At their core, PTFE backup rings serve one primary function: to prevent the extrusion and failure of softer elastomeric seals, like O-rings, in high-pressure applications. They act as a strong, supportive barrier that blocks the clearance gap an O-ring might otherwise be forced into. This foundational benefit is amplified by PTFE's unique material properties, including exceptional chemical resistance, an extremely wide temperature range, and a very low coefficient of friction.
The essential benefit of a PTFE backup ring is its ability to provide structural support to prevent seal failure under high pressure. However, its true value is realized in demanding applications where its inherent chemical inertness, thermal stability, and low-friction characteristics solve problems that other materials cannot.

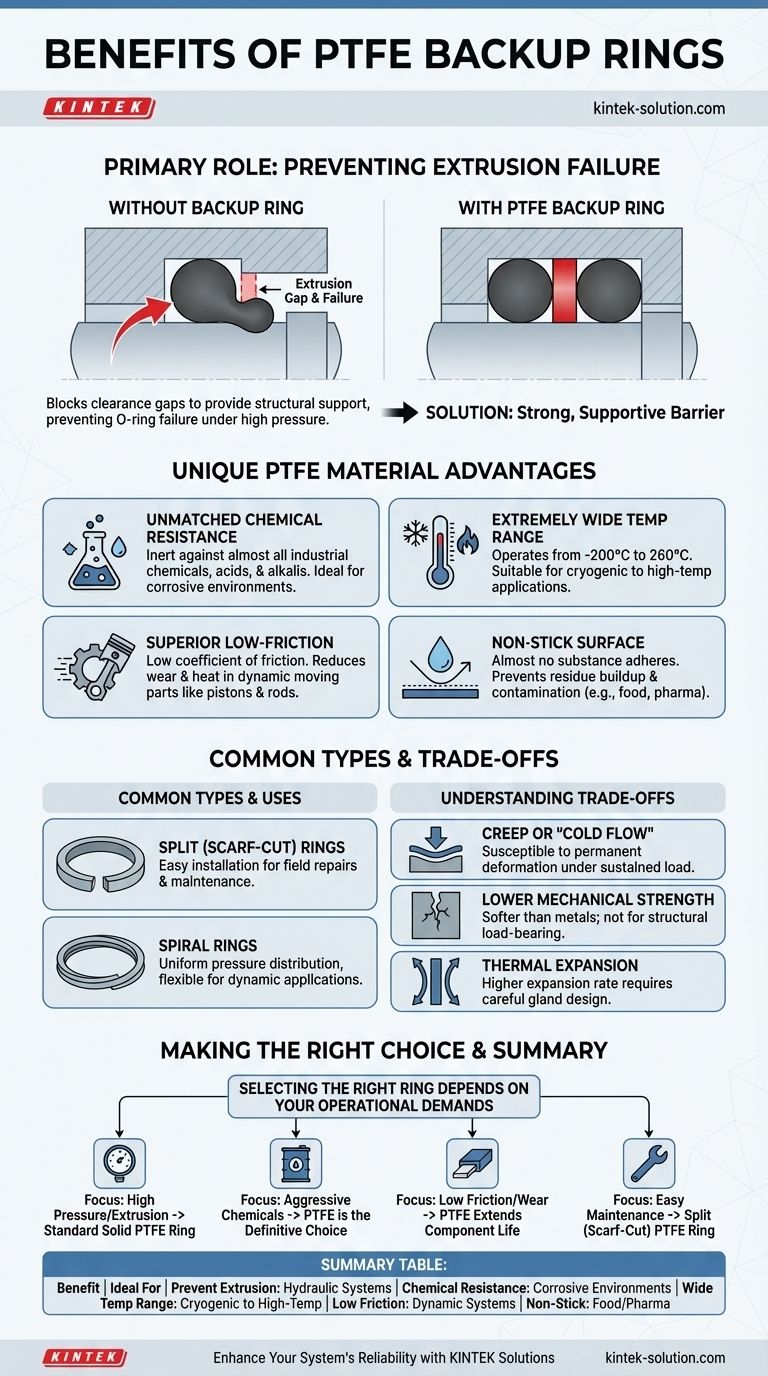
The Primary Role: Preventing Extrusion Failure
Under pressure, a simple O-ring is a highly effective seal. However, as pressure increases, the dynamics change, creating a significant risk of mechanical failure.
The Problem of Extrusion Gaps
Every sealing application has a small, necessary space between mating components called a clearance gap or extrusion gap. When system pressure becomes too high, it can force the softer O-ring material into this gap.
This process, known as extrusion, effectively "nibs" away at the seal, leading to rapid wear, leakage, and eventual system failure.
How Backup Rings Provide Support
A backup ring is a thin, rigid ring installed next to the O-ring on the low-pressure side of the gland. It is designed to be harder than the O-ring itself.
