a PTFE sheet and a polished stainless steel plate.
The PTFE Sliding Surface
PTFE is a fluoropolymer with an exceptionally low coefficient of friction, one of the lowest of any known solid material. This property allows it to slide effortlessly even under immense pressure from a bridge or building.
To handle these high compressive loads without deforming or squeezing out, the PTFE sheet is typically bonded within a recess in a mild steel backing plate.
The Polished Stainless Steel Plate
The PTFE pad slides against a highly polished stainless steel plate. The mirror-like finish is critical for minimizing friction, and the stainless steel provides excellent corrosion resistance, which is essential for long-term performance in exposed environments.
Like the PTFE, this stainless steel sheet is stitch-welded to its own mild steel backing plate for structural stability and to ensure it remains perfectly flat.
Understanding the Full Structural Assembly
The core sliding mechanism does not work in isolation. A series of other components are required to transfer loads from the structure and protect the bearing.
Top and Bottom Steel Plates
These thick steel plates serve as the primary structural elements of the assembly. The top plate is secured to the superstructure (like a bridge beam), and the bottom plate is anchored to the substructure (like a pier). They distribute the load evenly across the bearing components.
The Elastomeric (Rubber) Pad
In many designs, an elastomeric or rubber pad is integrated into the assembly, typically beneath the PTFE's backing plate. This component provides shock and vibration absorption, helping to dampen noise and buffer the structure from dynamic loads.
Guide Plates and Restraints
While the bearing is designed to allow free movement in one direction (e.g., longitudinal movement from thermal expansion), it often needs to restrict movement in another. Guide plates are steel bars welded to the assembly that constrain movement to a specific axis.
Anchor Bolts and Embedments
Anchor bolts and embedded steel plates are the physical connections that secure the entire bearing assembly to the concrete or steel of the structure itself, ensuring a robust transfer of all forces.
Protective Elements (Dust Covers)
The low-friction performance of the bearing is highly dependent on a clean sliding surface. Dust covers, often made of flexible materials, are installed to prevent debris, water, and contaminants from compromising the PTFE and stainless steel interface.
Critical Design Considerations
A manufacturer cannot simply produce a one-size-fits-all bearing. The final design is a direct response to the specific demands of the structure.
Accommodating Loads and Movement
The thickness of the steel plates, the size of the PTFE pad, and the inclusion of guide plates are all dictated by client specifications. These include the expected vertical load, the required longitudinal and lateral movement, potential uplift forces, and any rotational demands.
Material Integrity is Non-Negotiable
The choice of materials is functional. The high tensile strength of the steel backing plates prevents bending, while the corrosion resistance of stainless steel ensures a smooth, reliable sliding surface for the life of the structure. The bond between the PTFE and its backing plate is critical to prevent failure under load.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
When specifying or evaluating a PTFE bearing, understanding the role of each component allows you to focus on what matters most for your project's success.
- If your primary focus is accommodating simple thermal expansion: The quality of the PTFE and the mirror-finish of the stainless steel plate are the most critical elements.
- If your primary focus is managing complex, multi-directional forces: You must pay close attention to the design of the guide plates and the overall structural integrity of the backing plates.
- If your primary focus is long-term durability and low maintenance: The design of the dust covers and the grade of the corrosion-resistant stainless steel are paramount to performance.
Ultimately, recognizing how these individual parts function together as a system is key to designing and building resilient, long-lasting structures.
Summary Table:
| Component | Primary Function |
|---|---|
| Top & Bottom Steel Plates | Distribute structural loads and anchor the bearing. |
| PTFE Pad | Provides an ultra-low friction sliding surface. |
| Polished Stainless Steel Plate | Acts as the smooth, corrosion-resistant counter-surface for the PTFE. |
| Elastomeric Pad | Absorbs shock and vibration. |
| Guide Plates & Restraints | Control the direction of movement. |
| Anchor Bolts & Dust Covers | Secure the assembly and protect the sliding interface from contaminants. |
Need a reliable PTFE component solution for your structural bearing application?
KINTEK specializes in the precision manufacturing of high-performance PTFE components, including custom bearing pads, seals, and liners. Our expertise ensures the material integrity and dimensional accuracy critical for managing extreme loads and movement in demanding environments like bridge construction and heavy industrial projects.
We partner with engineers and manufacturers in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors, offering custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss how our PTFE components can contribute to the durability and success of your next project.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- Why is PTFE suitable for cryogenic or high-temperature applications? Unmatched Thermal Stability from -450°F to 500°F
- What are the key benefits of PTFE in custom fabrication? Unlock Performance in Extreme Conditions
- What is the working temperature range of PTFE? Master Extreme Heat and Cryogenic Applications
- What are the material advantages of machining Teflon? Unlock Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- What is PTFE commonly known as and what are its unique properties? Unlock Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance



















