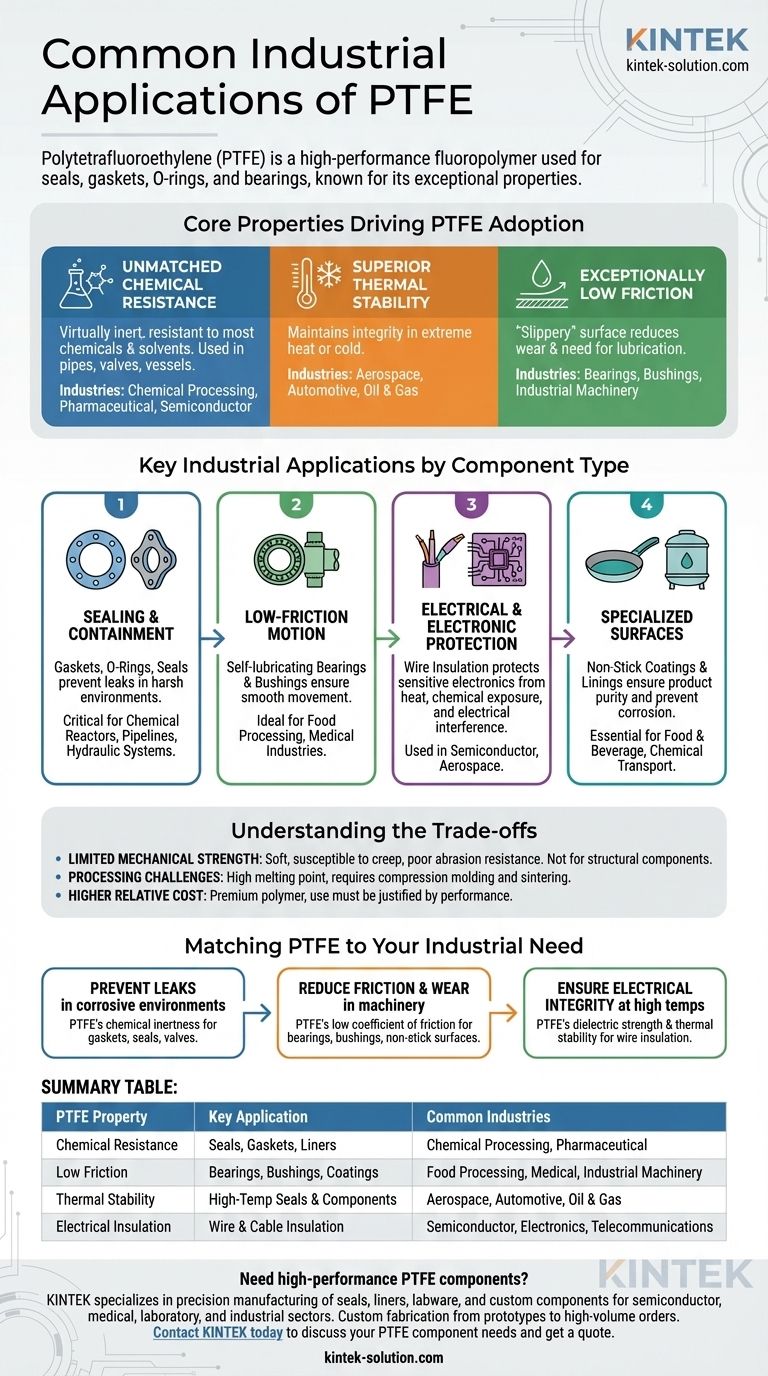
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a high-performance fluoropolymer used to manufacture a wide array of critical industrial components. Its most common applications include high-performance seals, gaskets, O-rings, and bearings. The material is also extensively used for electrical insulation, non-stick coatings on processing equipment, and specialized parts for chemically aggressive and high-temperature environments.
The widespread industrial adoption of PTFE is not accidental. It is a direct result of its rare combination of extreme chemical inertness, high thermal stability, and an exceptionally low coefficient of friction, making it a problem-solver in environments where other materials fail.
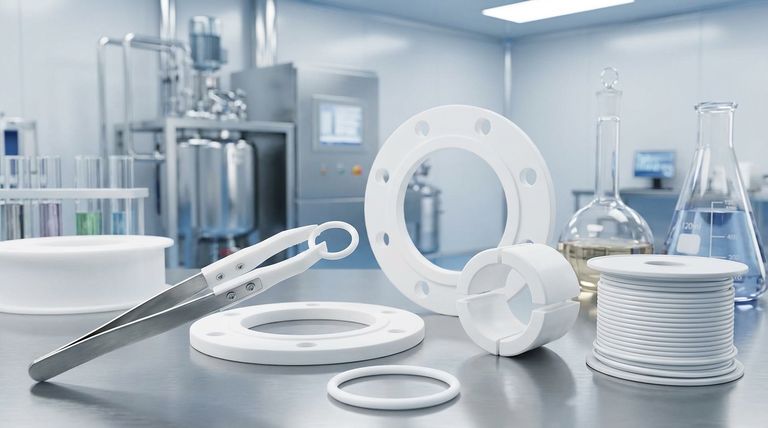

The Core Properties Driving PTFE Adoption
The value of PTFE in industrial settings stems from a unique set of material characteristics. Understanding these properties is key to understanding its applications.