By physically blocking the clearance gap, the backup ring provides a solid surface that prevents the O-ring from being pushed out of place. This allows the O-ring to maintain its proper shape and sealing force, even under pressures that would otherwise cause it to fail.
The Unique Material Advantages of PTFE
While many materials can be used for backup rings, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) offers a combination of properties that make it uniquely suited for high-performance and chemically aggressive environments.
Unmatched Chemical Resistance
PTFE is renowned for its chemical stability, remaining inert against nearly all industrial chemicals, acids, and alkalis. This makes it the default choice for equipment used in chemical processing, pipelines, and valves where corrosive media are present.
An Extremely Wide Operating Temperature Range
PTFE maintains its integrity across a vast temperature spectrum, typically from -200°C to 260°C (-328°F to 500°F). This makes it suitable for everything from cryogenic applications to high-temperature industrial processes.
Superior Low-Friction Performance
With an extremely low coefficient of friction, PTFE backup rings are ideal for dynamic applications involving moving parts like pistons and rods. This property reduces wear, minimizes heat generation, and improves the overall efficiency of the system.
Non-Stick Surface Properties
Almost no substance will adhere to a PTFE surface. This non-stick characteristic is crucial in applications where residue buildup or contamination must be avoided, such as in the food, beverage, and pharmaceutical industries.
Common Types and Their Uses
PTFE backup rings are not a one-size-fits-all solution. Different designs are optimized for specific installation and operational requirements.
Split (Scarf-Cut) Rings for Easy Maintenance
These rings are cut through at one point, typically at an angle (a scarf cut). This simple design feature allows the ring to be stretched or twisted slightly for easy installation over shafts or into glands without complete system disassembly.
This makes split rings highly practical for field repairs and routine maintenance where minimizing downtime is critical.
Spiral Rings for Dynamic Applications
A spiral backup ring is formed from a continuous coil of PTFE material. This helical construction provides more uniform pressure distribution and allows the ring to flex and conform better to mating surfaces, especially in dynamic sealing applications with side-to-side motion.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While highly effective, PTFE is not without its limitations. Understanding these is key to proper application.
Creep or "Cold Flow"
Under a constant, sustained load, PTFE can be susceptible to creep, which is a slow, permanent deformation. In static sealing applications with very high, prolonged pressure, this must be considered in the design of the gland.
Lower Mechanical Strength
Compared to harder plastics like PEEK or metals, PTFE is a relatively soft material. It is not intended as a structural load-bearing component and is best used within its specified pressure ratings to support an elastomeric seal.
Thermal Expansion
PTFE has a higher coefficient of thermal expansion than most metals. Engineers must account for this in the hardware design to ensure that clearance gaps remain within tolerance across the full expected operating temperature range.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right backup ring depends entirely on the operational demands of your system.
- If your primary focus is preventing extrusion in standard hydraulic systems: A standard, solid PTFE backup ring provides excellent and reliable performance.
- If your primary focus is operating in chemically aggressive environments: PTFE's near-universal chemical resistance makes it the definitive choice.
- If your primary focus is reducing friction and wear in dynamic seals: The low friction coefficient of PTFE is a key advantage that extends the life of moving components.
- If your primary focus is easy installation and field maintenance: A split (scarf-cut) PTFE ring is the ideal design to minimize downtime.
By understanding these core benefits and trade-offs, you can confidently specify PTFE backup rings to enhance the reliability and longevity of your most critical sealing systems.
Summary Table:
| Benefit | Key Feature | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Prevent Extrusion | Blocks clearance gaps to stop O-ring failure under high pressure | Hydraulic systems, high-pressure valves |
| Chemical Resistance | Inert against acids, alkalis, and industrial chemicals | Chemical processing, pipelines, corrosive environments |
| Wide Temperature Range | Operates from -200°C to 260°C (-328°F to 500°F) | Cryogenic to high-temperature applications |
| Low Friction | Reduces wear and heat in dynamic systems | Pistons, rods, moving components |
| Non-Stick Surface | Prevents residue buildup and contamination | Food, beverage, pharmaceutical industries |
Ready to solve your toughest sealing challenges? KINTEK specializes in manufacturing precision PTFE components, including custom backup rings, seals, liners, and labware for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether you need prototypes or high-volume orders, our expertise ensures reliable performance in demanding environments. Contact us today to discuss your specific requirements and enhance your system's reliability with KINTEK solutions!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What is PTFE commonly known as and what are its unique properties? Unlock Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- What are the base characteristics of PTFE? Unlocking Extreme Performance in Friction, Temperature, and Chemical Resistance
- What are the primary applications of PTFE fasteners and custom parts? Critical Solutions for Extreme Environments
- Why is PTFE suitable for cryogenic or high-temperature applications? Unmatched Thermal Stability from -450°F to 500°F
- What are the material advantages of machining Teflon? Unlock Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance



















