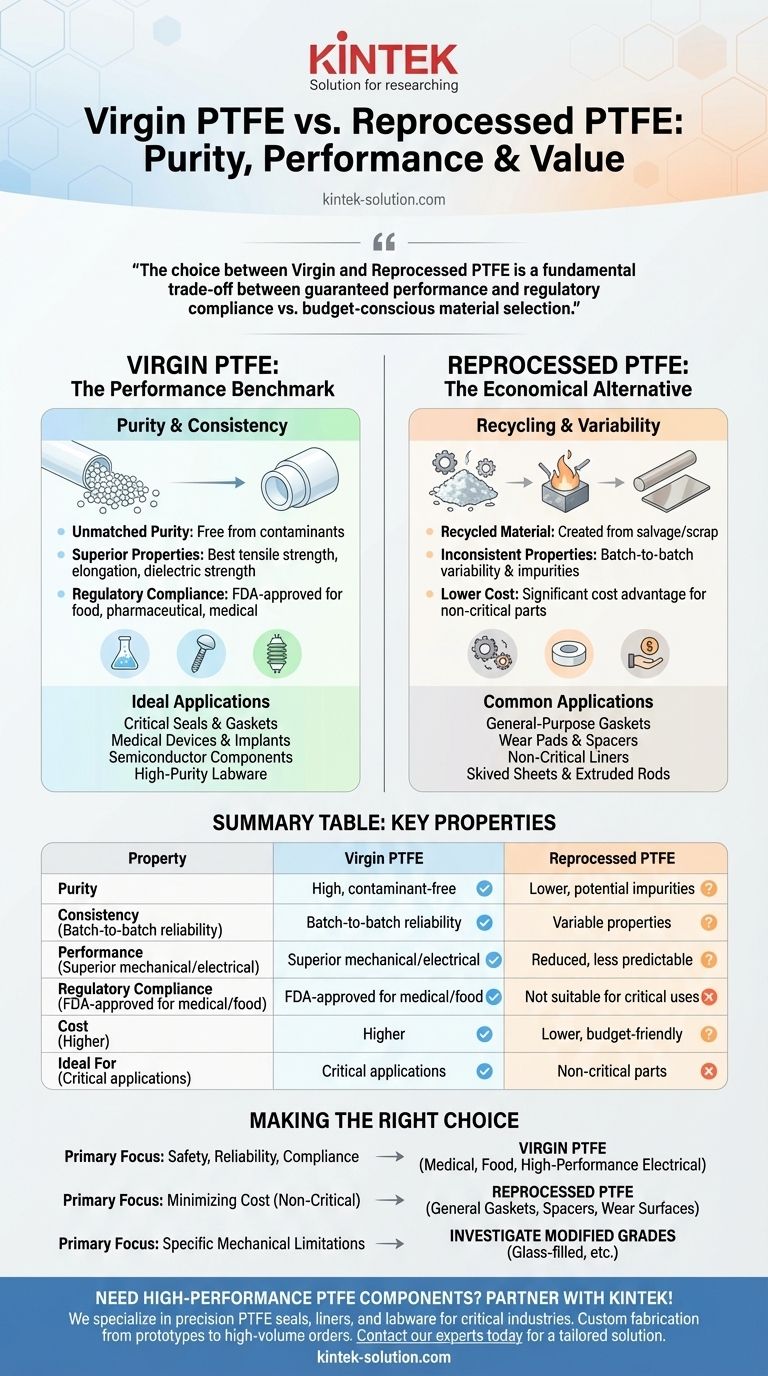
At its core, the distinction between Virgin PTFE and Reprocessed PTFE comes down to purity and performance. Virgin PTFE is a pure, first-run polymer made directly from raw materials, offering the highest quality and consistency. In contrast, Reprocessed PTFE is a recycled material created from scrap or used PTFE, resulting in less predictable properties and a lower cost.
The choice between Virgin and Reprocessed PTFE is a critical engineering decision. It is not merely about cost, but a fundamental trade-off between guaranteed performance and regulatory compliance on one side, and budget-conscious material selection for non-critical applications on the other.

Deconstructing Virgin PTFE: The Performance Benchmark
Virgin Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) represents the material in its purest, unmodified form. It serves as the baseline against which all other PTFE grades are measured.
### Unmatched Purity and Consistency
Because it is manufactured directly from new resin, Virgin PTFE is free from contaminants. This ensures that every batch has the same chemical composition and physical characteristics, providing predictable and repeatable results in manufacturing and end-use applications.
