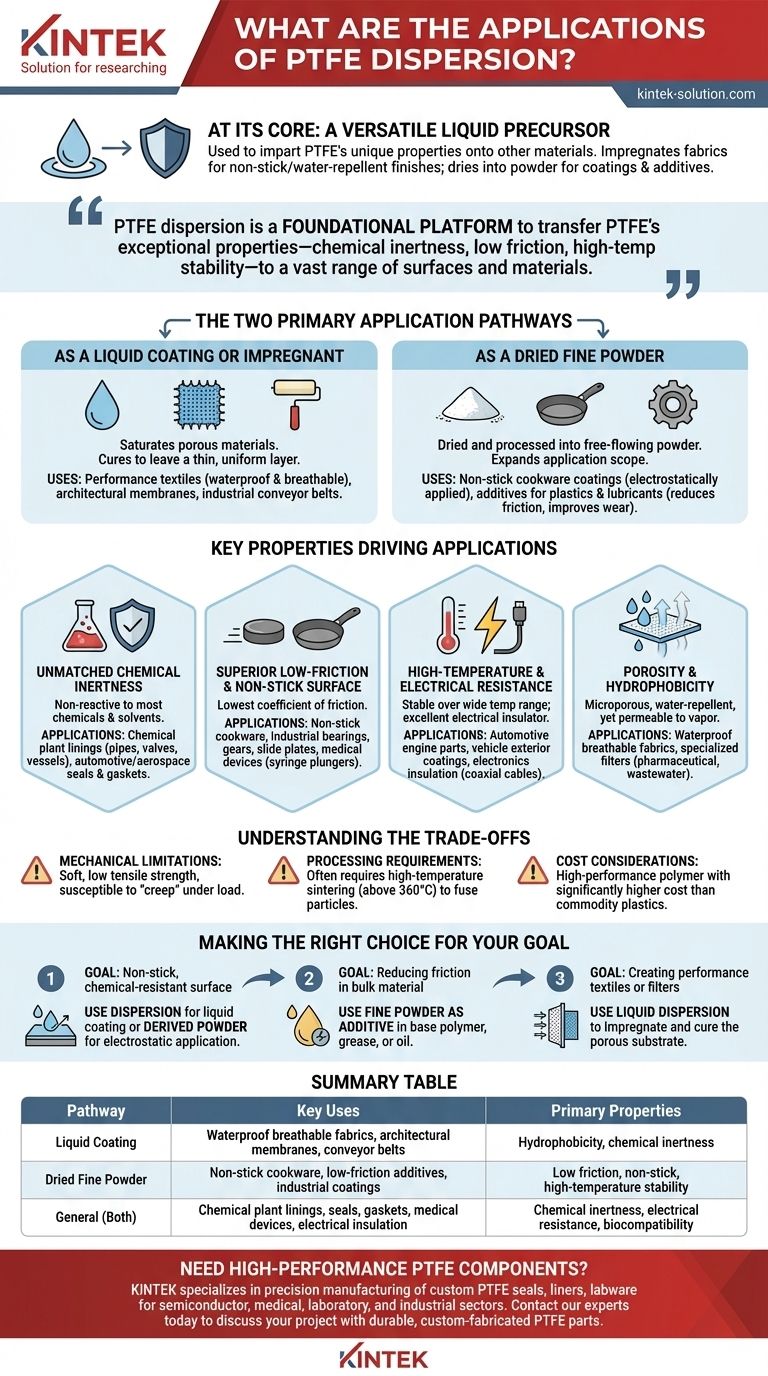
At its core, PTFE dispersion is a versatile liquid precursor used to impart the unique properties of Polytetrafluoroethylene onto other materials. In its liquid state, it is used to impregnate fabrics and create non-stick, water-repellent finishes. It can also be dried into a fine powder, which is then used to create the durable non-stick coatings on cookware or as an additive in industrial lubricants and plastics.
PTFE dispersion isn't a single application, but a foundational platform. Its true value lies in its ability to transfer the exceptional properties of solid PTFE—such as chemical inertness, low friction, and high-temperature stability—to a vast range of surfaces and materials.
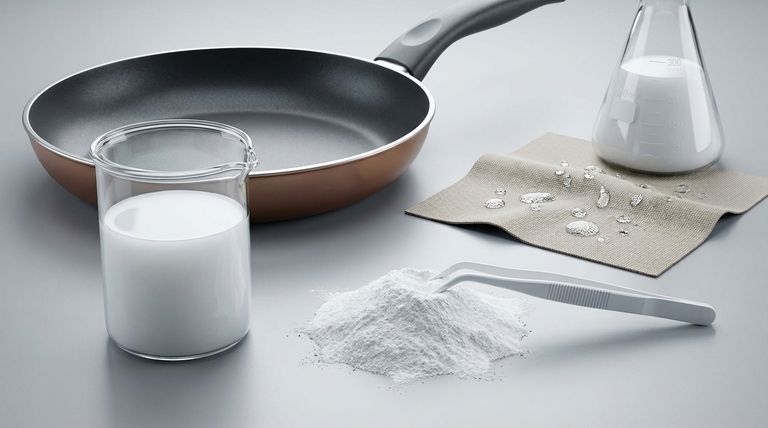

The Two Primary Application Pathways
PTFE dispersion is a milky-white aqueous solution containing tiny PTFE particles. Its utility stems from the two distinct ways it can be applied: either directly as a liquid or after being processed into a dry powder.
