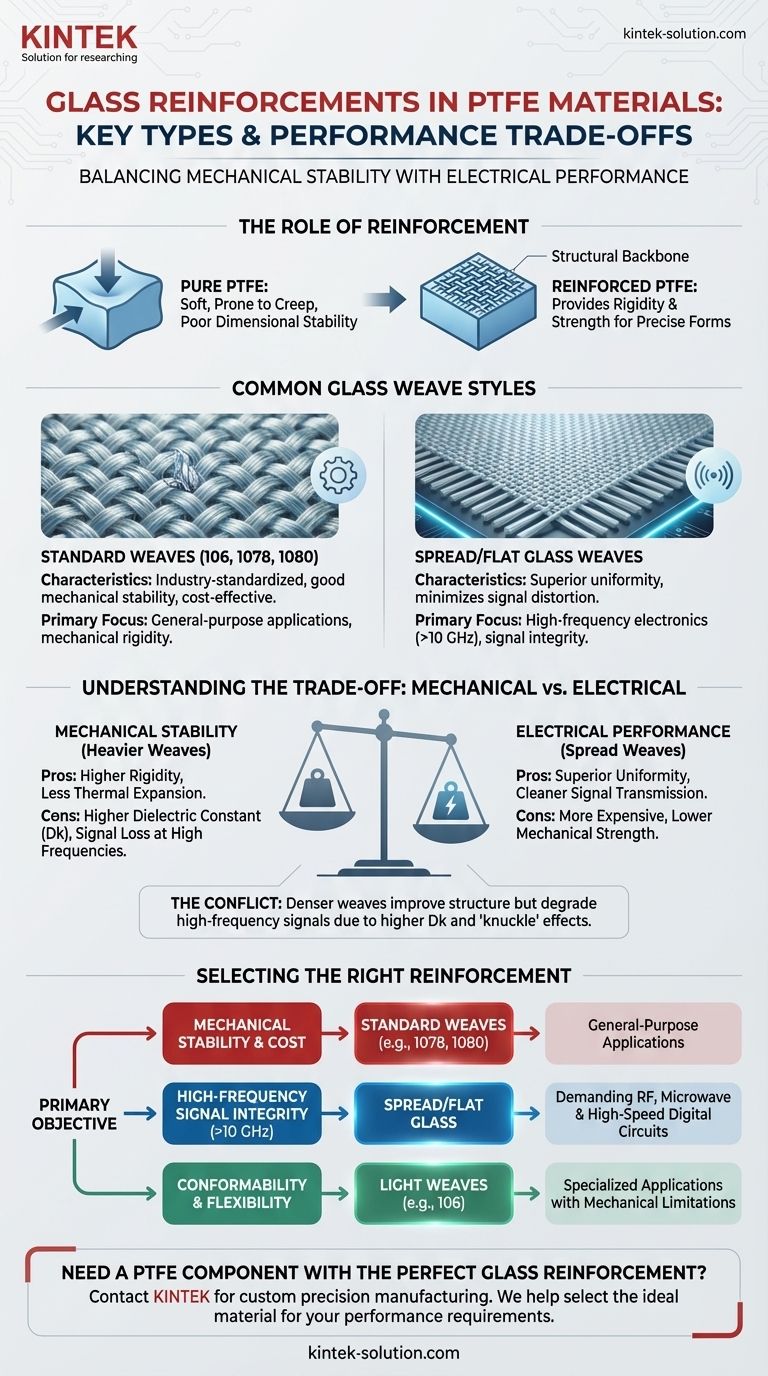
The most common types of glass reinforcements used in Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) based materials are designated by industry standards such as 106, 1078, and 1080. In addition to these traditional woven styles, more advanced spread or flat glass weaves are used for high-performance applications. These reinforcements are integrated into the PTFE matrix to improve mechanical properties like rigidity and dimensional stability, which are inherently poor in pure PTFE.
The choice of glass reinforcement in a PTFE composite is a critical engineering decision. It creates a fundamental trade-off between enhancing the material's mechanical stability and preserving its optimal electrical performance, especially for high-frequency electronics.

The Role of Reinforcement in PTFE Composites
Why Add Glass to PTFE?
Pure PTFE is known for its excellent dielectric properties and chemical inertness, but it is also a very soft material. It is prone to deformation under load (a phenomenon known as "creep") and has poor dimensional stability.
Adding a woven glass fabric acts as a structural backbone. This reinforcement provides the rigidity and strength needed for applications like printed circuit boards (PCBs), where maintaining physical form and precise dimensions is critical.