### Superior Physical and Electrical Properties
This purity translates directly to superior performance. Virgin PTFE exhibits the best tensile strength, elongation, and dielectric strength. Its properties as an excellent electrical insulator are most reliable in its virgin state.
### Regulatory Compliance for Critical Applications
Virgin PTFE is often the only grade that can meet strict regulatory standards. It is frequently FDA-approved for use in food processing, pharmaceutical, and medical applications where material purity is non-negotiable.
Understanding Reprocessed PTFE: The Economical Alternative
Reprocessed PTFE is created by salvaging and recycling scrap material from manufacturing processes. While it offers a significant cost advantage, this comes with inherent compromises.
### The Recycling Process and Its Impact
The process involves grinding down scrap PTFE and re-sintering it into solid forms like sheets or rods. This reprocessing can introduce impurities and break down the polymer's structure, altering its original properties.
### Inconsistent Properties and Impurities
The primary drawback of Reprocessed PTFE is variability. The properties can differ from batch to batch, and the presence of unknown impurities makes it unsuitable for applications where high purity or specific electrical insulation is required.
### Common Applications and Forms
Due to its lower cost and less reliable properties, Reprocessed PTFE is typically used for non-critical components. It is commonly found in skived sheets and extruded rods for applications like wear pads, gaskets, or spacers where ultimate performance is secondary to cost.
Critical Trade-offs: Performance vs. Cost
Choosing the right material requires a clear understanding of the application's demands and the risks involved. The decision almost always hinges on balancing performance requirements against budget constraints.
### The Risk of Contamination
For any application involving food, medical devices, or sensitive electronics, the risk of contamination from Reprocessed PTFE is too high. Virgin PTFE is the only safe choice in these environments.
### Mechanical and Electrical Predictability
If a component must withstand specific mechanical loads or provide reliable electrical insulation, the consistency of Virgin PTFE is essential. The unpredictable nature of Reprocessed PTFE can lead to premature failure.
### When Cost is the Primary Driver
For general-purpose, non-critical parts where dimensional stability and chemical inertness are the main requirements, Reprocessed PTFE can be a perfectly viable and cost-effective solution.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To select the appropriate material, you must clearly define the operational requirements and regulatory constraints of your project.
- If your primary focus is safety, reliability, or regulatory compliance: You must use Virgin PTFE. This applies to all food, medical, pharmaceutical, and high-performance electrical applications.
- If your primary focus is minimizing cost for non-critical components: Reprocessed PTFE is a suitable option for applications like general-purpose gaskets, spacers, or wear surfaces.
- If your primary focus is overcoming specific mechanical limitations: You should investigate modified or filled PTFE grades, such as glass-filled PTFE, which offer enhanced wear resistance and compressive strength.
Ultimately, understanding the fundamental difference between these materials empowers you to make an informed decision that aligns with both your budget and your performance requirements.
Summary Table:
| Property | Virgin PTFE | Reprocessed PTFE |
|---|---|---|
| Purity | High, contaminant-free | Lower, potential impurities |
| Consistency | Batch-to-batch reliability | Variable properties |
| Performance | Superior mechanical/electrical | Reduced, less predictable |
| Regulatory Compliance | FDA-approved for medical/food | Not suitable for critical uses |
| Cost | Higher | Lower, budget-friendly |
| Ideal For | Critical applications (medical, semiconductor) | Non-critical parts (gaskets, spacers) |
Need High-Performance PTFE Components? Partner with KINTEK!
Choosing the right PTFE material is crucial for your application's success. At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing precision PTFE components—including seals, liners, and labware—for semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial industries. Whether you require Virgin PTFE for critical compliance or cost-effective Reprocessed PTFE for non-critical uses, we offer custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders.
Let us help you balance performance, compliance, and cost. Contact our experts today for a tailored solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between suspension and dispersion polymerization of PTFE? Choose the Right Process for Your Application
- Which categories of chemicals show excellent compatibility with PTFE? Unmatched Chemical Resistance for Demanding Applications
- How is Teflon applied in the medical sector? Unlocking Biocompatibility and Sterility for Healthcare
- What are the fire safety properties of Teflon? Discover Its Non-Flammable Nature for Your Application
- Is there any real difference between PTFE and Teflon? The Critical Distinction for Engineers
- What certifications does the manufacturer of PTFE products have? Ensure Quality with ISO 9001 Certification
- How is PTFE used in pharmaceutical and medical applications? Essential for Safety & Efficiency
- What future advancements are expected in the recycling and reusability of PTFE? Discover New Chemical & Mechanical Breakthroughs



