Unmatched Chemical Resistance
PTFE is virtually inert and resistant to almost all industrial chemicals, solvents, and corrosive agents. This makes it an essential material in industries that handle aggressive substances.
You will find it lining pipes, valves, and vessels in chemical processing, pharmaceutical, and semiconductor manufacturing facilities.
Superior Thermal Stability
PTFE components maintain their integrity across a very wide range of temperatures. This stability is critical for applications involving extreme heat or cold.
This property ensures reliability in demanding sectors like aerospace, automotive, and oil & gas, where temperature fluctuations are common.
Exceptionally Low Friction
PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid material, giving it a characteristic "slippery" or non-stick quality.
This is the primary reason it is used for bearings, bushings, and surface coatings on industrial machinery, as it reduces wear and the need for lubrication.
High-Performance Electrical Insulation
PTFE is an excellent electrical insulator with high dielectric strength. It does not absorb water, ensuring its insulating properties remain stable even in humid conditions.
This makes it a top choice for insulating high-frequency wires and cables, especially in aerospace, electronics, and telecommunications.
Key Industrial Applications by Component Type
PTFE’s properties translate directly into specific, high-value components that solve critical engineering challenges across various industries.
Sealing and Containment (Gaskets, O-Rings, Seals)
The primary role of a seal or gasket is to prevent leaks. PTFE's ability to withstand harsh chemicals and extreme temperatures makes it the definitive material for this purpose.
These components are crucial in chemical reactors, pipelines, and hydraulic systems where failure could be catastrophic.
Low-Friction Motion (Bearings and Bushings)
In mechanical systems, PTFE bearings and bushings allow parts to move smoothly against each other with minimal wear.
Because they are self-lubricating, they are ideal for machinery in the food processing and medical industries, where external lubricants could cause contamination.
Electrical and Electronic Protection (Wire Insulation)
PTFE is used to coat wires and insulate internal components in transformers and other electronic devices.
Its role is to protect sensitive electronics from heat, chemical exposure, and electrical interference, a vital function in semiconductor and aerospace applications.
Specialized Surfaces (Non-Stick Coatings and Linings)
The non-stick property of PTFE is essential for equipment used in food and beverage manufacturing to ensure product purity and ease of cleaning.
Similarly, it is used to line tanks and transport systems for chemicals to prevent material adhesion and corrosion.
Understanding the Trade-offs of PTFE
While highly effective, PTFE is not a universal solution. Its limitations are as important to understand as its strengths.
Limited Mechanical Strength
PTFE is a relatively soft material. It can be susceptible to "creep," or deformation under a sustained load, and has poor abrasion resistance compared to harder polymers.
It is generally not used for structural components that must bear significant mechanical stress.
Processing Challenges
Due to its high melting point and high melt viscosity, PTFE cannot be processed using conventional melt-processing techniques like injection molding.
It requires specialized methods like compression molding and sintering, which can increase manufacturing complexity and cost.
Higher Relative Cost
PTFE is a premium, high-performance polymer. Its cost is higher than that of common plastics like polyethylene or polypropylene.
Its use must be justified by performance requirements that commodity materials cannot meet.
Matching PTFE to Your Industrial Need
To select PTFE effectively, you must align its core strengths with your primary operational challenge.
- If your primary focus is preventing leaks in corrosive environments: PTFE's chemical inertness makes it the definitive choice for gaskets, seals, and valve components in chemical processing or oil & gas.
- If your primary focus is reducing friction and wear in machinery: Its low coefficient of friction makes it ideal for creating self-lubricating bearings, bushings, and durable non-stick surfaces.
- If your primary focus is ensuring electrical integrity at high temperatures: Its combination of dielectric strength and thermal stability is essential for wire insulation and components in aerospace and electronics.
Ultimately, PTFE is the material of choice when standard polymers fail due to extreme chemical, thermal, or frictional demands.
Summary Table:
| PTFE Property | Key Industrial Application | Common Industries Served |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Seals, Gaskets, Liners | Chemical Processing, Pharmaceutical |
| Low Friction | Bearings, Bushings, Coatings | Food Processing, Medical, Industrial Machinery |
| Thermal Stability | High-Temp Seals & Components | Aerospace, Automotive, Oil & Gas |
| Electrical Insulation | Wire & Cable Insulation | Semiconductor, Electronics, Telecommunications |
Need high-performance PTFE components for your application?
KINTEK specializes in the precision manufacturing of PTFE seals, liners, labware, and custom components. We serve the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors, delivering solutions that withstand aggressive chemicals, extreme temperatures, and demanding mechanical requirements.
We offer custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders, ensuring your components meet exact specifications for performance and reliability.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your PTFE component needs and get a quote.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Volumetric Flasks for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Use
People Also Ask
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments
- What are the future considerations for machining Teflon? Mastering Material Challenges with Smart Tech
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments



