Reinforcements vs. Fillers: A Key Distinction
In composite materials, additives can be categorized as either reinforcements or fillers.
Reinforcements, such as glass fibers, primarily improve mechanical behavior. Their main purpose is to bear structural loads and enhance stiffness, much like rebar in concrete.
Fillers, which can be ceramic or metallic particles, are often added to modify other properties. While they can affect mechanical strength, their primary role is typically to tailor the material's thermal or electrical characteristics, such as its dielectric constant.
A Breakdown of Common Glass Weave Styles
Standardized Weaves (106, 1078, 1080)
These numerical designations refer to specific, industry-standardized styles of woven fiberglass cloth. They define characteristics like the yarn size, thickness, and the number of threads per inch in each direction.
While each has unique properties, the general principle is that a more substantial and tightly woven glass provides greater mechanical stability to the final PTFE laminate. These are the workhorse reinforcements for a wide range of applications.
Spread/Flat Glass Weaves
This represents an evolution in reinforcement technology, developed specifically for high-frequency electronics. In a spread weave, the glass yarn bundles are flattened and spread out before being woven into a fabric.
This process creates a much more uniform, homogenous material structure with fewer and smaller gaps in the weave. This uniformity is crucial for maintaining consistent electrical performance across the material.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Mechanical Stability vs. Electrical Performance
There is an inherent conflict between mechanical and electrical goals. A heavier, denser glass weave (like 1080) significantly improves the material's rigidity and reduces thermal expansion.
However, glass has a higher dielectric constant (Dk) and is more electrically "lossy" than pure PTFE. Therefore, adding more glass to the composite will raise the overall Dk and dissipation factor (Df), which can degrade signal performance at very high frequencies.
The Impact on Signal Integrity
For high-speed digital and RF/microwave circuits, the uniformity of the glass weave is critical. A standard weave creates a "knuckle and valley" effect, causing localized variations in the dielectric constant.
As a high-frequency signal travels across this non-uniform medium, parts of the signal can speed up or slow down, causing distortion and skew. The extreme uniformity of spread glass minimizes these variations, leading to cleaner signal transmission.
Cost and Manufacturability
Standard glass weaves like 1078 and 1080 are mature, widely available technologies and are generally more cost-effective.
The advanced processing required to create spread/flat glass makes these materials more expensive. The choice often comes down to balancing budget constraints against strict performance requirements.
Selecting the Right Reinforcement for Your Application
Choosing the correct material requires a clear understanding of your project's primary objective.
- If your primary focus is mechanical stability and cost-effectiveness: A standard, robust weave like 1078 or 1080 is often the most practical and reliable choice for general-purpose applications.
- If your primary focus is high-frequency signal integrity (>10 GHz): Spread/flat glass is the superior technical choice to minimize signal loss and distortion in demanding RF, microwave, and high-speed digital circuits.
- If your primary focus is conformability or flexibility: You should explore materials with very light glass weaves (like 106) or even unreinforced PTFE laminates, fully understanding their significant mechanical limitations.
Ultimately, selecting the right reinforcement is about deliberately matching the material's physical and electrical properties to the specific demands of your design.
Summary Table:
| Reinforcement Type | Key Characteristics | Primary Application Focus |
|---|---|---|
| Standard Weaves (106, 1078, 1080) | Good mechanical stability, cost-effective | General-purpose applications, mechanical rigidity |
| Spread/Flat Glass Weaves | Superior uniformity, minimizes signal distortion | High-frequency electronics (>10 GHz), signal integrity |
Need a PTFE Component with the Perfect Glass Reinforcement?
Choosing the right glass weave is critical to balancing mechanical stability and electrical performance for your application. The experts at KINTEK specialize in the precision manufacturing of custom PTFE components (seals, liners, labware, etc.) for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
We can help you select the ideal reinforcement—from standard to advanced spread weaves—to ensure your part meets exact performance requirements, whether for high-volume production or prototyping.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your project and leverage our expertise in custom PTFE fabrication.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the material advantages of machining Teflon? Unlock Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- What is the working temperature range of PTFE? Master Extreme Heat and Cryogenic Applications
- What are some common applications of machined PTFE? Leverage its Unique Properties for Demanding Applications
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? Unlock Unmatched Performance in Demanding Applications
- Why is PTFE suitable for cryogenic or high-temperature applications? Unmatched Thermal Stability from -450°F to 500°F



