As a Liquid Coating or Impregnant
In its liquid form, the dispersion is ideal for saturating porous materials. The water base evaporates during a curing process, leaving a thin, uniform layer of PTFE.
This method is used to create performance textiles, where the PTFE coating provides water repellency while allowing the fabric to remain breathable. It is also used to coat fiberglass cloth for architectural membranes and industrial conveyor belts.
As a Dried Fine Powder
The dispersion can be dried and processed into a fine, free-flowing powder. This powder form dramatically expands its application scope.
This powder is the key ingredient for the non-stick coatings on pots and pans, which are typically applied electrostatically before being sintered at high heat. The powder can also be blended into other materials, such as plastics, elastomers, and lubricants, to reduce their coefficient of friction and improve wear resistance.
Key Properties Driving the Applications
The specific uses of PTFE dispersion are all derived from the inherent, high-performance characteristics of the PTFE polymer itself.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
PTFE is non-reactive to nearly all industrial chemicals and solvents. This makes it an essential material for harsh environments.
Dispersion-based coatings are used to line pipes, valves, and vessels in chemical processing plants, protecting them from corrosion. This property also drives its use in seals and gaskets that must withstand aggressive fuels and lubricants in the automotive and aerospace industries.
Superior Low-Friction and Non-Stick Surface
PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid material, a quality often compared to wet ice on wet ice.
This property is fundamental to its use in non-stick cookware. It is also critical for industrial applications like low-friction bearings, gears, and slide plates. In medical devices, PTFE coatings on syringe plungers and guide wires ensure smooth, hygienic, and stick-free operation.
High-Temperature and Electrical Resistance
PTFE maintains its properties over a wide temperature range and is an excellent electrical insulator.
These characteristics make it ideal for automotive parts near the engine and for coating vehicle exteriors to protect against heat and environmental damage. In electronics, PTFE's dielectric properties are leveraged for insulating high-performance coaxial cables and internal hookup wires.
Porosity and Hydrophobicity
When processed correctly, PTFE can be made into a microporous membrane that is hydrophobic (water-repellent) but permeable to vapor.
This is the principle behind waterproof, breathable fabrics. This porous structure is also used to create highly specialized filters for the pharmaceutical, chemical, and wastewater treatment industries, enabling sterile filtration and the separation of aggressive chemicals.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While its properties are exceptional, PTFE is not a universal solution. Acknowledging its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Mechanical Limitations
PTFE is a relatively soft material with low tensile strength. It is susceptible to "creep," meaning it can slowly deform over time when under a constant load, which can be a factor in high-pressure seal design.
Processing Requirements
Applying PTFE coatings, especially those derived from powder, requires a high-temperature sintering step (typically above 360°C / 680°F) to properly fuse the particles into a durable film. This limits the types of substrate materials that can be coated.
Cost Considerations
PTFE is a high-performance specialty polymer, and its cost is significantly higher than that of commodity plastics. Its use is typically justified in applications where its unique combination of properties is a strict requirement.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The best way to leverage PTFE dispersion depends entirely on your end goal.
- If your primary focus is creating a non-stick, chemical-resistant surface: Use the dispersion for direct liquid coating or the derived powder for a more robust, heat-fused electrostatic application.
- If your primary focus is reducing friction in a bulk material: Use the fine powder derived from the dispersion as a performance additive in your base polymer, grease, or oil.
- If your primary focus is creating performance textiles or filters: Use the liquid dispersion to impregnate the porous substrate, followed by a controlled curing process.
By understanding that PTFE dispersion is a delivery system for exceptional properties, you can select the precise form and application method to solve your specific engineering challenge.
Summary Table:
| Application Pathway | Key Uses | Primary Properties Utilized |
|---|---|---|
| Liquid Coating/Impregnant | Waterproof breathable fabrics, architectural membranes, conveyor belts | Hydrophobicity, chemical inertness |
| Dried Fine Powder | Non-stick cookware, low-friction additives for plastics/lubricants, industrial coatings | Low friction, non-stick, high-temperature stability |
| General (Both Pathways) | Chemical plant linings, seals, gaskets, medical devices, electrical insulation | Chemical inertness, electrical resistance, biocompatibility |
Need High-Performance PTFE Components for Your Application?
KINTEK specializes in the precision manufacturing of custom PTFE components—including seals, liners, and labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether you require prototypes or high-volume orders, we deliver solutions that leverage PTFE's superior properties to meet your exact specifications.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your project with durable, custom-fabricated PTFE parts.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- How is Expanded PTFE (EPTFE) material constructed? A Deep Dive into the Microporous Transformation
- How does PTFE perform when exposed to sulfuric acid? Unmatched Chemical Resistance for Demanding Applications
- What is Teflon and what are its main components? Discover the Science Behind Non-Stick Performance
- What temperature range can PTFE withstand? Ensuring Reliable Performance in Extreme Electrical Environments
- What is the temperature range for using PTFE? Master Its Use from -200°C to +260°C
- What distinguishes Virgin PTFE from Reprocessed PTFE? Choose the Right Material for Your Application
- What is PTFE commonly known as? Discover the High-Performance Material Behind Teflon
- In which industries is Teflon commonly used? Essential for Chemical, Medical, and Aerospace



















